Java Program for Insertion in Doubly Linked List
Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Java
Let’s take a closer look at the Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Java programming. We will cover all the methods and positions for performing insertion effectively with coding implementation in Java programming language. Go through this page to get all the information related to Insertion In Doubly Linked List.
In a doubly linked list, insertion can be performed at the following positions:
- At the beginning
- At the end
- After a given node

Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Java
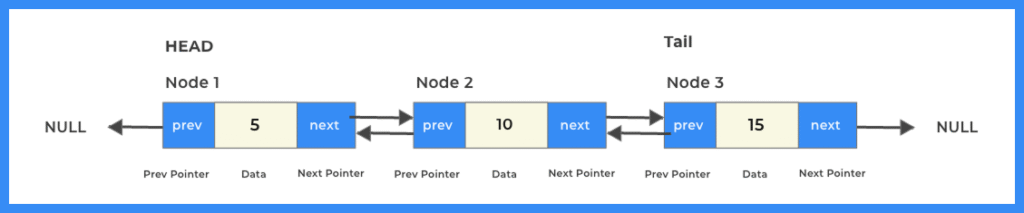
Doubly Linked List Structure
Doubly Linked List is a data structure consisting of nodes, where each node contains three parts:
- Data: Stores the value or data of the node.
- Next Pointer: Points to the next node in the list.
- Previous Pointer: Points to the previous node in the list.
This structure allows traversal in both forward and backward directions, making it more flexible than a singly linked list, which only allows forward traversal.
Example structure of a node in a doubly linked list:
Code Snippet of structure of a node
// Node Class
class Node{ int data; Node next, prev; Node(int x) // parameterized constructor { data = x; next = null; prev = null; } }
Practical Considerations and Optimizations
1. Memory Usage:
- Each node in a doubly linked list requires additional memory for the prev pointer, increasing overall memory consumption.
- Efficient memory management is essential, especially in large lists.
2. Maintaining a Tail Pointer:
Implementing a tail pointer reduces the time complexity of insertion at the end from O(n) to O(1), enabling direct access to the last node without traversal.
3. Pointer Updates:
Proper handling of prev and next pointers during insertion is crucial to prevent memory leaks and maintain data integrity, particularly when inserting at the beginning or after a specific node.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Java
- Insertion in a doubly linked list is a fundamental operation that involves adding new nodes at specific positions within the list.
- Unlike a singly linked list, each node in a doubly linked list contains two pointers, one pointing to the next node and another pointing to the previous node.
- This bidirectional structure enables more flexible insertion operations, allowing nodes to be added at the beginning, at a specific position, or at the end of the list.
In Java, implementing insertion operations requires careful management of these pointers to maintain the integrity of the list.
Types of Insertion in Doubly Linked List using Java:
1. For Insertion in the Beginning of the List:
Algorithm:
- Create a new node.
- Set the new node’s next to the current head.
- If the head is not null, set the current head’s prev to the new node.
- Update the head to the new node.

class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
Node head;
// Insert at the beginning
public void insertAtBeginning(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = head;
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
System.out.println("Inserted " + data + " at the beginning");
}
// Display the list
public void display() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList dll = new DoublyLinkedList();
dll.insertAtBeginning(10);
dll.insertAtBeginning(20);
dll.insertAtBeginning(30);
dll.display();
}
}
Inserted 10 at the beginning Inserted 20 at the beginning Inserted 30 at the beginning 30 20 10
Space Complexity = O(1)
2. For Insertion in the End:
Algorithm:
- Create a new node.
- Traverse to the last node.
- Update the next of the last node to the new node.
- Update the prev of the new node to the last node.

// Insert at the end
public void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
} else {
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = current;
}
System.out.println("Inserted " + data + " at the end");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList dll = new DoublyLinkedList();
dll.insertAtEnd(40);
dll.insertAtEnd(50);
dll.insertAtEnd(60);
dll.display();
}
Output:
Inserted 40 at the end Inserted 50 at the end Inserted 60 at the end 40 50 60
Space Complexity = O(1)
3. For Insertion at the Specific Position:
Algorithm:
- Create a new node.
- Traverse to the given node.
- Update the new node’s next to the given node’s next.
- Update the new node’s prev to the given node.
- Update the given node’s next to the new node.
- Update the next node’s prev to the new node (if it exists)

// Insert after a given node
public void insertAfter(int data, int after) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
Node current = head;
while (current != null && current.data != after) {
current = current.next;
}
if (current == null) {
System.out.println("Node " + after + " not found.");
return;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
newNode.prev = current;
if (current.next != null) {
current.next.prev = newNode;
}
current.next = newNode;
System.out.println("Inserted " + data + " after " + after);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList dll = new DoublyLinkedList();
dll.insertAtEnd(70);
dll.insertAtEnd(80);
dll.insertAfter(75, 70);
dll.insertAfter(85, 80);
dll.display();
}
public int getLength(Node node) {
int size = 0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while (node != null) {
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
Inserted 70 at the end Inserted 80 at the end Inserted 75 after 70 Inserted 85 after 80 70 75 80 85
Space Complexity = O(1)
Conclusion
Insertion in a doubly linked list offers flexible node placement but requires careful pointer management to maintain list structure.
Optimizing with a tail pointer significantly reduces insertion time complexity at the end, making it more efficient for frequent insertions.
Proper memory management and pointer updates ensure robust and error free implementations.
Learn DSA
FAQ's for Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Java
Answer:
Insertion in a Doubly Linked List in Java means adding a new node into the list while updating both the next and prev pointers so that the list remains correctly connected in both directions.
Answer:
Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Java can be done at three main positions: at the beginning, at the end, or at a specific position in the middle of the list.
Answer:
It is more flexible because each node contains a reference to both the previous and next nodes, making backward and forward movement easier during insertion.
Answer:
Best way to perform insertion in a Doubly Linked List in Java is to update four pointers carefully: the new node’s next, the new node’s prev, and the surrounding nodes’ next and prev pointers.
Answer:
Yes, insertion in Doubly Linked List in Java is allowed when the list is empty. The new node simply becomes the head (and the tail) of the list.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment