C++ program to check whether linked list is palindrome or not
How to check if the given singly linked list is palindrome or not in C++?
A given list is said to be palindrome if it is same as original when reversed. For example, 1331, 178871, are palindrome. Here, in this article, we will be discussing how we can write a C++ program to check whether a linked list is palindrome or not along with its steps and algorithm.
To do this we will reach the end of the linked list using recursion and check if the data in the first node is equal to data in the last node and so on.
Steps to write a C++ program to check whether a linked list is palindrome or not
Following steps are to be followed to check if the given linked list is palindrome or not.
- Initialize the variables and declare the functions.
- One to create linked list.
- Second to display linked list.
- Now make a recursive function to compare first and last node, second and second last node and so on.
- Now check() function is used to check if linked list is palindrome or not.
- Print result after comparing.
Syntax
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
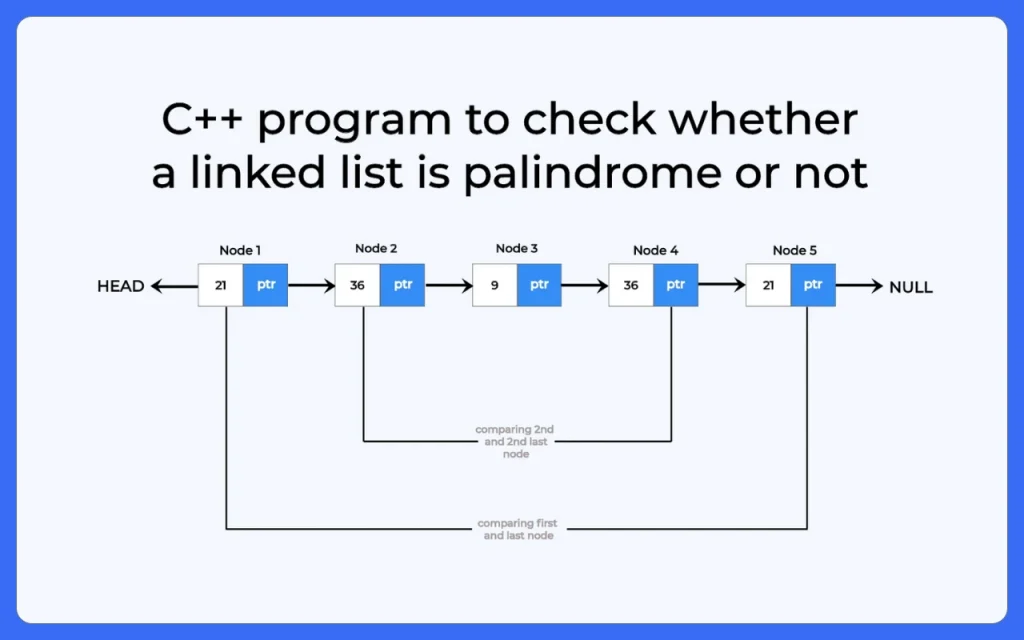
Algorithm to check if a linked list is palindrome or not
Following algorithm is used to check if the given linked list is palindrome or not
CHECKPALINDROME(STRUCT NODE **LEFT, STRUCT NODE* RIGHT)
- IF RIGHT==NULL
- RETURN 1
- RES= CHECKPALINDROME(LEFT,RIGHT->NECXTPTR)&&((*LEFT)->NUM==RIGHT->NUM)
- (*LEFT)=(*LEFT)->NEXTPTR
- RETURN RES
CHECK(STRUCT NODE* STNODE)
- RETURN CHECKPALINDROME(&STNODE,STNODE)
- EXIT
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program to check if a linked list is palindrome or not C++
A C++ program to check if a linked list is palindrome or not determines whether the sequence of elements in the list reads the same forward and backward. It efficiently uses techniques like reversing the second half or using a stack to compare node values for palindrome validation.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int num;
node *nextptr;
} *stnode; //node constructed
void make (int n);
int checkPalindrome (struct node **left, struct node *right);
int check (struct node *stnode);
void display ();
int main ()
{
int n, num;
cout << "Enter the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
make (n);
cout << "\nLinked list data: \n";
display ();
if (check (stnode))
cout << "\nLinked list is Palindrome";
else
cout << "\nLinked list is not Palindrome";
return 0;
}
void make (int n) //function to create linked list.
{
struct node *frntNode, *tmp;
int num, i;
stnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << "Memory can not be allocated";
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node 1: "; cin >> num;
stnode->num = num;
stnode->nextptr = NULL; //Links the address field to NULL
tmp = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
frntNode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (frntNode == NULL) //memory cannot be allotted if frntnode is NULL
{
cout << "Memory can not be allocated";
break;
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node " << i << ": "; // Entering data in nodes. cin >> num;
frntNode->num = num;
frntNode->nextptr = NULL;
tmp->nextptr = frntNode;
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
}
void display () //function to diplay linked list
{
struct node *tmp;
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << "List is empty";
}
else
{
tmp = stnode;
cout << "Linked List\t";
while (tmp != NULL)
{
cout << tmp->num << "\t"; tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
int checkPalindrome (struct node **left, struct node *right) // Function to check if linked list is palindrome or not
{
if (right == NULL)
return 1;
int res = checkPalindrome (left, right->nextptr)
&& ((*left)->num == right->num);
(*left) = (*left)->nextptr;
return res;
}
int check (struct node *stnode) // Function to check if linked list is palindrome or not recursively
{
return checkPalindrome (&stnode, stnode);
}
Output:
Enter the number of nodes: 5 Enter the data for node 1: 21 Enter the data for node 2: 36 Enter the data for node 3: 9 Enter the data for node 4: 36 Enter the data for node 5: 21 Linked list data: Linked List 21 36 9 36 21 Linked list is Palindrome
Explanation:
- The linked list is created in the make() function, where each node is dynamically allocated and linked using user-provided data.
- In display(), the program iterates from the head node to print all node values in sequence.
- The recursive checkPalindrome() compares nodes from both ends by moving right forward and updating left after each call.
- Each recursive return verifies matching values between symmetric nodes, confirming if the list remains identical when reversed.
- The check() function starts the palindrome validation by passing the head reference to the recursive function.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Function | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| make() | O(n) | O(1) |
| display() | O(n) | O(1) |
| checkPalindrome() | O(n) | O(n) |
| Overall | O(n) | O(n) |
To wrap it up:
This program efficiently checks whether a linked list is a palindrome by using recursion to compare elements from both ends. It eliminates the need for extra data structures while maintaining a clean and logical approach.
The method ensures accuracy by validating nodes during recursive backtracking, making it a simple yet effective solution for palindrome verification in linked lists.
FAQs
We can find the middle of the linked list, reverse the second half, and then compare both halves node by node to check if it’s a palindrome.
The overall time complexity is O(n) since each node is visited a constant number of times during traversal and reversal.
If done using pointer manipulation, the space complexity is O(1), but using a stack requires O(n) extra space.
Yes, by using a stack to store elements while traversing, you can compare values in reverse order without altering the list structure.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment