Perfect Number in Python
Check Whether or Not the Number is a Perfect Number in Python
Given an integer input as a number, the objective is to check whether or not a number is a Perfect Number in Python Language. Therefore, we write a program to Check Whether or Not the Number is a Perfect Number in Python Language.
Example Input : 28 Divisors : [1, 2, 4, 7, 14] Sum = 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14 = 28 Output : It's a Perfect Number

Perfect Number
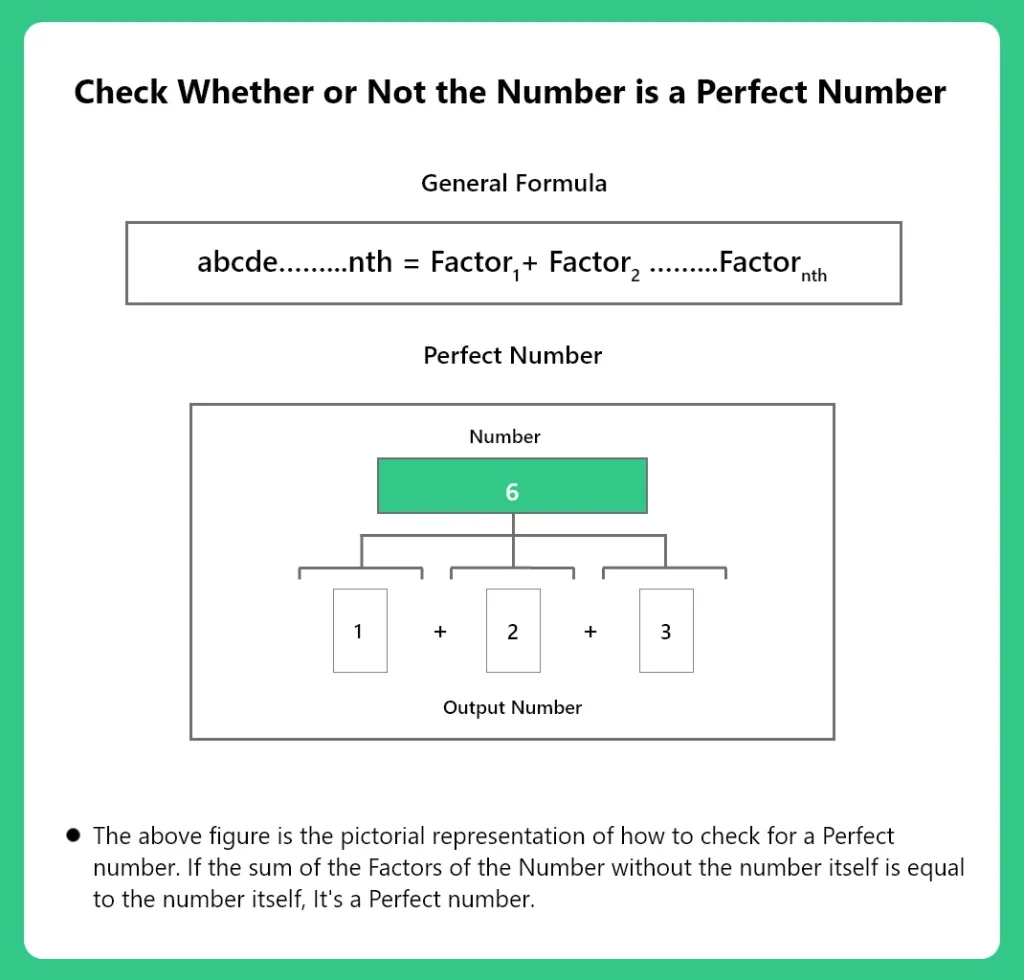
A Number that can be represented as the sum of all the factors of the number is known as a Perfect Number.
Let's Try and understand it better using an example
Let's Try and understand it better using an example
Example Input : 28 Output : It's a Perfect Number Explanation : Number = 28 28 = 1 + 2 + 14 + 4 + 7 as the number 28 has factors 1, 2, 4, 7 and 14. We sum them up and check whether they match the original number.As we can see from the above example, number 28 is a Perfect Number. Make sure you don't include the number itself as a factor.
Check whether or not the number is Perfect Number in Python
- Method 1: Using Simple Iteration I
- Method 2: Using Simple Iteration II
- Method 3: Using Simple Iteration III
- Method 4: Using Recursion
- Method 5: Using Factors
We’ll discuss the above-mentioned methods in detail in the upcoming sections.
Method 1: For Loop Iteration between [1, num]
For number num
- Initialise sum = 0
- Run an in ‘i’ iteration b/w [1, num]
- For any i satisfying (num % i == 0)
- If sum == num, its a perfect number
- Add to the sum
Let’s implement the above mentioned logic in Python Language.
Python Code
Run
n = 28
sum = 0
for i in range(1, n):
if n % i == 0:
sum = sum + i
if sum == n:
print("The number is a Perfect number")
else:
print("The number is not a Perfect number")
Output
The number is a Perfect number
Method 2: While Loop Iteration between [1, num]
For number num
- Initialise sum = 0
- Run an in ‘i’ iteration b/w [1, num]
- For any i satisfying (num % i == 0)
- If sum == num, its a perfect number
- Add to the sum
Run
num = 28
sum = 0
i = 1
while i < num:
if num % i == 0:
sum += i
i += 1
if sum == num:
print("The number is a Perfect number")
else:
print("The number is not a Perfect number")
Output
The number is a Perfect number
Method 3: Iteration between [1, num/2+1]
This method uses fact that all the divisors of the number can be found in the range (1, num/2)
Example –
Divisors of 28 = {1, 2, 4, 7, 14}
Run
num = 28
sum = 0
for i in range(1, num//2 + 1):
if num % i == 0:
sum = sum + i
if sum == num:
print("The number is a Perfect number")
else:
print("The number is not a Perfect number")
Output
The number is a Perfect number
Method 4: Using recursion
We use recursion to find if the number is perfect or not.
Run
sum_n = 0
def getSumDivisors(num, i):
global sum_n
# since, all factors can be found will num/2
# we will only check in this range
if i <= num // 2:
if num % i == 0:
sum_n = sum_n + i
i += 1
# recursively call isPerfect
getSumDivisors(num, i)
# returns the sum
# when i becomes > num/2
return sum_n
num = 28
if getSumDivisors(num, 1) == num:
print("The number is a Perfect number")
else:
print("The number is not a Perfect number")
Output
The number is a Perfect number
Method 5: Factors come in pairs
This method uses observations that all factors come in pairs.
All Factors come in pairs
For n = a * b (For each a there exists a unique b)
Example 1 : 100
(1,100), (2, 50), (4, 25), (5, 20), (10, 100)
Example 2 : 28
(1, 28), (2, 14), (4, 7)
Note : We will need to ignore pair of 1. As it will be the number itself.
Example 1 : 100
(1,100), (2, 50), (4, 25), (5, 20), (10, 100)
Example 2 : 28
(1, 28), (2, 14), (4, 7)
Note : We will need to ignore pair of 1. As it will be the number itself.
Shorten the Loop
We can shorten the loop running between [1, num] to [1, √num]
Since we will find all pairs before √num (n = sqrt(n) * sqrt(n))
Example: For 28, all pairs can be found before √28 = 5.2
Since we will find all pairs before √num (n = sqrt(n) * sqrt(n))
Example: For 28, all pairs can be found before √28 = 5.2
Python Code
Run
n = 28
sump = 0
for i in range(1, int(pow(n, 0.5))):
if n % i == 0:
# For n : (1, n) will always be pair of divisor
# acc to def., we must ignore adding num itself as divisor
# when calculating for perfect number
if i == 1:
sump += i
# Example For 100 (10,10) will be one pair
# But, we should add value to the sum just once
elif i == n / i:
sump += i
# add both pairs as divisors
# For any divisor i, n/i will also be a divisor
else:
sump += i + n / i
if sump == n:
print("The number is a Perfect number")
else:
print("The number is not a Perfect number")
# Time complexity: O(sqrt(N))
# Space complexity: O(1)
Output
The number is a Perfect number
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
- Positive or Negative number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Even or Odd number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of First N Natural numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of N natural numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of numbers in a given range: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Greatest of two numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Greatest of the Three numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Leap year or not: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Prime number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Prime number within a given range: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of digits of a number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Reverse of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Palindrome number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Armstrong number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Armstrong number in a given range : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Fibonacci Series upto nth term : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Find the Nth Term of the Fibonacci Series : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Factorial of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Power of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Factor of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Strong number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Perfect number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Automorphic number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Harshad number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Abundant number : C| C++ | Java | Python
- Friendly pair : C | C++ | Java | Python






n=int(input())
a=0
i = 1
while i < n:
if (n % i == 0):
a+=i
i = i + 1
if a==n:
print("The number is a Perfect number")
else:
print("The number is not a Perfect number")
Hey !!
We’d suggest you to join our Discord Channel for all your technical queries.
n=int(input(“enter a number : “))
l=[i for i in range(1,n) if(n%i==0)]
if(sum(l)==n):
print(“Perfect number”)
else:
print(“not a perfect number”)
n1 = int(input())
k = 0
for i in range(1, n1):
if n1%i == 0:
k = k + i
if k == n1:
print(‘Perfect number {}’.format(n1))
else:
print(‘Not perfect number{}’.format(n1))
a=int(input())
c=[]
s=0
for i in range(1,a):
if(a%i==0):
c.append(i)
for i in c:
s+=i
if(s==a):
print(“perect”)
else:
print(“not perfect”)