Armstrong Numbers between Two Intervals using Java

Find the Armstrong Numbers in a given Interval in Java
Given two integers high and low for limits as inputs, the objective is to write a code to Find the Armstrong Numbers in a given Interval in Java.
Example
Input : 10 1000
Output : 153 370 371 407
Find the Armstrong Numbers in a given Range using Java
Given two integer inputs as high and low, the objective is to find all the Armstrong Numbers that falls under the limits [Low,High] interval. Before Going into the Explanation let’s understand the problem and the definition of Armstrong Numbers.
Armstrong Number
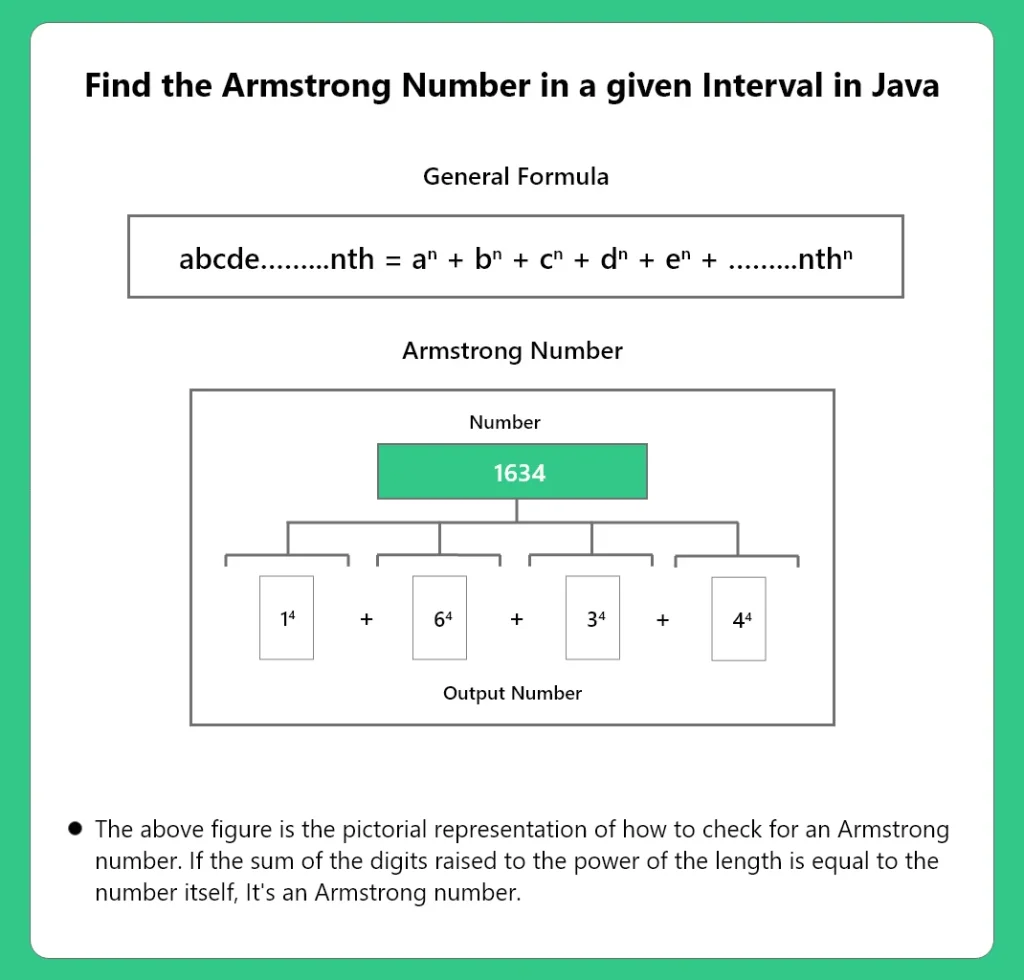
In number theory, an Armstrong number or a Narcissistic number in a given number base b is a number that is the sum of its own digits each raised to the power of the number of digits.
A number is an Armstrong Number if and only if it can be represented in the following form,
A number is an Armstrong Number if and only if it can be represented in the following form,
abcd...nth = pow(a,n) + pow(b,n) + pow(c,n) + pow(d,n) + .... pow(nth,n)Here are some example to understand the definition
Example 1 Input : 120 Output : No 120 is not a Armstrong number. 1*1*1 + 2*2*2 + 0*0*0 = 9 Example 2 Input : 1253 Output : No 1253 is not a Armstrong Number 1*1*1*1 + 2*2*2*2 + 5*5*5*5 + 3*3*3*3 = 723
From the above explanation we gather that to check if a number is it must be represented in the above stated equation. We then check
Java Code
Method 1
This is a simple iterative method to find all Armstrong numbers between two ranges –
Run
//Java program to print armstrong numbers between two intervals
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LearnCoding2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter lower and upper ranges : ");
int low = sc.nextInt();
int high = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Armstrong numbers between "+ low + " and " + high + " are : ");
// loop for finding and printing all armstrong numbers between given range
for(int num = low ; num <= high ; num++)
{
int sum = 0, temp, digit, len;
len = getOrder(num);
temp = num;
// loop to extract digit, find ordered power of digits & add to sum
while(temp != 0)
{
// extract digit
digit = temp % 10;
// add power to sum
sum = sum + (int) Math.pow(digit,len);
temp /= 10;
};
if(sum == num)
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
private static int getOrder(int num) {
int len = 0;
while (num!=0)
{
len++;
num = num/10;
}
return len;
}
}Output
Enter lower and upper ranges : 1 1000 Armstrong numbers between 1 and 1000 are : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 153 370 371 407
Working
Working of the above code is given below –
- Ask the user to enter two ranges, one starting range and the second ending range.
- Use a loop to find all Armstrong numbers between starting range and ending range.
- Use the logic for checking number is Armstrong or not for every number between the given range and then display the result.
Method 2 (Recursive)
This method uses a recursive approach to find Armstrong sum. You can check recursion in Java here
Run
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LearnCoding2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter lower and upper ranges : ");
int low = sc.nextInt();
int high = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Armstrong numbers between "+ low + " and " + high + " are : ");
// loop for finding and printing all armstrong numbers between given range
for(int num = low ; num <= high ; num++)
{
int len = getOrder(num);
if(num == getArmstrongSum(num, len))
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
private static int getOrder(int num) {
int len = 0;
while (num!=0)
{
len++;
num = num/10;
}
return len;
}
private static int getArmstrongSum(int num, int order) {
if(num == 0)
return 0;
int digit = num % 10;
return (int) Math.pow(digit, order) + getArmstrongSum(num/10, order);
}
}
Output
Enter lower and upper ranges : 1 1000 Armstrong numbers between 1 and 1000 are : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 153 370 371 407
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
- Positive or Negative number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Even or Odd number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of First N Natural numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of N natural numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of numbers in a given range: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Greatest of two numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Greatest of the Three numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Leap year or not: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Prime number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Prime number within a given range: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of digits of a number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Reverse of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Palindrome number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Armstrong number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Armstrong number in a given range : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Fibonacci Series upto nth term : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Find the Nth Term of the Fibonacci Series : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Factorial of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Power of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Factor of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Strong number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Perfect number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Automorphic number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Harshad number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Abundant number : C| C++ | Java | Python
- Friendly pair : C | C++ | Java | Python






public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int c=0;
int s=0;
for(int i=1; i<=1000; i++)
{
if(amstrong(i))
{
System.out.print(i+" ");
c++;
s=s+i;
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sum :"+s);
System.out.println("Count :"+c);
System.out.println("Avg :"+s/c);
}
public static boolean amstrong(int n)
{
int s=0;
int n1=n;
while(n!=0)
{
int d=n%10;
s=s+(d*d*d);
n=n/10;
}
return n1==s;
}
}
Kindly join our channel for technical queries.
Kindly join our Discord channel for technical queries.
Our mentors are available on Discord who will help you in technical queries.
public class armstrongInRange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 1000;
for (int i = num1; i<num2; i++){
int check;
int rem;
int sum = 0;
check = i;
while(check != 0)
{
rem = check % 10;
sum = sum + (rem * rem * rem);
check = check / 10;
}
if(sum == i){
System.out.println(""+i+" is an Armstrong number.");
}
}
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Armstrong number in a given range :
int start=1;
int end =500;
for(int i=start;i<=end;i++)
{
if(amstrong(i))
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
static boolean amstrong(int n)
{
int original=n;
int sum=0;
int digit=digits(n);
while(n!=0)
{
int rem=n%10;
sum += (int) Math.pow(rem,digit);
n=n/10;
}
return sum==original;
}
static int digits(int n)
{
int count =0;
while (n!=0)
{
count++;
n=n/10;
}
return count;
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArmstrongBetweenTwoNumbers {
public static void main(String args[]){
int num1, num2;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter the first number ::”);
num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(“Enter the second number ::”);
num2 = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = num1; i<num2; i++){
int check, rem, sum = 0;
check = i;
while(check != 0) {
rem = check % 10;
sum = sum + (rem * rem * rem);
check = check / 10;
}
if(sum == i){
System.out.println(""+i+" is an Armstrong number.");
}
}
}
Class sd{public static void main (String []args){
int n1,n2,last,total,n,rem;
System.out.println(” enter a first no”);
Scanner s= new Scanner (System.in);
n1=s.nextInt();
System.out.println(” enter a second no”);
n2= s.nextInt();
for(int i= n1; i0){
rem=n%10;
last=last+(rem*rem*rem);
n=n/10;
}
if(total==last){
System.out.println(last);
}}}
package ppjava;
import java.util.*;
public class ArmSeries {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter start no: “);
int s = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(“Enter second no: “);
int l = sc.nextInt();
int r=0;
for(;s0) {
int d= a%10;
r= r+(d*d*d);
a=a/10;
}
if(r==s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
sc.close();
}
}
for(int i = start ; i <= end ; i++)
{
n = i;
int length=String.valueOf(i).length();
sum = 0;
//logic for checking number is armstrong or not
while(n != 0)
{
int pick_last = n % 10;
sum = sum + Math.pow(pick_last, length);
n = n / 10;
}
if(sum == i)
System.out.println(i);
}