JAVA program for Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List
Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List in Java is a fundamental data structure operation that allows you to add a new node after the current last node of the list. This operation is very important for building dynamic data structures such as music playlists, navigation systems, history management, and many real time applications where elements must be added at the end in a continuous manner.
Since a doubly linked list stores both previous and next references, insertion at the end becomes more efficient and organized compared to a singly linked list.
Java Program for Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List
What Does Insertion at the End Mean?
A doubly linked list node contains three fields:
- prev — points to the previous node
- next — points to the next node
Insertion at the end means:
- Creating a new node.
- Placing it after the current last node (tail).
- Updating both next and prev pointers properly.
Example:
Before insertion:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30
Insert 40 at the end.
After insertion:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
The new node becomes the last node of the list.
Understanding Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List using Java helps you learn:
- Efficient node attachment.
- Bi directional reference updates.
- Difference between singly and doubly linked lists.
- How tail based operations work?
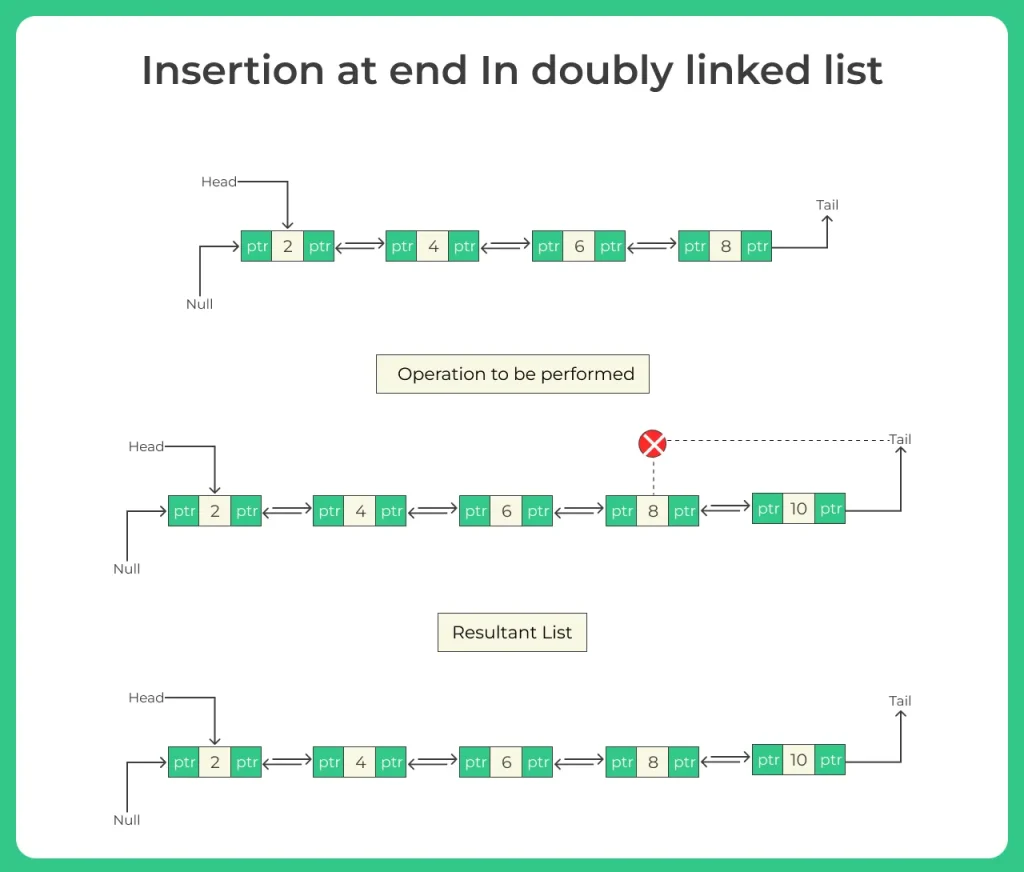
1. Create a new node with given data.
2. If the list is empty, make the new node the head.
3. Otherwise, traverse the list until the last node (where next == null).
4. Set last node’s next to the new node.
5. Set new node’s prev to the last node.
6. Set new node’s next to null.
This ensures correct forward and backward connections.
Methods for Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Here to perform Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List using Java programming, we have mentioned 2 different methods:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method for Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 1: Simple Traversal from Head
Algorithm:
- Create a new node with given data.
- If head == null, return new node as head.
- Create a pointer temp = head.
- Traverse until temp.next == null.
- Set temp.next = newNode.
- Set newNode.prev = temp.
- Set newNode.next = null.
- Return the head.
Java Code:
class InsertEndDoubly {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static Node insertAtEnd(Node head, int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
return newNode;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = temp;
newNode.next = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.prev = head;
head.next.next = new Node(30);
head.next.next.prev = head.next;
System.out.println("Before insertion:");
printList(head);
head = insertAtEnd(head, 40);
System.out.println("After insertion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30 Insert: 40
Output:
10 20 30 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method for Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 2: Using Tail Pointer
Algorithm:
This method keeps track of the last node, allowing insertion in constant time.
- Maintain a tail pointer in your class.
- Create a new node.
- If list is empty:
Set head = newNode
Set tail = newNode
Else:
Set tail.next = newNode
Set newNode.prev = tail
Move tail = newNode
Java Code:
class DoublyLinkedList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node head;
Node tail;
public void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
return;
}
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = tail;
newNode.next = null;
tail = newNode;
}
public void printList() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
list.insertAtEnd(5);
list.insertAtEnd(15);
list.insertAtEnd(25);
list.insertAtEnd(35);
System.out.println("After insertion at end:");
list.printList();
}
}
Input:
Insert: 5, 15, 25, 35
Output:
5 15 25 35
Space Complexity: O(1)
Comparison between both methods:
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Traversal | O(n) | O(1) |
| Tail Pointer | O(1) | O(1) |
Insertion at the end of a doubly linked list highlights the advantage of having both forward and backward links in a data structure.
- While simple traversal takes linear time, the use of a tail pointer enables constant time insertion, making the operation significantly more efficient for large datasets.
- This operation strengthens understanding of bidirectional pointer management, memory organization, and dynamic list growth.
Learning Java Program for Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List prepares you for implementing complex data structures such as deques, operating system schedulers, and advanced memory handling systems.
FAQ's for Insertion at the End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Answer:
It means adding a new node after the current last node by updating both next and previous pointers.
Answer:
Yes, especially when using a tail pointer, it runs in constant time O(1).
Answer:
It is optional, but it makes insertion at the end much faster.
Answer:
It is used in queues, browsers, music playlists, and dynamic data systems.
Answer:
Go to the last node and attach the new node by updating the next and prev references.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment