JAVA Program for Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List
Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java is an important operation that allows you to insert a new node at a specific position in an already existing doubly linked list. This operation is widely used in real world applications where data needs to be inserted dynamically at a specific location without breaking the structure of the list.
Java Program for Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List
What Does Insertion at the Nth Position Mean?
In a doubly linked list, each node contains:
- data
- prev pointer (points to previous node)
- next pointer (points to next node)
Insertion at the Nth position means adding a new node at a specific index, while keeping the rest of the list connected properly.
Example:
Original list:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 40 ⇆ 50
Insert 30 at position 3
Result:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40 ⇆ 50
The new node is placed at the Nth spot and all links are updated properly.
Learning Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java helps you understand:
- Precise node positioning
- Bidirectional pointer manipulation
- Handling edge cases (beginning, middle, end)
- Data organization in real world applications
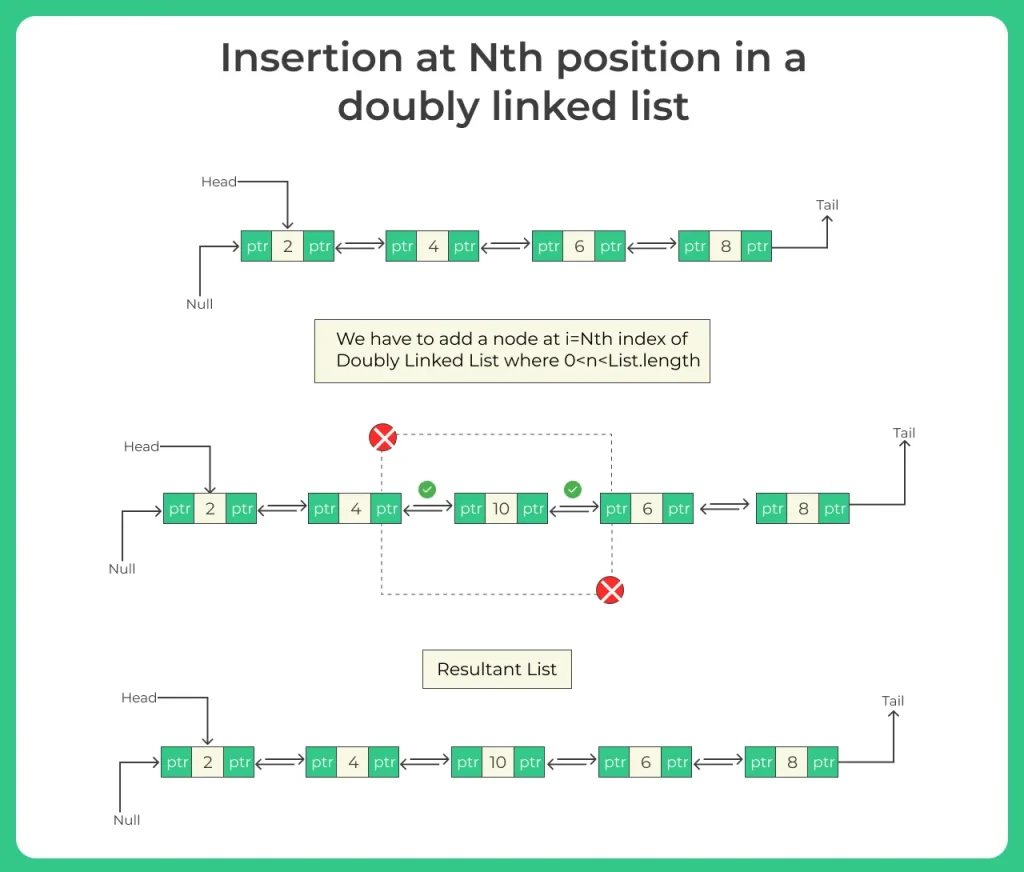
1. If n == 1 → Insert at beginning
2. Traverse the list to reach the (n-1)th node
3. Create a NEW node
4. Connect it with the previous and next nodes
5. Update both next and prev pointers
6. Ensure no links are broken.
Methods for Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Here for Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java, following methods can be applicable:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method for Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 1: Iterative Traversal Approach
Algorithm:
- Create a new node with the given value.
- If position == 1:
- Set newNode.next = head
- If head is not null, set head.prev = newNode
- Update head = newNode
- Return head
- Traverse the list using pointer temp till (position – 1)th node.
- If temp == null, insertion is not possible.
- Set:
- newNode.next = temp.next
- newNode.prev = temp
If temp.next != null, set temp.next.prev = newNode
Set temp.next = newNode
Return head.
Java Code:
class InsertAtNthDoubly {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static Node insertAtPosition(Node head, int data, int position) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// Insert at beginning
if (position == 1) {
newNode.next = head;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = newNode;
}
return newNode;
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < position - 1 && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp == null) {
return head;
}
newNode.next = temp.next;
newNode.prev = temp;
if (temp.next != null) {
temp.next.prev = newNode;
}
temp.next = newNode;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
Node second = new Node(20);
Node third = new Node(40);
head.next = second;
second.prev = head;
second.next = third;
third.prev = second;
System.out.println("Before insertion:");
printList(head);
head = insertAtPosition(head, 30, 3);
System.out.println("After insertion at 3rd position:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 40 Insert: 30 at position 3
Output:
10 20 30 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method for Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 2: Using Doubly Linked List Class
Algorithm:
- Maintain a head in class
- Traverse to (n-1)th node
- Insert new node between prev and next nodes
- If position is 1, shift head
- If end is reached, insert as tail
Java Code:
class DoublyLinkedListNthInsert {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev, next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node head;
public void insertAtPosition(int data, int position) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (position == 1) {
if (head != null) {
head.prev = newNode;
}
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < position - 1 && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp == null) return;
newNode.next = temp.next;
newNode.prev = temp;
if (temp.next != null) {
temp.next.prev = newNode;
}
temp.next = newNode;
}
public void printList() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedListNthInsert list = new DoublyLinkedListNthInsert();
list.insertAtPosition(10, 1);
list.insertAtPosition(20, 2);
list.insertAtPosition(40, 3);
System.out.println("Before:");
list.printList();
list.insertAtPosition(30, 3);
System.out.println("After insertion at position 3:");
list.printList();
}
}
Input:
10 20 40 Insert: 30 at position 3
Output:
10 20 30 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Conclusion:
Insertion at the Nth position in a doubly linked list demonstrates the power of bidirectional linking in data structures.
- By maintaining both prev and next pointers, the structure allows smooth and controlled insertion between any two nodes.
- While traversal is still required to reach the correct position, the insertion itself is handled efficiently with constant pointer manipulation.
- This operation highlights the importance of reference management in memory based data structures and builds a strong foundation for more advanced topics such as deletion at the Nth position, reversing a doubly linked list, and implementing circular list structures.
Mastering Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java is essential for developing high performance data handling applications.
FAQ's for Insertion at the Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List
Answer:
It is the process of inserting a new node at a specific position in a doubly linked list by updating both previous and next pointers correctly.
Answer:
By traversing up to the (n-1)th node and linking the new node between the existing nodes using prev and next references.
Answer:
Yes, it is a very popular interview question in Java and DSA based technical rounds worldwide.
Answer:
It is used in text editors, browser history, playlist management, and dynamic sequence applications.
Answer:
Because it maintains backward links, making the pointer adjustment more reliable and efficient.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment