Deletion from end in Singly Linked List in Java
Java Program for Deletion from end in Singly Linked List
Here, you will learn how Deletion from End in Singly Linked List in Java works through simple explanations, proper algorithms, and complete Java code examples.
This problem is frequently asked in coding interviews because it tests pointer logic and edge case handling.

Deletion from end in Singly Linked List in Java
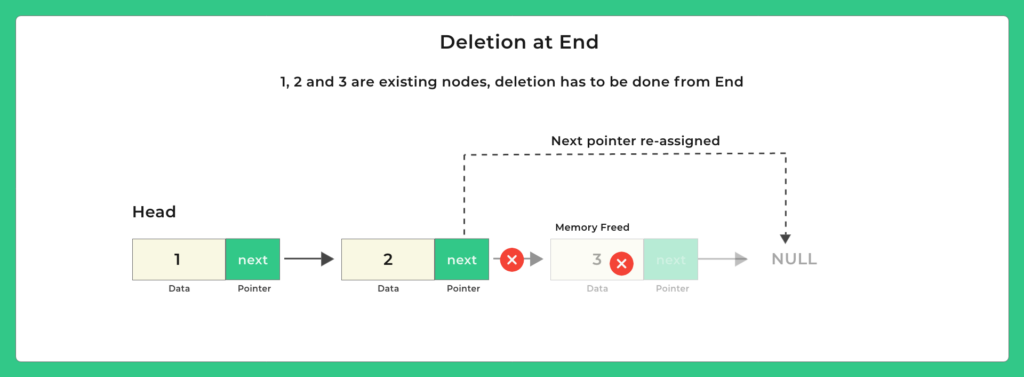
In a singly linked list, deleting from the end means removing the last node and making the second last node the new tail.
Example:
10 → 20 → 30 → 40
After deleting the last node (40):
10 → 20 → 30
Understanding Deletion from End in Singly Linked List in Java helps you learn:
- How to traverse nodes
- How to detect the last and second-last nodes
- Edge case handling like deleting from an empty list or single-node list
- Pointer manipulation
This is also a base operation for more advanced tasks like deleting nth node from end, reversing, and circular list handling.
1. Traverse the list until you reach the second last node
2. Set its next pointer to null
3. This disconnects the last node, which Java’s garbage collector will clean up
2. If list has one node → deletion makes head = null
This operation takes linear time because traversal is necessary.
Approaches to Deletion from End in Singly Linked List in Java
We will cover 2 methods:
- Method 1: Iterative Traversal to Find the Second-Last Node
- Method 2: Using Index Counter (Traverse Twice)
Each approach includes:
- Step by step algorithm
- Complete Java code
- Example input and output
- Time and space complexities
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods for Deletion from End in Singly Linked List in Java
Method 1: Iterative Traversal to Find the Second Last Node
Algorithm:
- If head is null, return null (empty list).
- If head.next is null, return null (single node list).
- Initialize temp = head.
- Traverse until temp.next.next == null (stop at second-last node).
- Set temp.next = null.
- Return updated head.
Java Code:
class DeleteEnd {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node deleteFromEnd(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next = new Node(25);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteFromEnd(head);
System.out.println("After deletion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
5 15 25
Output:
5 15
Space Complexity: O(1)
Methods for Deletion from End in Singly Linked List in Java
Method 2: Two Traversal Approach (Find Length First)
Algorithm:
- If head is null, return null.
- Traverse once to calculate list length len.
- If length is 1, return null.
- Traverse again to (len – 1)th node (second-last).
- Set its next to null.
- Return head.
Java Code:
class DeleteEndLengthMethod {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node deleteLast(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
int len = 0;
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
len++;
temp = temp.next;
}
if (len == 1) return null;
temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < len - 1; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(30);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteLast(head);
System.out.println("After deletion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30
Output:
10 20
Space Complexity: O(1)
Conclusion....
Deletion from the end of a singly linked list is a fundamental operation that demonstrates how pointer based structures work without random access because nodes must be accessed sequentially, identifying the second last node is essential before deletion.
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Iterative (Second Last Node) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Two Traversal Length Method | O(n) | O(1) |
This highlights one of the key characteristics of linked lists:
- Efficient insertions and deletions only when node references are known.
- Both methods discussed perform the same task with linear time complexity and constant space.
- The approach of deleting from the end forms the basis for more advanced operations such as deleting the nth node from the end, reversing a list, and implementing queue like structures.
Understanding how Deletion from End in Singly Linked List in Java works builds a stronger foundation for mastering linked list manipulation and algorithmic reasoning.
FAQ's related to Deletion from End in Singly Linked List in Java
Answer:
It means removing the last node and updating the second last node to become the new tail.
Answer:
You traverse the list until you reach the second last node and set its next pointer to null.
Answer:
Yes, it is linear time O(n), which is required because traversal is necessary.
Answer:
No, only pointer updates are needed, so space complexity is O(1).
Answer:
Because a singly linked list does not have backward links, so traversal is required to reach the last node.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment