JAVA Program for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List
Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List in Java
In this article you will learn the complete logic behind Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List in Java, along with algorithms, examples, and clean Java Code.
Insertion at the beginning of a doubly linked list is one of the most common operations in data structures. This topic is important because it demonstrates how pointer manipulation works in both directions in a doubly linked list.

Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List in Java
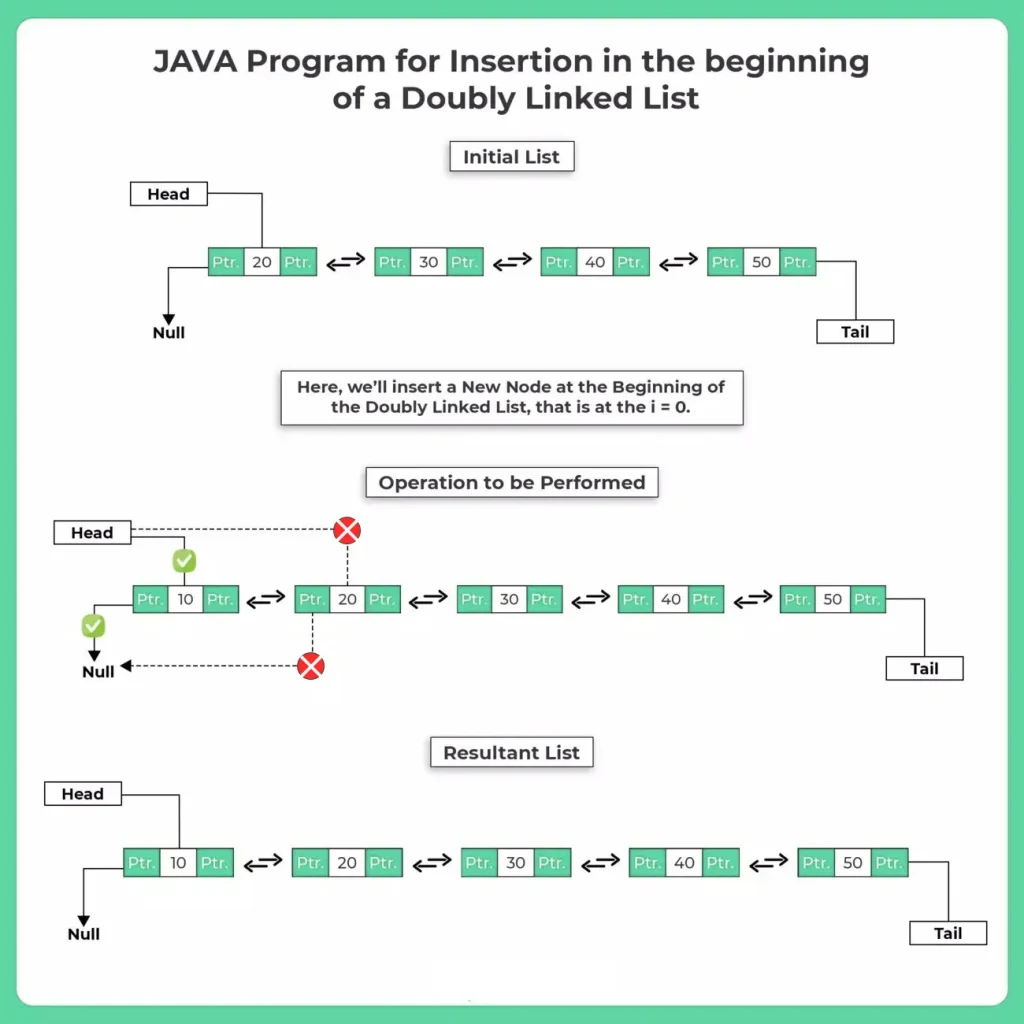
What Does Insertion at the Beginning Mean?
Doubly linked list contains nodes where each node has:
- data
- prev pointer (points to previous node)
- next pointer (points to next node)
Insertion at the beginning means creating a new node and placing it before the current head, making it the new head of the list.
Example:
Before insertion:
20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
Insert 10 at beginning →
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
Both prev and next links must be updated properly.
Understanding Java Program for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List helps you learn:
- How forward and backward pointers work
- Creating new nodes and reassigning references
- Handling empty list situations
- Preparing for coding interviews
This operation is foundational for building editors, browsers, playlist management, and many real-world linked structures.
1. Create a new node.
2. Set newNode.next = head.
3. If list is not empty, set head.prev = newNode.
4. Set newNode as the new head.
5. Return updated head.
Methods for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Here we have basically 2 approaches for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List:
- Method 1: Basic Pointer Manipulation (Iterative)
- Method 2: Using a Doubly Linked List Class Structure
Each includes algorithm, Java code, sample I/O, and complexities.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List
Method 1: Basic Pointer Manipulation
Algorithm:
Create a new node with given data.
Set newNode.prev = null.
Set newNode.next = head.
If head is not null, set head.prev = newNode.
Set head = newNode.
Return new head.
Java Code:
class DoublyInsertBeginning {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static Node insertAtBeginning(Node head, int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.prev = null;
newNode.next = head;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = newNode;
}
return newNode;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(20);
head.next = new Node(30);
head.next.prev = head;
System.out.println("Before insertion:");
printList(head);
head = insertAtBeginning(head, 10);
System.out.println("After insertion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
20 30 Insert: 10
Output:
10 20 30
Space Complexity: O(1)
Methods for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 2: Using a Doubly Linked List Class
Algorithm:
- Inside DLL class, create method insertAtBeginning.
- Create new node.
- Point its next to the current head.
- Set head’s prev to new node (if list not empty).
- Update head to new node.
- No return needed since head is a class variable.
Java Code:
class DoublyLinkedList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node head;
public void insertAtBeginning(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev = null;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = newNode;
}
head = newNode;
}
public void printList() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
list.insertAtBeginning(40);
list.insertAtBeginning(30);
list.insertAtBeginning(20);
System.out.println("After multiple insertions at beginning:");
list.printList();
}
}
Input:
Insert: 20, 30, 40
Output:
40 30 20
Space Complexity: O(1)
To wrap it up….
Insertion at the beginning of a doubly linked list is an essential operation that showcases how bidirectional pointer management works in linked structures.
- Since each node maintains both a previous and next link, inserting at the start requires updating pointers in both directions while ensuring the head reference changes correctly.
- Operation runs in constant time because no traversal is needed, making it efficient for real time data handling.
Learning Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List in Java helps build a strong understanding of memory references, pointer adjustments, and foundational list manipulation techniques that serve as the basis for advanced data structure operations.
FAQ's for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Answer:
It means adding a node before the current head and updating both next and prev pointers.
Answer:
Create a new node, connect its next to the head, update head’s prev, and move the head to the new node.
Answer:
The new node becomes the head without any pointer complications.
Answer:
Yes, doubly linked list insertion requires updating both directions.
Answer:
Yes, but logic differs, inserting at the beginning is the simplest case.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java






