Harshad number or not using Java
Harshad number or not using Java :
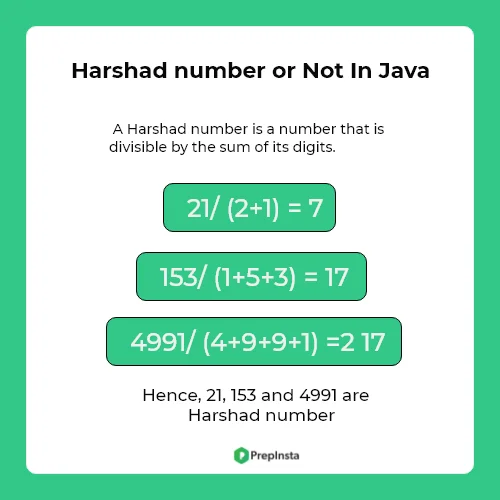
Harshad number is a number or an integer in base 10 which is completely divisible by sum of its digits.
For better understanding let us consider an example.
Example :
- Suppose a number 24 .
- Calculate the sum of digits of the number (2 + 4) = 6 .
- Check whether the number entered by user is completely divisible by sum of its digits or not.
Below are first few Harshad Numbers represented in base 10 :
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 18, 20………
In this article, we will create a java program to check whether the number entered by the user is Harshad number or not.

Working :
Step 1 : Ask the user to enter an integer.
Step 2 : Declare two variables, one for storing sum of digits and second for storing copy of the original number.
Step 3 : Use a while loop to perform continuous operations till the value of the integer do not becomes 0.
Step 4 : Use a statement to pick the last digit of the integer..
Step 5 : Perform addition and store the result in every iteration.
Step 6 : Restore the integer value by removing last digit in every iteration of the loop.
Step 7 : Repeat the Steps from 3 to 6 till the integer value do not becomes 0.
Step 8 : Compare that whether the sum of digits of the integer is equal to the given integer or not.
- If this gets true , then the given number is Harshad Number.
- Else the number is not a Harshad Number.
Code in Java :
//Java program to check whether a number is harshad number or not
// Online Java Compiler
// Use this editor to write, compile and run your Java code online
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//make a copy of original number
int n = 47;
//declare a variable to store sum of digits
int result = 0;
//perform logic for calculating sum of digits of a number
while(n != 0)
{
int pick_last = n % 10;
result = result + pick_last;
n = n / 10;
}
/*use condition to check whether the number entered by
user is completely divisible by its sum of digits or not*/
if(n % result == 0)
System.out.println("Harshad Number");
else
System.out.println("Not a Harshad Number");
}
}
Output :
Enter a number : 18
Harshad Number
Enter a number : 345
Not a Harshad Number
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
- Positive or Negative number: C | C++ | Java
- Even or Odd number: C | C++ | Java
- Sum of First N Natural numbers: C | C++ | Java
- Sum of N natural numbers: C | C++ | Java
- Sum of numbers in a given range: C | C++ | Java
- Greatest of two numbers: C | C++ | Java
- Greatest of the Three numbers: C | C++ | Java
- Leap year or not: C | C++ | Java
- Prime number: C | C++ | Java
- Prime number within a given range: C | C++ | Java
- Factorial of a number: C | C++ | Java
- Sum of digits of a number: C | C++ | Java
- Reverse of a number : C | C++ | Java
- Palindrome number: C | C++ | Java
- Armstrong number : C | C++ | Java
- Armstrong number in a given range : C | C++ | Java
- Fibonacci Series upto nth term : C | C++ | Java
- Factorial of a number : C | C++ | Java
- Power of a number : C | C++ | Java
- Factor of a number : C | C++ | Java
- Strong number : C | C++ | Java
- Perfect number : C | C++ | Java
- Automorphic number : C | C++ | Java
- Harshad number : C | C++ | Java
- Abundant number : C| C++ | Java
- Friendly pair : C | C++ | Java




public class Harshadnumber {
public static void Harshad(int num)
{
int temp=num;
int rem;
int sum=0;
while(num>0)
{
rem=num%10;
sum=sum+rem;
num=num/10;
}
if(temp%sum==0)
{
System.out.println(“is Harshad”);
}
else
{
System.out.println(“not”);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int num=24;
Harshad(num);
}
}
Hey there, Kindly join our Discord server for all the technical and subject related queries.
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int sum=0,i,r,temp;
temp=n;
while(n!=0)
{r=n%10;
sum=sum+r;
n=n/10;}
if(temp%sum==0)
System.out.println(“yesh”);
else
System.out.println(“not”);
}}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int Num = sc.nextInt();
int Sum = 0;
int temp = Num;
while (temp!=0){
int rem = temp%10;
Sum+=rem;
temp/=10;
}
if(Num%Sum==0){
System.out.println(Num+” “+”is a Harshad Number”);
}
else
{
System.out.println(Num+” “+”is not a Harshad Number”);
}
}
}
//Harshad Number: Number which is completely divisible by sum of its digits like 12 = 1+2 = 3 can divide 12
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = 0;
System.out.println(“Enter a no: “);
int num = sc.nextInt();
int n = num;
while(n != 0){
int rem = n%10;
sum += rem; //summing the digits of given number
n /= 10;
}
if(num % sum == 0) //checking if the no is divisible by sum or not
System.out.println(“No. is Harshad”);
else
System.out.println(“Not a Harshad number”);
}
}
class HashatNumber
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int sln = 1;
for(int num = 1;num<=100;num++)
{
int temp= num;
int sum= 0;
while(temp!=0)
{
int ld= temp%10;
sum= sum+ld;
temp= temp/10;
}
if(num%sum==0)
{
System.out.println(sln+") "+num);
sln++;
}
}
}
}
class HashadNumber
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int sln = 1;
for(int num = 1;num<=100;num++)
{
int temp= num;
int sum= 0;
while(temp!=0)
{
int ld= temp%10;
sum= sum+ld;
temp= temp/10;
}
if(num%sum==0)
{
System.out.println(sln+") "+num);
sln++;
}
}
}
}