0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Java program for deletion in doubly linked list
Java Program for Deletion in Doubly Linked List
Now Since we’ve already learnt enough about the Insertion Operation in a Doubly Linked List, let’s learn about the Deletion operation. We have three kinds of deletion in singly linked list in the same way we have three kinds of deletion in doubly linked list are as follows:
- Deletion at the beginning of the linked list.
- Deletion at Nth node/in middle of the linked list.
- Deletion at the end of the linked list.

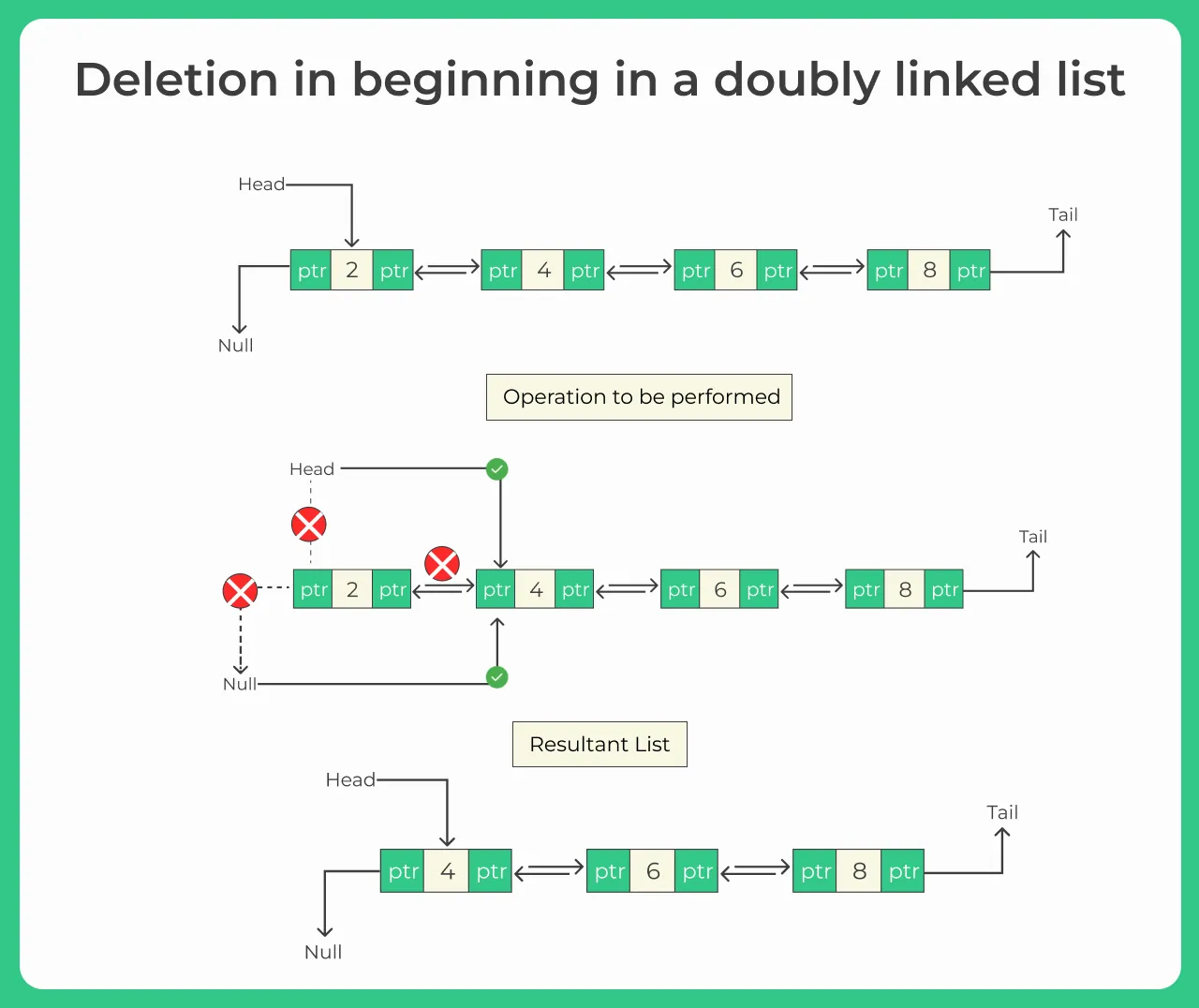
Deletion from the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List
For deletion at the beginning first we have to create a linked list and have to check if the list is empty or not. If it is empty then both head and tail points towards the new node . if it is not empty then we can delete our first node very easily.
Algorithm
- if (head == null) // if ended loop closed
- make ptr = head
- make head = head->next
- make head->prev = NULL
- free the pointer node
- END.
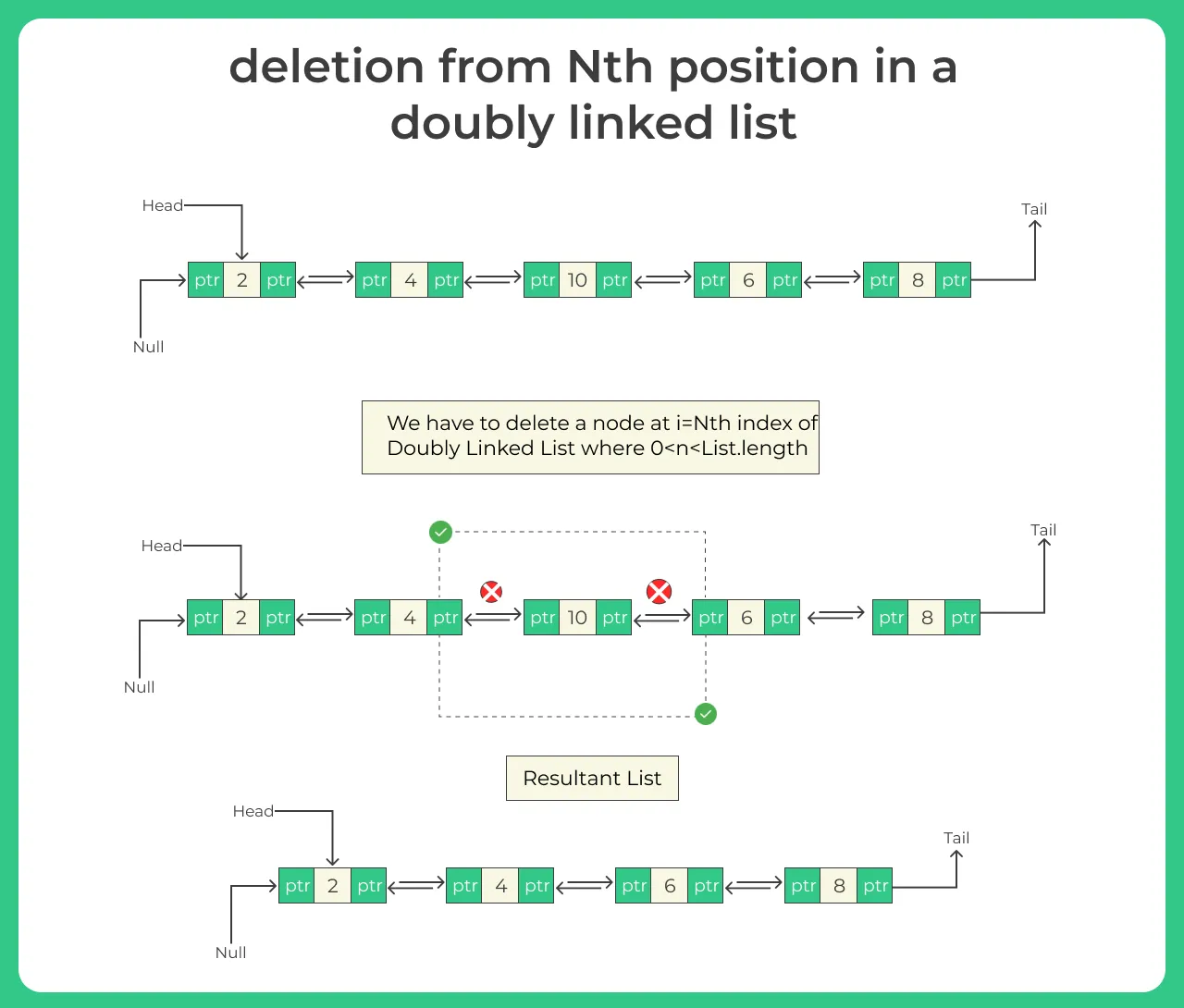
Deletion from the Specific Position of a Doubly Linked List
Deleting the nth node is as simple as it was in singly linked list. For deleting the node on nth node we have to go through the same process of deletion in beginning but there is a slight change this time we have to delete the nth node. So when you insert a function of deletion it should be for nth node.
Algorithm
- if (head == null) // if ended
- make temp = head so we can freely move our pointer
- temp->data= node
- make temp = temp->next // loop ended
- Make pointer ptr = temp->next
- temp->next = ptr->next
- make ptr->next->prev = temp
- free temp node
- END
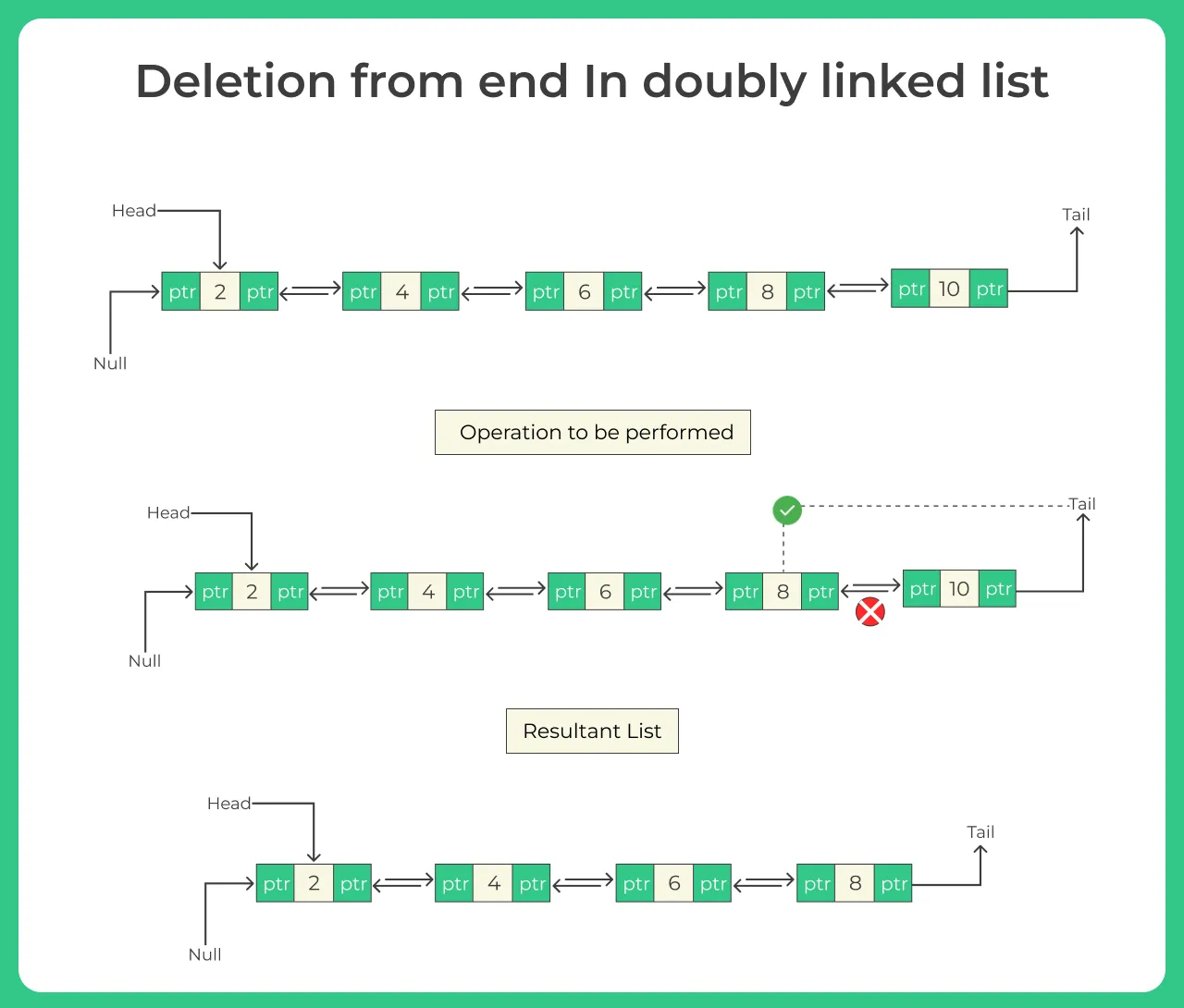
Deletion from the End of a Doubly Linked List
Here we have to delete the node from the end. It requires the traversing of list in order to reach the last node of the doubly linked list and after that we can run loop to delete a node from the end of the doubly linked list.
Algorithm.
- (head == null) then return.
- make temp = head
- while temp ->next != NULL
- make temp = temp->next // [loop ended]
- make temp->previous->next = NULL
- Free temp node
- Return
Java code for deletion in a doubly linked list
import java.lang.*;
class DoublyLinkedList
{
Node head;
// not using parameterized constructor would by default
// force head instance to become null
// Node head = null; // can also do this, but not required
// Node Class
class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node (int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
public void insertBeginning (int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node freshNode = new Node (data);
freshNode.next = head;
freshNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (head != null)
head.prev = freshNode;
// changing head to this
head = freshNode;
}
// function for deleting first node
public void deleteInitial ()
{
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return;
}
else
{
//testing for the presence of a single node in the list, If not, Then head and tail will be re-directed
if (head != null)
{
head = head.next;
}
//if only one node exist both head and tail will be redirected to null
else
{
head = null;
}
}
}
// function for deleting last node
public void deleteLast ()
{
if (head == null)
{
return;
}
else
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp = temp.prev;
temp.next = null;
}
else
{
head = null;
}
}
}
// function for deleting Nth node
public void deletenth (int n)
{
if (head == null)
{
return;
}
else
{
Node current = head;
int pos = n;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
{
current = current.next;
}
if (current == head)
{
head = current.next;
}
else if (current == null)
{
current = current.prev;
}
else
{
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
//Delete the middle node
current = null;
}
}
void printList ()
{
//Node current will point to head
Node curr = head;
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return;
}
while (curr != null)
{
//Prints each node by increasing order of the pointer
System.out.print (curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println ();
}
}
class Main
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
DoublyLinkedList doublylist = new DoublyLinkedList ();
doublylist.insertBeginning (3);
doublylist.insertBeginning (2);
doublylist.insertBeginning (1);
doublylist.insertBeginning (4);
doublylist.insertBeginning (7);
System.out.println ("List before deletion : ");
doublylist.printList ();
doublylist.deleteInitial ();
System.out.println ("List after deleting first node : ");
doublylist.printList ();
doublylist.deleteLast ();
System.out.println ("List after deleting last node : ");
doublylist.printList ();
doublylist.deletenth (2);
System.out.println ("List after deleting 2nd node : ");
doublylist.printList ();
}
}
Output
List before deletion : 7 4 1 2 3 List after deleting first node : 4 1 2 3 List after deleting last node : 4 1 2 List after deleting 2nd node : 4 2
import java.lang.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
class Main
{
static Node insertBeginning(Node head, int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if(head !=null)
head.prev = newNode;
// changing head to this
head = newNode;
return head;
}
// function for deleting first node
static Node deleteInitial ( Node head)
{
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return head;
}
else
{
//testing for the presence of a single node in the list, If not, Then head and tail will be re-directed
if (head != null)
{
head = head.next;
}
//if only one node exist both head and tail will be redirected to null
else
{
head = null;
}
}
return head;
}
// function for deleting last node
static Node deleteLast (Node head)
{
if (head == null)
{
return head;
}
else
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp = temp.prev;
temp.next = null;
}
else
{
head = null;
}
}
return head;
}
// function for deleting Nth node
static Node deletenth (int n, Node head)
{
if (head == null)
{
return head;
}
else
{
Node current = head;
int pos = n;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
{
current = current.next;
}
if (current == head)
{
head = current.next;
}
else if (current == null)
{
current = current.prev;
}
else
{
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
//Delete the middle node
current = null;
}
return head;
}
static void printList (Node head)
{
//Node current will point to head
Node curr = head;
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return;
}
while (curr != null)
{
//Prints each node by increasing order of the pointer
System.out.print (curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println ();
}
// required for insertAfterPosition() method
static int getLength(Node node){
int size=0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while(node!=null)
{
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = insertBeginning(head,3);
head = insertBeginning(head,2);
head = insertBeginning(head,1);
head = insertBeginning(head,4);
head = insertBeginning(head,7);
System.out.println ("List before deletion : ");
printList (head);
head = deleteInitial (head);
System.out.println ("List after deleting first node : ");
printList (head);
head= deleteLast(head);
System.out.println ("List after deleting last node : ");
printList (head);
head=deletenth (2,head);
System.out.println ("List after deleting 2nd node : ");
printList (head);
}
}
Output
List before deletion : 7 4 1 2 3 List after deleting first node : 4 1 2 3 List after deleting last node : 4 1 2 List after deleting 2nd node : 4 2
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java

 0
0



Login/Signup to comment