C Program for Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list
Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list
In this section we will study C Program for Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list in which the task is to insert element at leftmost of the linked list.The doubly linked allow us to traverse in both the directions from left to right and right to left.Also in the doubly linked list every node of the linked list contain double pointers or links so that we have to maintain more number of pointers in doubly linked list as compared to the singly linked list.
For Example:- Input : 25 4 51 20 9
Enter the element to insert at the beginning of the linked list : 33
Output : 33 25 4 51 20 9

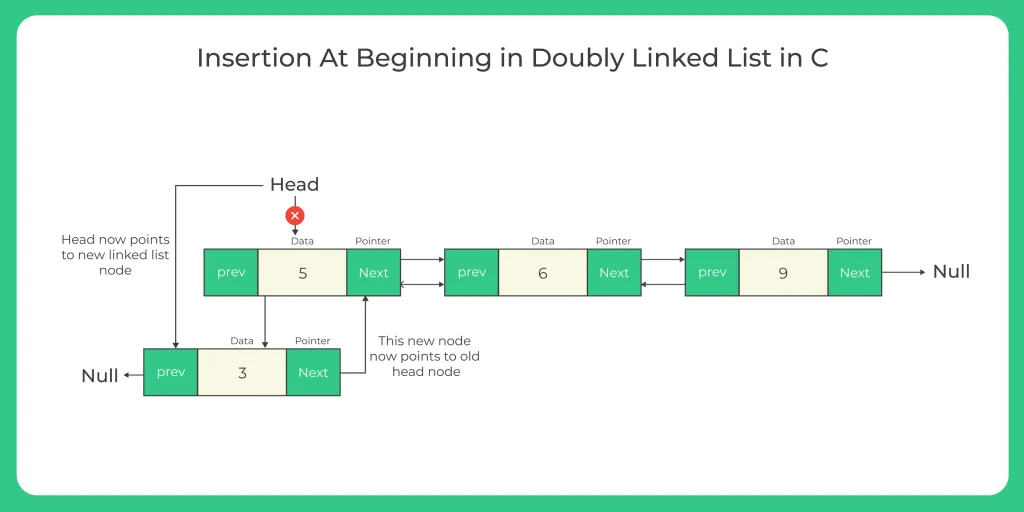
Steps used to inserting element in the doubly linked list:-
- Take a new_node then we put new_node with data has to be inserted at the beginning of the linked list.
- The next ptr of the new_node is instanced of the head node and the prev ptr is instanced to null.
- The prev ptr of the head node is instanced to the new_node.
- After that the new_node is made as the head node.
- Return the new_node.
Learn how to create a struct node of a doubly linked list
Syntax :-
struct node
{
struct node *prev;
int data;
struct node *next;
} 
Algorithm for inserting element in the linked list:-
Step 1 : IF POINTER = NULL
Step 2 : ASSIGN NEW NODE = POINTER
Step 3 : ASSIGN POINTER = POINTER -> NEXT
Step 4 : ASSIGN NEW NODE -> DATA = VALUE
Step 5 : ASSIGN NEW NODE -> PREV = NULL
Step 6 : ASSIGN NEW NODE -> NEXT = START
Step 7 : ASSIGN HEAD -> PREV = NEW NODE
Step 8 : ASSIGN HEAD = NEW NODE
Step 9 : RETURN
C Program for Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
//If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// *head->prev = newNode; would not work it has (*head) must be used
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
// function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("List in Forward direction: ");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nList in backward direction: ");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
/*Need & i.e. address as we
need to change head address only needs to traverse
and access items temporarily
*/
insertStart (&head, 12);
insertStart (&head, 16);
insertStart (&head, 20);
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not
need to change head address
*/
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
List in Forward direction: 20 16 12 List in backward direction: 12 16 20



Login/Signup to comment