Fold a Linked List in Java
Java Program to Fold a Linked List
Folding a linked list is an important interview problem and in this article you will learn how to Fold a Linked List in Java using simple explanations, algorithms, and clean code.
This problem is frequently asked in coding tests and helps developers understand linked list pointer manipulation.

How to Fold a Linked List in Java
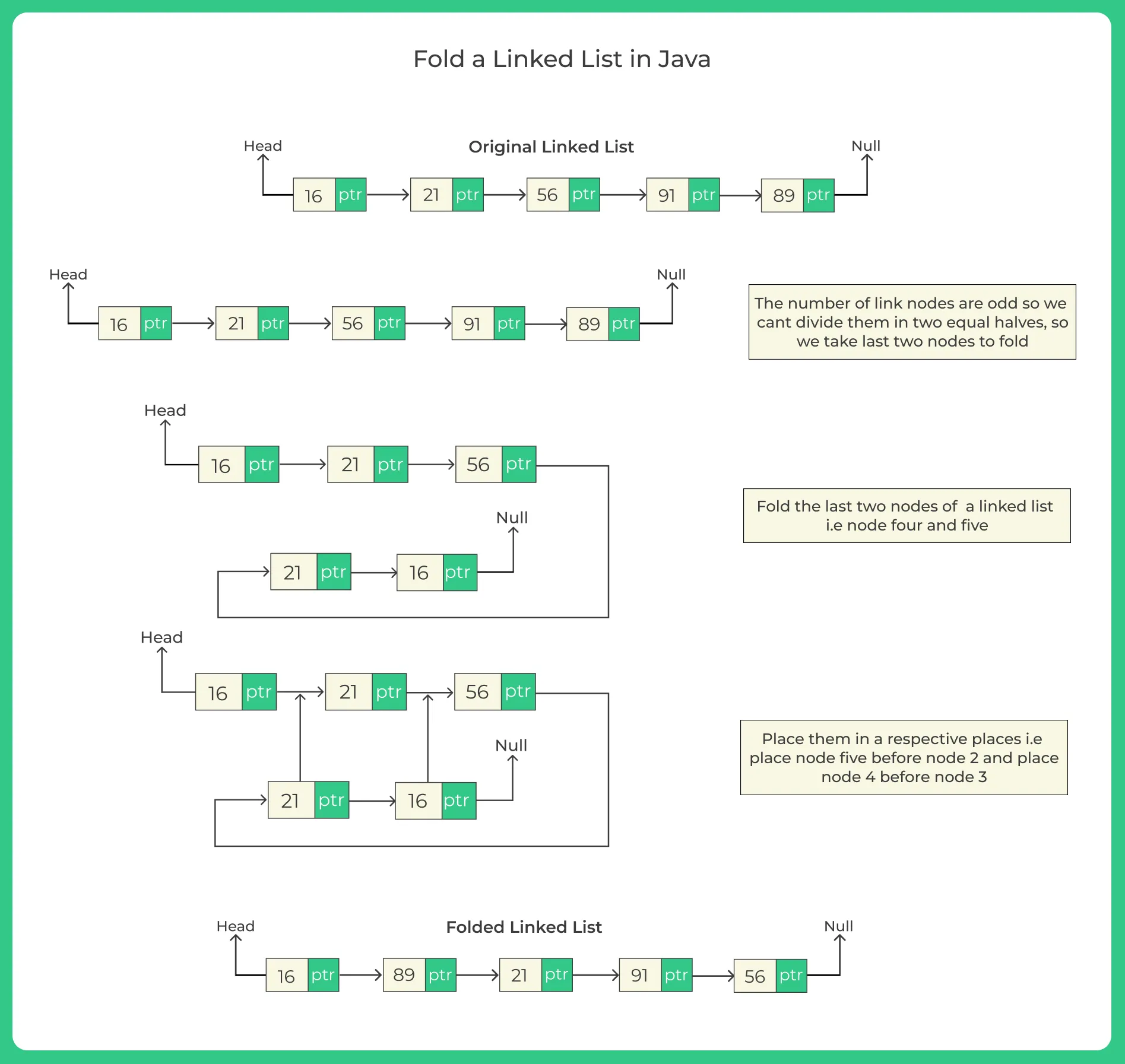
Folding a linked list means rearranging the nodes such that the last node becomes the second, the second last becomes the fourth, and so on.
It converts a list like:
1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5
Into:
1 → 5 → 2 → 4 → 3
You always take one from the front, one from the back, and fold them together.
1. Linked list traversal.
2. Pointer manipulation.
3. Middle element finding
4. Recursion and stack control
Theoretical Explanation of Folding a Linked List
To Fold a Linked List in Java, two main concepts are used:
1. Finding the Middle of a Linked List
Using slow and fast pointers, you find the middle so you can split the list into two halves.
2. Reversing the Second Half
You reverse the right half so you can merge it with the left side in alternating order.
3. Merging Two Halves Alternately
You take one node from the first half, then one from the reversed second half, and connect them.
Methods to Fold a Linked List in Java
Here we will discuss 2 approaches to fold a linked list in Java:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods to Fold Linked List in Java
Method 1: Using Middle + Reverse + Merge (Iterative)
Algorithm:
Let head be the start of the list.
Use slow and fast to find the middle node.
Split the list into two halves:
First half begins at head
Second half starts at mid.next
- Reverse the second half using pointers prev, curr, next.
- Merge both halves:
Use pointers first and second.
Connect first.next to second, then move both ahead.
- Stop when second half ends.
- Return the folded list head.
Java Code:
class FoldLinkedList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
// Method 1: Middle + Reverse + Merge
public static Node foldList(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// Find middle
Node slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// Reverse second half
Node second = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
Node prev = null, curr = second, next;
while (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
second = prev;
// Merge halves
Node first = head;
while (second != null) {
Node temp1 = first.next;
Node temp2 = second.next;
first.next = second;
second.next = temp1;
first = temp1;
second = temp2;
}
return head;
}
// Utility to print list
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Example
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Original List:");
printList(head);
head = foldList(head);
System.out.println("Folded List:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
1 2 3 4 5
Output:
1 5 2 4 3
Space Complexity: O(1)
Methods to Fold Linked List in Java Programming
Method 2: Recursion Based Folding
Algorithm:
Create a global pointer left starting at head.
Create a recursive function fold(Node right, int depth, int size).
Move right to the end using recursion.
During the return phase:
- If depth > size / 2:
Store left.next in temp
Connect left.next to right
Connect right.next to temp
Move left forward
- If depth > size / 2:
- If depth == size / 2, set right.next = null.
- Start recursion with right = head, depth = 0.
- Return folded list head.
Java Code:
class FoldListRecursion {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
static Node left;
public static Node foldList(Node head) {
left = head;
int size = getSize(head);
foldHelper(head, 0, size);
return head;
}
private static void foldHelper(Node right, int depth, int size) {
if (right == null) return;
foldHelper(right.next, depth + 1, size);
if (depth > size / 2) {
Node temp = left.next;
left.next = right;
right.next = temp;
left = temp;
} else if (depth == size / 2) {
right.next = null;
}
}
private static int getSize(Node head) {
int count = 0;
while (head != null) {
head = head.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
// Utility print
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Example
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Original List:");
printList(head);
foldList(head);
System.out.println("Folded List:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
1 2 3 4 5
Output:
1 5 2 4 3
Space Complexity: O(n)
Comparison between both methods:
| Method Name | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Middle + Reverse + Merge (Iterative) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Recursion-Based Folding | O(n) | O(n) |
So, you learned how to Fold a Linked List in Java using both iterative and recursive approaches.
You also saw algorithms, Java code, complexities, and comparison. The iterative method is preferred due to its efficient time and space usage. Understanding this concept improves your linked list handling skills and prepares you for coding interviews.
FAQ's related to Fold a Linked List in Java
Answer:
It means rearranging the list in such a way that the last node comes after the first, the second last after the second, and so on.
Answer:
The iterative method using middle + reverse + merge is the best because it uses constant space.
Answer:
Yes, recursion can fold the list but uses extra stack space.
Answer:
Yes, the links are changed, so the original order is lost unless you clone the list.
Answer:
No, folding rearranges nodes from both ends, while reversing simply flips the order.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment