Search an element in a linked list in Java
Program to Search an Element in a linked list
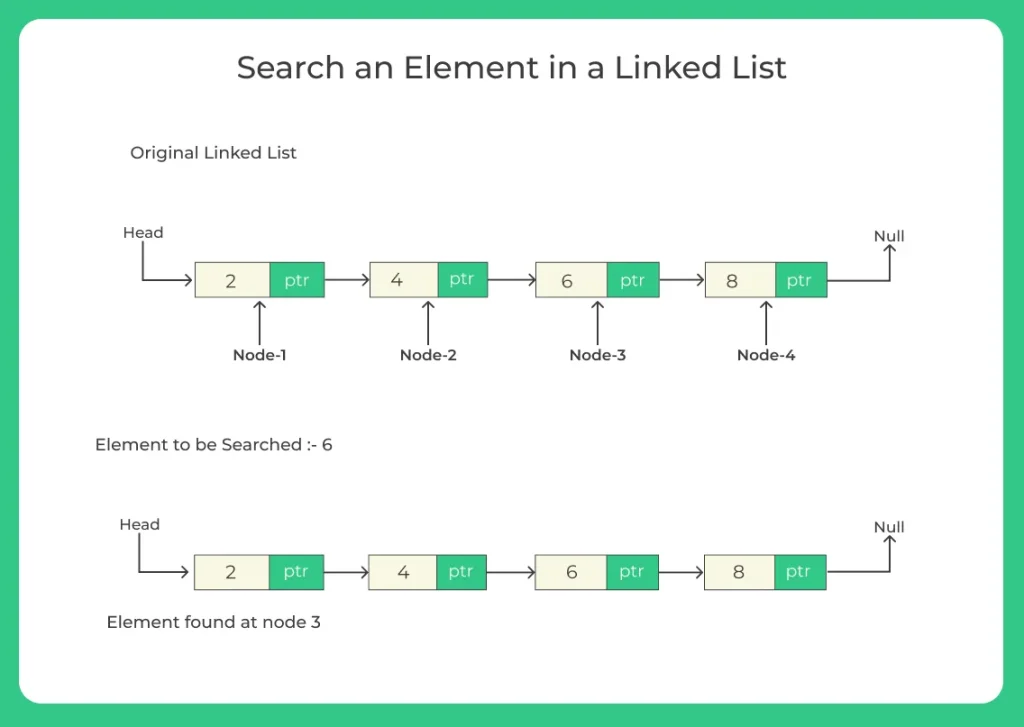
Search an element in a linked list in Java is a basic operation used to find the position of a specific element. Since linked lists do not support direct access by index, the search process involves traversing the list from the head node and comparing each element with the target value.
If a match is found, the function returns the position of that element.
Otherwise, it continues until the end of the list, indicating the element is not present if no match is found.

Searching an Element in a Linked List in Java
Linked List is a linear data structure where each element (called a node) contains:
- Data: The actual value stored.
- Next: A pointer/reference to the next node in the list.
Unlike arrays, linked lists do not store elements in contiguous memory locations.
This makes operations like insertion and deletion efficient compared to arrays, but searching is slower since random access is not possible.
Types of Searches in Linked List
There are two common methods to search for an element in a singly linked list:
- Iterative Search
- Recursive Search
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
3 Approaches for Search an Element in a Linked List in Java
1. Iterative Approach for Search an element in a linked list in java
Algorithm:
- Start from the head of the linked list.
- Traverse through each node one by one.
- At each node, compare the node’s data with the target key.
- If found, return the position (or true).
- If the end is reached and the key is not found, return false.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class IterativeSearchLinkedList {
Node head;
// Append new node at the end
public void append(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
// Iterative search
public boolean search(int key) {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
if (current.data == key) return true;
current = current.next;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
IterativeSearchLinkedList list = new IterativeSearchLinkedList();
list.append(5);
list.append(10);
list.append(15);
System.out.println("Searching 10: " + list.search(10)); // true
System.out.println("Searching 99: " + list.search(99)); // false
}
}
Searching 10: true Searching 99: false
2. Recursive Approach to Search an element in a linked list
Algorithm:
- Base Case: If head is null, return false.
- If head.data == key, return true.
- Else, recursively call the function with head.next.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class RecursiveSearchLinkedList {
Node head;
// Append new node at the end
public void append(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
// Recursive search
public boolean search(Node node, int key) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (node.data == key) return true;
return search(node.next, key);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RecursiveSearchLinkedList list = new RecursiveSearchLinkedList();
list.append(1);
list.append(2);
list.append(3);
System.out.println("Searching 2: " + list.search(list.head, 2)); // true
System.out.println("Searching 9: " + list.search(list.head, 9)); // false
}
}
Searching 2: true Searching 9: false
3. Index Based Approach to Search an element in a linked list
Goal:
Given the head of a singly linked list and a key k, return the index (0-based) of the node where node.data == k.
Return -1 if the key is not found.
Steps:
- Initialize a pointer current to point to the head of the linked list.
- Initialize an integer index = 0 to track the position.
- Repeat while current is not null:
- If current.data == key, return index.
- Else, move current to current.next and increment index.
If the loop finishes without finding the key, return -1.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class IndexSearchLinkedList {
Node head;
// Append a node to the end of the list
public void append(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
// Search for the index of a key in the linked list
public int searchIndex(int key) {
Node current = head;
int index = 0;
while (current != null) {
if (current.data == key) {
return index; // key found
}
current = current.next;
index++;
}
return -1; // key not found
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
IndexSearchLinkedList list = new IndexSearchLinkedList();
// Add elements to the list
list.append(10);
list.append(20);
list.append(30);
list.append(40);
list.append(50);
// Search for values
int key1 = 30;
int key2 = 100;
int result1 = list.searchIndex(key1);
int result2 = list.searchIndex(key2);
if (result1 != -1)
System.out.println("Element " + key1 + " found at index: " + result1);
else
System.out.println("Element " + key1 + " not found");
if (result2 != -1)
System.out.println("Element " + key2 + " found at index: " + result2);
else
System.out.println("Element " + key2 + " not found");
}
}
Element 30 found at index: 2 Element 100 not found
Conclusion
Searching in a singly linked list requires traversing nodes one by one, hence linear time complexity.
Two main approaches: Iterative (space-efficient) and Recursive (more readable but less memory efficient).
- For frequent search operations, linked lists are not ideal, consider using indexed or hashed data structures.
- Always choose the right data structure based on the dominant operation (search, insert, delete, etc.).
FAQ's related to Search an element in a linked list in Java
Answer:
Value based search: Returns true or false depending on whether the key exists in the list.
Index based search: Returns the position (index) of the key in the list if found, otherwise -1.
Answer:
Iterative search is more efficient in terms of space (O(1)), and it avoids stack overflow for large lists.
Recursive search is more elegant and concise but uses O(n) space due to recursive calls. So, iterative is generally preferred in production environments.
Answer:
The standard search method (both iterative and recursive) **returns the index of the first occurrence only. To return all positions, you would need to modify the algorithm to continue searching even after the first match.
Answer:
- Use a Tail Pointer: speeds up append operations to O(1).
- Convert to Doubly Linked List: enables efficient two way traversal.
- Add Sentinel (Dummy) Nodes: simplifies insert/delete edge cases.
- Maintain Size Variable: allows O(1) access to list length.
- Combine with Hash Map: enables faster search (O(1) lookup).
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment