C++ program to search an element in the linked list

How to search an element in Singly Linked List in C++?
Searching an element in linked list can be simplified as finding if the element is present in the linked list or not. To check if the item is present in the list or not we need to iterate through the whole list and have to check if the iterated element is equal to the item we need to search.
In this article we will learn how to write a C++ program to search an element in the linked list. This article also consists of steps and algorithm for the same.
Steps to write a program to search an element in linked list in C++
Writing a program to search an element in a linked list in C++ involves traversing the list node by node and comparing each node’s data with the target value. If a match is found, the program reports the element’s presence; otherwise, it confirms that the element doesn’t exist in the list. This helps efficiently locate data within dynamically linked structures.
These steps are followed if we want to search an element in the linked list.
- Define syntax to create linked list.
- Initialize the variables.
- Create a function named makeList() to create the linked list.
- Now create a function to display list that will be used to print the list when required.
- Now create a search function to search the element.
- If element is present in the linked list print element found
- Else print element is not present in the list.
How to define a linked list?
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
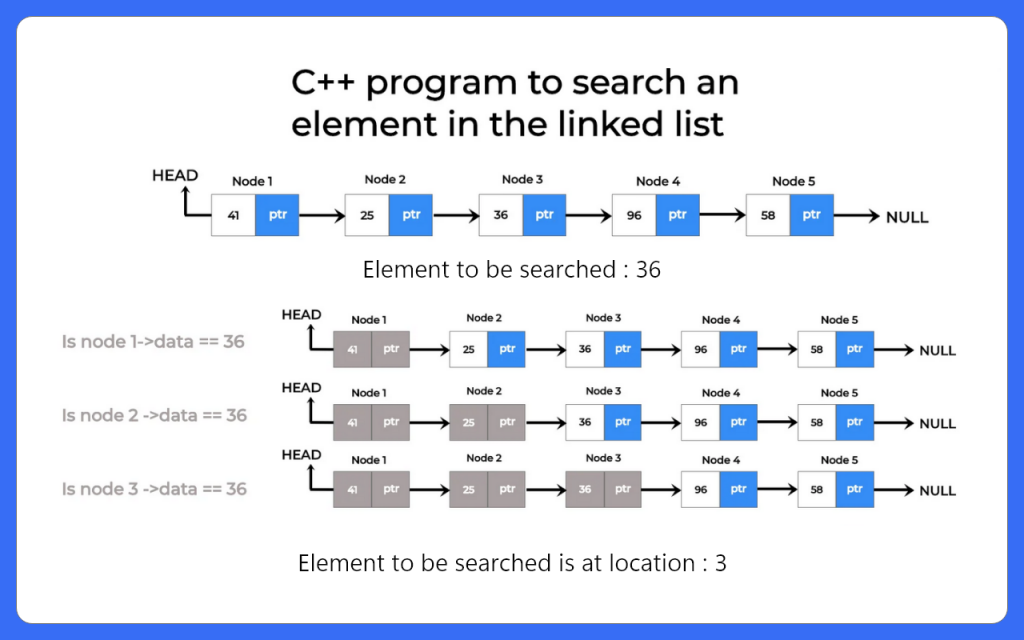
Algorithm to search an element in linked list
Following algorithm is followed for searching an element in the linked list.
- IF STNODE==NULL
- EXIT
- ElSE WHILE(TMP!=NULL)
- If TMP-> NUM== ITEM
- RETURN PRESENT
- ELSE IF FLAG==N
- RETURN NOT PRESENT
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ Program to search element in linked list
A C++ program to search an element in a linked list helps locate a specific value by traversing each node sequentially until the desired data is found or the list ends.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int num;
node* nextptr;
} *stnode; // node defined
void makeList(int n);
void display();
void searchList(int item);
int main() {
int n, item;
cout << "Enter the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
makeList(n);
cout << "\nLinked list data: \n";
display();
cout << "\nEnter element you want to search: "; cin >> item;
searchList(item);
return 0;
}
void makeList(int n) {
struct node* frntNode, *tmp;
int num, i;
stnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (stnode == NULL) {
cout << "Memory can not be allocated";
}
else {
cout << "Enter the data for node 1: "; cin >> num;
stnode->num = num;
stnode->nextptr = NULL; // Links the address field to NULL
tmp = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
frntNode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (frntNode == NULL) {
cout << "Memory can not be allocated";
break;
}
else {
cout << "Enter the data for node " << i << ": "; cin >> num;
frntNode->num = num;
frntNode->nextptr = NULL;
tmp->nextptr = frntNode;
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
// Clear the input buffer
cin.ignore(numeric_limits::max(), '\n');
}
void display() {
struct node* tmp;
if (stnode == NULL) {
cout << "No data found in the list";
}
else {
tmp = stnode;
cout << "Linked List: ";
while (tmp != NULL) {
cout << "\t" << tmp->num;
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void searchList(int item) {
struct node* tmp;
int i = 0;
tmp = stnode;
bool found = false;
if (stnode == NULL) {
cout << "Empty List\n"; } else { while (tmp != NULL) { i++; if (tmp->num == item) {
cout << "Item found at location: " << i << endl; found = true; } tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
if (!found) {
cout << "Item not found" << endl;
}
}
}
Output:
Enter the number of nodes: 5 Enter the data for node 1: 41 Enter the data for node 2: 25 Enter the data for node 3: 36 Enter the data for node 4: 96 Enter the data for node 5: 58 Linked list data: Linked List: 41 25 36 96 58 Enter element you want to search: 36 Item found at location: 3
Explanation:
- The program creates a singly linked list by allocating memory for each node and taking user input.
- Nodes are linked sequentially starting from the head pointer stnode.
- The display function traverses the list and prints all node values.
- The searchList function searches for a given element and shows its position if found.
- The program checks for successful memory allocation and handles empty list cases.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
Create Linked List (makeList()) |
O(n) | O(n) | Creates and links n nodes sequentially. |
Display Linked List (display()) |
O(n) | O(1) | Traverses all nodes once to print data. |
Search Element (searchList()) |
O(n) | O(1) | Traverses nodes to find the item; constant extra space used. |
| Overall Program | O(n) | O(n) | Linear time operations; space grows with number of nodes. |
To wrap it up:
This PrepInsta guide demonstrates how to effectively search for an element in a C++ linked list. It explains the process step by step, from creating the linked list structure to traversing nodes and comparing each value with the target element. The clear algorithm and structured approach make it easy to follow and implement.
By practicing this program, beginners can strengthen their understanding of linked list operations and traversal techniques. The included code examples and explanations provide a practical way to learn essential data structure concepts in C++.
FAQs
No, a linked list does not need to be sorted. You can search any element by traversing the list sequentially from the head to the end.
If the element is not present, the program will traverse all nodes and inform that the element was not found.
Yes, recursion can be used by checking the current node and then calling the function on the next node until the element is found or the list ends.
Not really. Searching in a linked list takes O(n) time, which is similar to an unsorted array and slower than binary search on a sorted array.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment