Doubly Linked List Insertion and Deletion in Java
Java Program for Insertion and Deletion in Doubly Linked List
Lets have a look on the code for Doubly Linked List Insertion and Deletion in Java. We will look at different methods available to do so and both deletion and insertion at various positions possible.

Doubly Linked List Introduction
Just like a singly linked list in Java, a doubly-linked list is also a non-contiguous data structure.
Which is basically a chain of nodes connected to one another.
Each node has the following –
- Data
- Next Node reference
- Previous Node reference
- Head reference
The head reference basically denotes the first node(start) of the doubly linked list.
Some versions also contain something called as tail reference which denotes the last node in the doubly linked list.

Possible positions to insert or delete
We can insert or delete at the following positions in the doubly linked list –
- At start
- At end
- In the middle (After a position)
Below are programs for all positions insertion/deletion in Java.
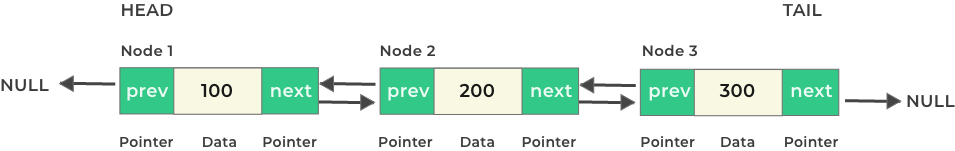
Structure of a Node in Doubly Linked List Java
Below is how a node is initialized in Java for a Doubly Linked List –
// Node Class
class Node{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
} Doubly Linked List Insertion in Java
Let us look at the program below –
import java.lang.*;
class DoublyLinkedList {
Node head;
// not using parameterized constructor would by default
// force head instance to become null
// Node head = null; // can also do this, but not required
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
public void insertBeginning(int data) {
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node freshNode = new Node(data);
freshNode.next = head;
freshNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (head != null)
head.prev = freshNode;
// changing head to this
head = freshNode;
}
public void insertEnd(int data) {
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node freshNode = new Node(data);
// assign data
// since this will be the last node its next will be NULL
freshNode.next = null;
//if we are entering the first node
if (head == null) {
head = freshNode;
freshNode.prev = null;
return;
}
Node last = head;
// traverse to the current last node
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
// assign current last node's next to this new node
// assign new node's previous to this last node
last.next = freshNode;
freshNode.prev = last;
// new_node becomes the last node now
}
public void insertAfterPosition(int n, int data) {
int len = getLength(head);
// if insertion position is 0 means entering at start
if (n == 0) {
insertBeginning(data);
return;
}
// means inserting after last item
if (n == len) {
insertEnd(data);
return;
}
// else insertion will happen somewhere in the middle
if (n < 1 || len < n)
System.out.println("Invalid position");
else
{
Node freshNode = new Node(data); // can remove null assignments also (constructor takes care of these) // added just for explanation purpose
freshNode.next = null;
freshNode.prev = null; // nthNode used to traverse the Linked List
Node nthNode = head; // traverse till the nth node
while (--n > 0) {
nthNode = nthNode.next;
}
Node nextNode = nthNode.next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous to this new node
nextNode.prev = freshNode;
// new_node's next assigned to (n+1)th node
freshNode.next = nextNode;
// new_node's previous assigned to nth node
freshNode.prev = nthNode;
// assign nth node's next to new_node
nthNode.next = freshNode;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node node = head;
Node end = null;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
System.out.print("\nIn forward: ");
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
end = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("\nIn backward: ");
while (end != null) {
System.out.print(end.data + " ");
end = end.prev;
}
System.out.println();
}
// required for insertPosition() method
public int getLength(Node node) {
int size = 0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while (node != null) {
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
DoublyLinkedList doublylist = new DoublyLinkedList();
doublylist.insertBeginning(3);
doublylist.insertBeginning(2);
doublylist.insertBeginning(1);
doublylist.printList();
doublylist.insertEnd(4);
doublylist.insertEnd(6);
doublylist.insertEnd(7);
doublylist.insertEnd(8);
doublylist.printList();
//Inserts after 4th position
doublylist.insertAfterPosition(4,5);
doublylist.printList();
}
}
Output
In forward: 1 2 3 In backward: 3 2 1 In forward: 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 In backward: 8 7 6 4 3 2 1 In forward: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 In backward: 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
import java.lang.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
class Main
{
static Node insertBeginning(Node head, int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if(head !=null)
head.prev = newNode;
// changing head to this
head = newNode;
return head;
}
static Node insertEnd(Node head, int data) {
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// assign data
// since this will be the last node its next will be NULL
newNode.next = null;
//if we are entering the first node
if(head==null){
head = newNode;
newNode.prev = null;
return head;
}
Node last = head;
// traverse to the current last node
while(last.next!=null)
last = last.next;
// assign current last node's next to this new node
// assign new node's previous to this last node
last.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = last;
// new_node becomes the last node now
return head;
}
static Node insertAfterPosition(int n, int data, Node head) {
int len = getLength(head);
// if insertion position is 0 means entering at start
if(n == 0){
head = insertBeginning(head, data);
return head;
}
// means inserting after last item
if(n == len){
head = insertEnd(head, data);
return head;
}
// else insertion will happen somewhere in the middle
if(n < 1 || len < n) System.out.println("Invalid position");
else { Node newNode = new Node(data);
// can remove null assignments also (constructor takes care of these)
// added just for explanation purpose
newNode.next = null;
newNode.prev = null;
// nthNode used to traverse the Linked List
Node nthNode = head;
// traverse till the nth node
while(--n > 0){
nthNode = nthNode.next;
}
Node nextNode = nthNode.next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous to this new node
nextNode.prev = newNode;
// new_node's next assigned to (n+1)th node
newNode.next= nextNode;
// new_node's previous assigned to nth node
newNode.prev = nthNode;
// assign nth node's next to new_node
nthNode.next = newNode;
}
return head;
}
static void printList(Node temp) {
Node end = null;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
System.out.print("\nIn forward: ");
while(temp!=null)
{
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
end = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.print("\nIn backward: ");
while (end != null) {
System.out.print(end.data + " ");
end = end.prev;
}
System.out.println();
}
// required for insertAfterPosition() method
static int getLength(Node node){
int size=0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while(node!=null)
{
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = insertBeginning(head,3);
head = insertBeginning(head,2);
head = insertBeginning(head,1);
printList(head);
head = insertEnd(head,4);
head = insertEnd(head,6);
head = insertEnd(head,7);
head = insertEnd(head,8);
printList(head);
//Inserts after 4th position
head = insertAfterPosition(4,5,head);
printList(head);
}
}
Output
In forward: 1 2 3 In backward: 3 2 1 In forward: 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 In backward: 8 7 6 4 3 2 1 In forward: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 In backward: 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Doubly Linked List Deletion in Java
Let us look at the program below –
import java.lang.*;
class DoublyLinkedList
{
Node head;
// not using parameterized constructor would by default
// force head instance to become null
// Node head = null; // can also do this, but not required
// Node Class
class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node (int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
public void insertBeginning (int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node freshNode = new Node (data);
freshNode.next = head;
freshNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (head != null)
head.prev = freshNode;
// changing head to this
head = freshNode;
}
// function for deleting first node
public void deleteInitial ()
{
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return;
}
else
{
//testing for the presence of a single node in the list, If not, Then head and tail will be re-directed
if (head != null)
{
head = head.next;
}
//if only one node exist both head and tail will be redirected to null
else
{
head = null;
}
}
}
// function for deleting last node
public void deleteLast ()
{
if (head == null)
{
return;
}
else
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp = temp.prev;
temp.next = null;
}
else
{
head = null;
}
}
}
// function for deleting Nth node
public void deletenth (int n)
{
if (head == null)
{
return;
}
else
{
Node current = head;
int pos = n;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
{
current = current.next;
}
if (current == head)
{
head = current.next;
}
else if (current == null)
{
current = current.prev;
}
else
{
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
//Delete the middle node
current = null;
}
}
void printList ()
{
//Node current will point to head
Node curr = head;
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return;
}
while (curr != null)
{
//Prints each node by increasing order of the pointer
System.out.print (curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println ();
}
}
class Main
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
DoublyLinkedList doublylist = new DoublyLinkedList ();
doublylist.insertBeginning (3);
doublylist.insertBeginning (2);
doublylist.insertBeginning (1);
doublylist.insertBeginning (4);
doublylist.insertBeginning (7);
System.out.println ("List before deletion : ");
doublylist.printList ();
doublylist.deleteInitial ();
System.out.println ("List after deleting first node : ");
doublylist.printList ();
doublylist.deleteLast ();
System.out.println ("List after deleting last node : ");
doublylist.printList ();
doublylist.deletenth (2);
System.out.println ("List after deleting 2nd node : ");
doublylist.printList ();
}
}
Output
List before deletion : 7 4 1 2 3 List after deleting first node : 4 1 2 3 List after deleting last node : 4 1 2 List after deleting 2nd node : 4 2
import java.lang.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
class Main
{
static Node insertBeginning(Node head, int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if(head !=null)
head.prev = newNode;
// changing head to this
head = newNode;
return head;
}
// function for deleting first node
static Node deleteInitial ( Node head)
{
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return head;
}
else
{
//testing for the presence of a single node in the list, If not, Then head and tail will be re-directed
if (head != null)
{
head = head.next;
}
//if only one node exist both head and tail will be redirected to null
else
{
head = null;
}
}
return head;
}
// function for deleting last node
static Node deleteLast (Node head)
{
if (head == null)
{
return head;
}
else
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp = temp.prev;
temp.next = null;
}
else
{
head = null;
}
}
return head;
}
// function for deleting Nth node
static Node deletenth (int n, Node head)
{
if (head == null)
{
return head;
}
else
{
Node current = head;
int pos = n;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
{
current = current.next;
}
if (current == head)
{
head = current.next;
}
else if (current == null)
{
current = current.prev;
}
else
{
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
//Delete the middle node
current = null;
}
return head;
}
static void printList (Node head)
{
//Node current will point to head
Node curr = head;
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return;
}
while (curr != null)
{
//Prints each node by increasing order of the pointer
System.out.print (curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println ();
}
// required for insertAfterPosition() method
static int getLength(Node node){
int size=0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while(node!=null)
{
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = insertBeginning(head,3);
head = insertBeginning(head,2);
head = insertBeginning(head,1);
head = insertBeginning(head,4);
head = insertBeginning(head,7);
System.out.println ("List before deletion : ");
printList (head);
head = deleteInitial (head);
System.out.println ("List after deleting first node : ");
printList (head);
head= deleteLast(head);
System.out.println ("List after deleting last node : ");
printList (head);
head=deletenth (2,head);
System.out.println ("List after deleting 2nd node : ");
printList (head);
}
}
Output
List before deletion : 7 4 1 2 3 List after deleting first node : 4 1 2 3 List after deleting last node : 4 1 2 List after deleting 2nd node : 4 2
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment