Deletion of nth node in Linked List in Java
Java Program for Deletion of nth node in Linked List
In this guide, you will learn how to Delete nth Node in Linked List in Java using simple explanations, clear algorithms, and complete Java code.
Deleting a specific node from a linked list is an essential operation in data structures. This problem is frequently asked in coding interviews because it tests your understanding of pointer manipulation and edge-case handling.

What is deletion of nth node in Linked List in Java?
Given a singly linked list and a position n, your task is to remove the node present at the nth position (1-based index).
Example:
10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 50
If n = 3, remove the third node (30):
10 → 20 → 40 → 50
Understanding Delete nth Node in Linked List in Java helps you learn:
- Node traversal logic
- Boundary condition handling
- Pointer updates
- Efficient node deletion
This operation strengthens your base for more complex linked list operations like deleting from end, folding lists, and reversing.
1. Traverse the list to reach the node just before nth node
2. Change its next pointer to skip the nth node
3. Java garbage collector handles memory cleanup
4. Special case: deleting the head node (n = 1)
This operation requires careful pointer adjustment to avoid breaking the list.
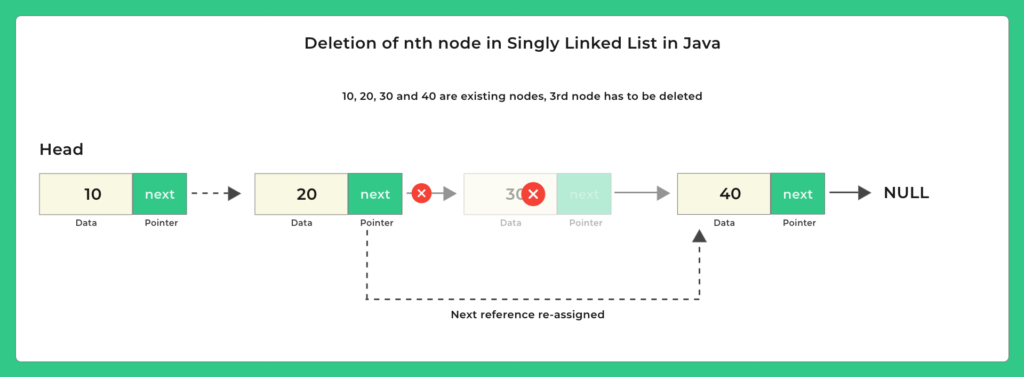
Method for Deletion of nth Node in Linked List in Java
Deletion of nth Node in Linked List in Java Programming can be performed using 2 methods, mentioned as follows:
Each method includes:
- Step by step algorithm
- Java code
- Example input and output
- Time and space complexity
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods for Deletion of nth node in Linked List in Java
Method 1: Simple Iterative Traversal
Algorithm:
- If head is null, return null.
- If n == 1, update head to head.next and return new head.
- Initialize temp = head.
- Move temp to the (n – 2)th node using a loop.
- Let target = temp.next be the node to delete.
- Point temp.next to target.next.
- Disconnect target.next.
- Return updated head.
Java Code:
class DeleteNthNode {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node deleteNth(Node head, int n) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (n == 1) {
Node newHead = head.next;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1 && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp == null || temp.next == null) return head;
Node target = temp.next;
temp.next = target.next;
target.next = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(30);
head.next.next.next = new Node(40);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteNth(head, 3);
System.out.println("After deletion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30 40 n = 3
Output:
10 20 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method for Deletion of nth node in Linked List in Java
Method 2: Two Pointer Technique
Algorithm:
Create a dummy node pointing to head (helps handle n = 1 easily).
Initialize two pointers: fast = dummy, slow = dummy.
Move fast ahead by n nodes.
Move both pointers until fast.next becomes null.
Now slow.next is the nth node to delete.
Skip the node: slow.next = slow.next.next.
Return dummy.next (updated head).
Java Code:
class DeleteNthNodeTwoPointer {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node deleteNth(Node head, int n) {
Node dummy = new Node(0);
dummy.next = head;
Node fast = dummy, slow = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < n && fast != null; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
if (fast == null) return head;
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next = new Node(25);
head.next.next.next = new Node(35);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteNth(head, 2);
System.out.println("After deletion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
5 15 25 35 n = 2
Output:
5 25 35
Space Complexity: O(1)
Comparison between Methods to Delete nth node in Linked List in Java
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Iterative Traversal | O(n) | O(1) |
| Two-Pointer Technique | O(n) | O(1) |
Deleting the nth node from a linked list is a fundamental operation in data structures, and mastering it helps you build a strong foundation for advanced linked list manipulation.
The operation requires careful pointer adjustments because removing a node affects the links between its neighbors.
- Both iterative traversal and two-pointer techniques achieve the same goal, but the two pointer method generalizes better for additional variations such as deleting from the end.
- Since linked lists rely on pointers instead of index based access, understanding deletion logic is essential for efficient list modification.
Overall, knowing how to Delete nth Node in Linked List in Java improves your understanding of memory management, list traversal patterns, and edge-case handling in linear data structures.
FAQ's related to Deletion of nth node in Linked List in Java
Answer:
It means removing the node present at position n and reconnecting the surrounding nodes properly.
Answer:
You traverse the list to the (n-1)th node, then skip the nth node using pointer manipulation.
Answer:
Then the head node is removed and the next node becomes the new head.
Answer:
The operation is ignored because nth node does not exist.
Answer:
It simplifies edge cases like deleting the first node.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment