OS Menu
- OS Home
- Introduction
- CPU Scheduling
- What is Process?
- Process Lifecyle
- Process Control Block
- Process Scheduling
- Context Switching
- CPU Scheduling
- FCFS Scheduling
- SJF (non-preemptive)
- SJF (Preemptive - SRTF)
- Round Robin
- Priority Scheduling
- Convoy Effect
- Scheduler Vs Dispatcher
- Preemptive Vs non
- Preemptive scheduling
- Non preemptive scheduling
- Process Synchronization
- Deadlock
- Popular Algorithms
- Memory Management
- Memory Management Introduction
- Partition Allocation Method
- First Fit
- First Fit (Intro)
- First Fit in C
- First Fit in C++
- First Fit in Python
- First Fit in Java
- Best Fit
- Best Fit (Intro)
- Best Fit in C
- Best Fit in C++
- Best Fit in Java
- Worst Fit
- Worst Fit (Intro)
- Worst Fit in C++
- Worst Fit in C
- Worst Fit in Java
- Worst Fit in Python
- Next Fit
- First fit best fit worst fit (Example)
- Memory Management 2
- Memory Management 3
- Page Replacement Algorithms
- LRU (Intro)
- LRU in C++
- LRU in Java
- LRU in Python
- FIFO
- Optimal Page Replacement algorithm
- Optimal Page Replacement (Intro)
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in C
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in C++
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in Java
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in Python
- Thrashing
- Belady’s Anomaly
- Static vs Dynamic Loading
- Static vs Dynamic Linking
- Swapping
- Translational Look Aside Buffer
- Process Address Space
- Difference between Segmentation and Paging
- File System
- Off-campus Drive Updates
- Get Hiring Updates
- Contact us
PREPINSTA PRIME
Batch Operating System
Batch Operating System
Batch Operating system groups jobs that perform similar type of functions. These groups are treated as a batch and are executed at the same time.
This article explores the concept of batch operating systems in detail highlighting their key characteristics, advantages, and continued relevance in certain computing environments today, especially in large scale data processing and legacy systems.
Overview of a Batch Operating System
A batch operating system is a type of operating system that processes a series of tasks, known as jobs, without requiring constant user intervention.
Unlike interactive systems, which rely on user input for each task, batch systems execute a set of jobs in sequence, one after another. This approach allows for efficient utilization of computer resources and streamlines the execution of repetitive tasks.
Batch Processing in Modern Computing
While interactive and time-sharing systems dominate the modern computing landscape, batch processing remains relevant in various scenarios. In data-intensive environments, such as financial institutions and scientific research centers, batch processing is utilized for large-scale data analysis, report generation, and bulk data processing tasks. Batch systems continue to provide efficient and reliable processing capabilities for such workloads.
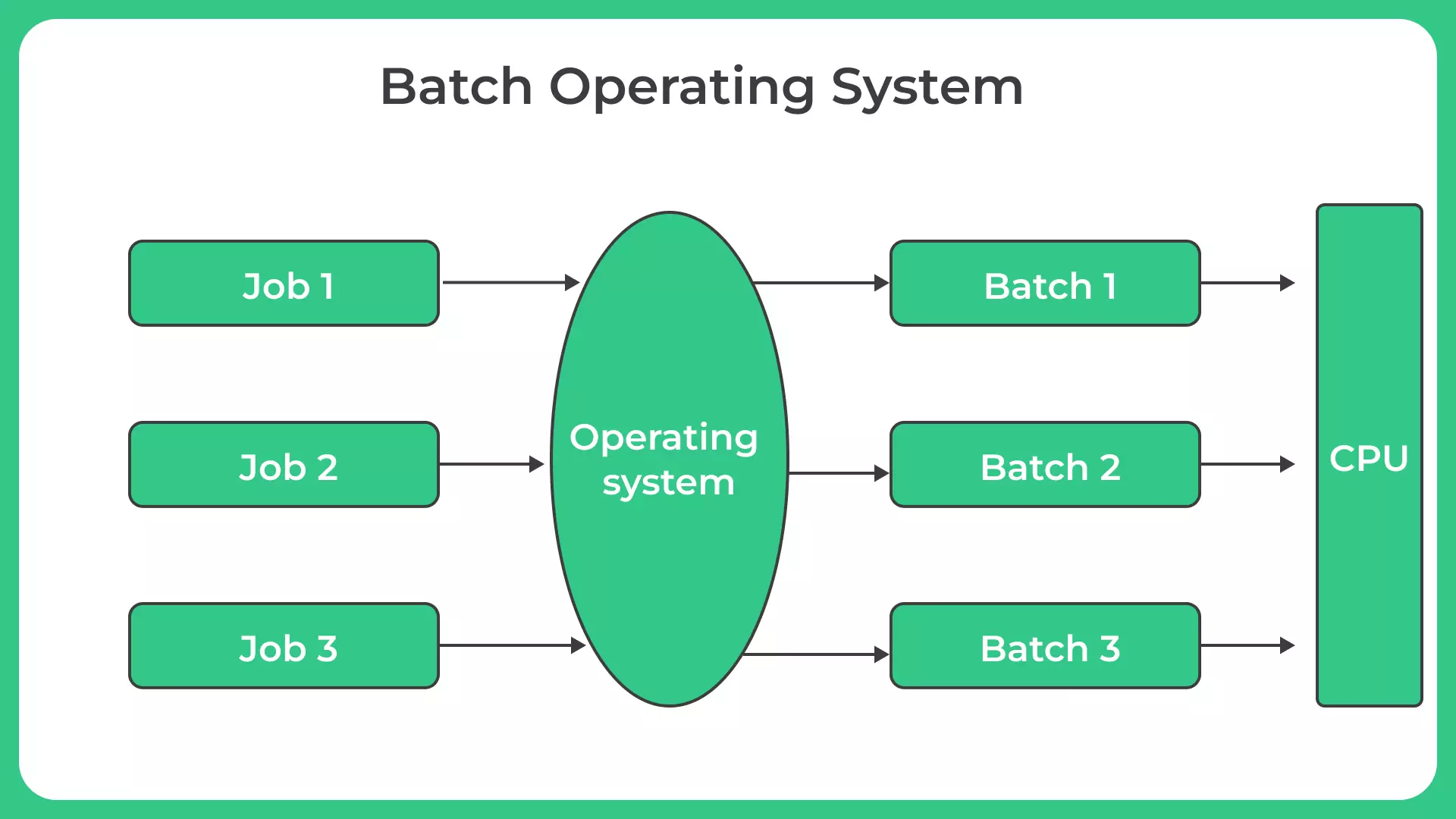
- Job Sequencing: Batch operating systems execute tasks in a sequential order, known as job sequencing, without requiring constant user intervention.
- Minimal User Interaction: Batch systems minimize the need for user interaction by automating the execution of tasks, allowing users to submit jobs and let the system handle their processing.
- Queue-Based Processing: Batch systems typically employ a queue-based mechanism for job scheduling and resource allocation, ensuring efficient utilization of system resources.
- Priority-Based Execution: Jobs in a batch operating system can be assigned priority levels, allowing for the execution of higher-priority jobs before lower-priority ones.
Prepare for Interview with us:
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Batch systems allow for continuous processing of tasks without manual intervention, maximizing resource utilization and increasing productivity.
- Improved Throughput: By executing jobs in batches, batch operating systems can process a large number of tasks sequentially, resulting in higher throughput and faster job execution.
- Streamlined Execution: Batch systems simplify the execution of repetitive tasks by automating the process, reducing the need for user interaction and minimizing errors.
- Better Control over Resources: Jobs can be prioritized and scheduled based on their requirements, allowing for effective resource allocation and optimal utilization of system resources.
- Scalability: Batch systems can handle large volumes of data and scale to accommodate increasing workloads, making them suitable for data-intensive applications.
- No User Interaction: Users cannot directly interact with the system while the job is being processed, making it less flexible for real time tasks.
- Difficult Debugging: Errors are only detected after the job is complete, making it harder to identify and fix issues quickly.
- High Turnaround Time: Since jobs are processed in batches, users may have to wait a long time for their jobs to be executed and results to be returned.
- Idle Resources: If there’s a delay in batch submission or in between jobs, system resources like CPU and memory may remain underutilized.
- Complex Job Scheduling: Efficient scheduling is hard to achieve, especially when jobs have varying priorities and resource requirements.
Modern Implementations and Applications of Batch Operating Systems
Although the prominence of batch operating systems has diminished in the era of interactive and time sharing systems, they still find application in specific domains. Industries that require large scale data processing, such as finance, healthcare, and scientific research, rely on batch systems for their computational needs. These systems offer reliability, efficiency, and scalability for processing vast amounts of data and executing complex calculations.
Conclusion
Batch operating systems have left a lasting impact on the field of operating systems. Their ability to efficiently process large volumes of data and execute repetitive tasks without constant user intervention has made them indispensable in various industries.
While the focus of modern computing has shifted towards interactivity and real-time responsiveness, batch systems still find relevance in specific domains.
As technology continues to advance, the future of batch operating systems lies in adapting to new challenges and embracing emerging paradigms.
FAQs
Jobs that require repetitive processing, such as payroll, billing, or report generation, are ideal for batch systems. These jobs benefit from automation and efficient resource usage.
Yes, modern batch processing is often integrated with cloud services to scale workloads and manage large data sets efficiently.
By automating tasks and running jobs during off-peak hours, batch systems reduce manual workload and optimize system performance.
No, they typically run on standard hardware but may be optimized for systems handling large volumes of data or high throughput computing.

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates

Login/Signup to comment