C Menu
- Basics of C
- Basics of C Programming
- Features of C Programming
- Preprocessors in C Programming
- History of C Programming
- Low Level Programming
- Why C is Middle Level Language
- Introduction to C programming
- Structure of a C program
- Input-Output Functions
- Difference between Compiler and Interpreter
- Assembler v/s Compiler v/s Interpreter v/s Linker v/s Loader
- Basics to Code
- Operators in C
- Operators in C
- Precedence Associativity Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Ternary Operators in C
- Size of Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Comma Operators
- Format Specifiers in C
- Difference between %d and %i
- Difference between %f, %e, %E and %g
- How to print% using printf
- How to print \ using printf
- How to print “” using printf
- What is the use of %p in C
- Library Functions in C
- pow() in C
- sqrt() in C
- Storage Classes in C
- Conditional statements and Decision Making in C
- DataType & Functions in C
- Arrays, String, Structure, Union and Enum
- Pointer in C
- Library Function in C
- Library function in C
- math.h in c
- Library function math.h acos
- Library function math.h acosh
- Library function math.h asin
- Library function math.h asinh
- Library function math.h atan
- Library function math.h atan2
- Library function math.h atanh
- Library function math.h cbrt
- Library function math.h cell
- Library function math.h cos
- Library function math.h cosh
- Library function math.h exp
- Library function math.h fabs
- Library function math.h floor
- Library function math.h hypot
- Library function math.h log
- Library function math.h log10
- Library function math.h pow
- Library function math.h sin
- Library function math.h sinh
- Library function math.h sqrt
- Library function math.h tan
- Library function math.h tanh
- Library function studio.h clearerr
- Library function string.h strcat
- Library function string.h strcmp
- Library function string.h strcpy
- Library function string.h strlen
- File Handling
- Dynamic Memory Allocation
- Miscellaneous Topics in C
- Miscellaneous Coding Questions
PREPINSTA PRIME
Tokens in C
Tokens in C
Tokens are called building block of C programming, that means only with the help of tokens a C program can be created. Every small part that is used in the program is called tokens. In C programming, some INDIVIDUAL words and characters are fixed, whose functions are fixed, called tokens. It is the smallest element of C program. There are some internal tokens we need to know while writing a program in C to understand the most basic to the syntax of the C language.
Tokens in C
Tokens are called building block of C programming, that means only with the help of tokens a C program can be created.
- every small part that is used in the program is called tokens.
- In C programming, some INDIVIDUAL words and characters are fixed, whose functions are fixed, called tokens.
- It is the smallest Lexial unit of C program.
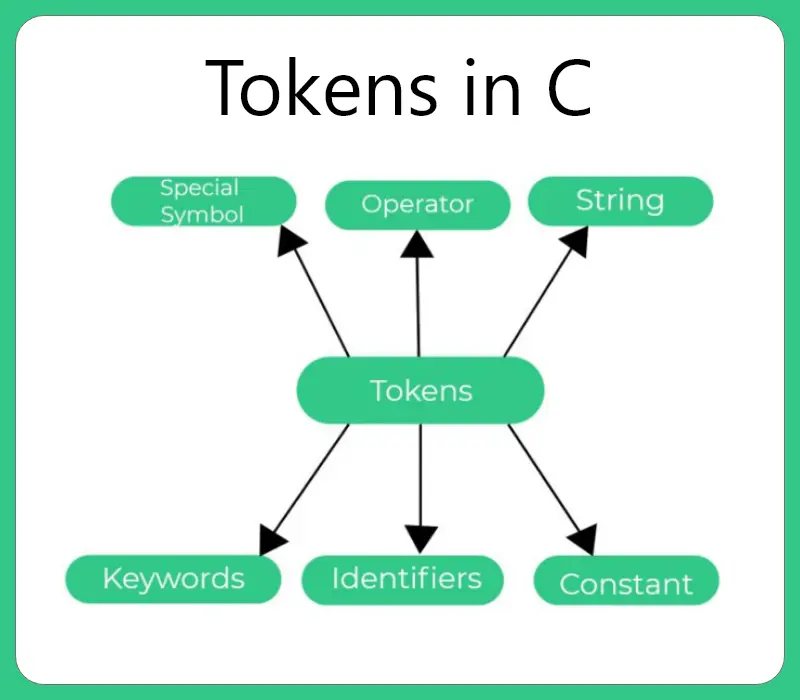
There are some internal tokens we need to know while writing a program in C to understand the most basic to the syntax of the C language.
Some internal tokens are:-
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Constants
- Strings
- Special Symbols
- Operators
for example, look at the program below. this program is used in the correct order of tokens.
#include
int main()
{
printf("my name is somya");
printf("%d",4);
}
KEYWORDS
Keywords are predefined statements ,operators reserved words which have a special meaning to the compiler while execution, they are a part of it and can not be used as an identifier. C language provides 32 keywords. every keyword has a special meaning. each keyword is defined to do a specific job. Here is a list of some identifiers given below
| auto | else | long | switch |
| break | enum | register | typedef |
| case | double | return | union |
| char | float | short | unsigned |
| const | for | signed | void |
| continue | goto | sizeof | volatile |
| default | if | static | while |
| do | int | struct | _Packed |
IDENTIFIERS
In a simple language an identifier is the name of a variable (integer,float(decimal),character) given to a variable or constant for a program just like a math problem. It can start anywhere from A to Z or a to z or underscore ( _ ) and you may or may not add more to the later by integer digits or more letters or underscores .
But one should always remember that C is a case-sensitive programming language .So identifiers like Goku, goku, _goku, goku1 ,Goku1 are all different identifiers .
Note : C doesn’t allow punctuation’s like ! @ $ % & * in identifiers so make sure you don’t have a g@ku or goku! named identifier .
Identifiers are the names that give you variables,constants and functions. these are some rules to give to these names that you follow, if you don’t follow then there is an error in the program.
- In Identifiers @, %, -characters can not be used.
- C is a Case sensitive language, So more and More both are said to be different identifiers.
- In Identifiers, we can not use operators.
- It can start anywhere from A to Z or a to z or underscore ( _ ) and you may or may not add more to the later by integer digits or more letters or underscores.
- you can either start an identifier with either a character or underscore. Digits can not be started from identifiers.
Example:-
_old //identifier 2name //not identifier person-name //not identifier person_2_old //identifier.
CONSTANTS
Constant is a value, which does not change in program execution.
- constant value is fixed.
- it is also known as Literals.
- it does not matter where we use it in program,its meaning always fixed.
- it is also like normal variables.
Types of Constants:-
1.Integer constant -The whole values used in the C program are called integer constant.
Like: 1,53,677 e.t.c.
2.Character constant – The different characters used in the C program are called character constant.
Like: f, v, s, w, # e.t.c.
3.Float constant – In C program, such numeric value in which the digit after the decimal is called float constant.
Like: 4.44444, 34.6634 etc.
4.String constant – many literal characters are placed under string literal.
Like: “rat”, “prep”,etc.
STRINGS
The group of characters is known as strings. which are always enclosed in double quote. it is also said to be array of characters.it is used to stored data of class,mobile numbers , name etc. At the end of the string there is always a special character, which is known as null. its indicate the end of the string.
Declaration of Strings:-
char string[20] = {‘p’,’r’,’e’,’p’,’I’,’n’,’s’,’t’,’a’,’\0′};
char string[20] = “prepInsta”;
char string[] = “prepInsta”;
SPECIAL SYMBOL:-
Some special symbols are used in C programming. symbols means alphabet, exclude the digits using some symbols in C programming.In C programming some special symbol are used in C having some special meaning and cannot be use in other purpose.
The following symbols are:-
Braces {}:- these curly braces are used to show the starting and ending of a block of code containing some executable statement.
Parentheses ():- Parentheses are used to specify the function call and function parameter.
Brackets []:- this is the opening and closing brackets. it is used as array element reference. these stipulate the single and multidimensional subscripts.
Comma (,) :- it is used to separate more then one statement.
Asterick (*) :- used to create pointer variable.
Assignment variable:- used to assign values.
Semicolon:- In C program after every statement we have to put a semicolon (;) which tells the compiler the statement ends there .For example
printf("Kamehameha");
return 6;It indicates the end of one logical entity.
OPERATORS
Operators is special symbol which is used to perform mathematical operation like, addition, subtraction, division, multiplication.Different types of symbols are used to perform different type of mathematical and logical operation in C programming is known as operators. that symbols.
types of operator:-
- Unary Operator:– unary operators are those operators, which require only single operands is known as unary operator.
Example:- increment and decrements operator.
2. Binary Operator:- Those operators, which require two operands is known as binary operator.
Binary operators are:–
- Arithmetic operator
- Logical operator
- Bitwise operator
- Conditional operator
- Relational operator
- Assignment operator
3.Ternary operator:- These operators which require three operands are known as ternary operator.
Example:– Conditional operator (?:).

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates

Easy to understand
good concepts
Thank you for your appreciation and also we want you to know that we are more than happy to help you and serve you better!!!
Great
Thanks for the appreciation Prakash
Hello ! In the identifiers and keywords section given that keywords start with lower case letters and it contains only lower case letters . But _Packed keyword given in the list does not matches . can you please clear my dought . Thankyou
It is basically not a keyword but a qualifier, which is used to remove padding between members of structures or unions.