C++ program to append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list

How to append the last n nodes of a linked list to its beginning?
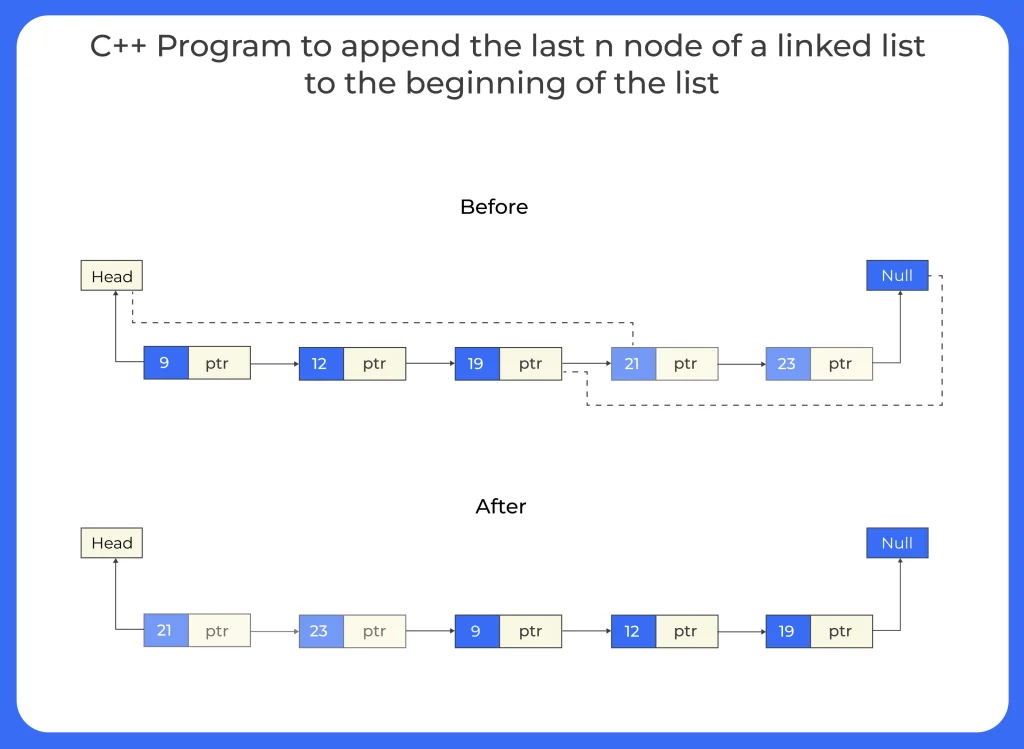
In this article, we will learn how we can extract those n nodes and write a C++ program to append the last n nodes of a lined list to the beginning of the list. Appending last n nodes of a linked list to its beginning can be understood in a very simple way, it means to dig out or extract last n nodes of the linked list and append then to the beginning of the list.
To append the last n nodes of a linked list to its beginning, first identify the split point by counting the nodes, then detach the last n nodes and link them in front of the original head. This efficiently rearranges the list without creating new nodes.
Steps to write a C++ program to append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list
To append last n nodes to the beginning of the list we need to follow the following steps
- Construct nodes and initialize the variables.
- Create methods to build list
- Now create a method to display or print the list.
- Now we will extract last n nodes from the list using append function.
- In the main function, first print last n nodes and then print remaining starting nodes.
In this way last n nodes will get append to beginning of the list.
Syntax
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
Algorithm to append last n nodes to the beginning of the list
To dig out last n nodes we need to follow following algorithm.
- WHILE (LAST!=NULL && I<N-K-1)
- LAST=LAST->NEXT
- I++
- END WHILE
- NODE *SECOND = LAST->NEXT
- LAST->NEXT=NULL
- RETURN SECOND
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program to append the last n nodes of a linked list to its beginning in C++
This C++ program moves the last n nodes of a linked list to the front, maintaining their original order. It helps efficiently rearrange the list without creating a new one.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class node
{
public:
int data;
node *next;
//Constructor
node (int d)
{
data = d;
next = NULL;
}
};
void insertAtTail (node * &head, int data) //function to insert new element at tail of the list
{
if (head == NULL)
{
head = new node (data);
return;
}
node *tail = head;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = new node (data);
}
int buildList (node * &head) //function to build the list.
{
int n;
cout << "Enter the size of list:"; cin >> n;
cout << endl;
int a = n;
cout << "Enter data of the nodes\n"; while (n--) { int data; cin >> data;
insertAtTail (head, data); //New element will be inserted at end.
}
return a;
}
void display (node * node)
{
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
node *append (node * head, int k, int n) //function to find last n nodes
{
node *last;
last = head;
int i = 0;
int ok = n - k - 1;
while (last != NULL && i < ok) { last = last->next;
i++;
}
node *second = last->next;
last->next = NULL;
return second;
}
int main () //main function
{
int k;
node *head = NULL;
int n = buildList (head);
cout << "Linked list data: ";
display (head);
cout << "\nEnter the value of 'n': "; cin >> k;
node *temp = append (head, k, n);
cout <<
"\nAfter appending the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list\n";
cout << "Linked list data: ";
display (temp); // printing last n nodes
display (head); //printing remaining nodes
}
Output:
Enter the size of list:5 Enter data of the nodes 12 25 36 47 58 Linked list data: 12 25 36 47 58 Enter the value of 'n': 3 After appending the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list Linked list data: 36 47 58 12 25
Explanation:
- The node class defines each linked list node with data and a next pointer, and the constructor initializes these values.
- insertAtTail adds a new node at the end of the list; if the list is empty, the new node becomes the head.
- buildList takes user input to create the linked list by repeatedly calling insertAtTail.
- append moves the last k nodes to the beginning by breaking the list at the correct position and returning the new head.
- display traverses and prints the list from any given node, showing the data in order.
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
Insert at Tail (insertAtTail) | O(n) – traverses to the end of the list | O(1) – only a pointer is used |
Build List (buildList) | O(n²) – n insertions, each may traverse up to n nodes | O(1) – apart from the linked list storage |
Display (display) | O(n) – traverses the entire list | O(1) |
Append Last k Nodes (append) | O(n) – traverses to the node before last k nodes | O(1) |
| Overall (main) | O(n²) – dominated by buildList function | O(n) – for storing all nodes in memory |
To wrap it up:
This C++ program efficiently appends the last ‘n’ nodes of a linked list to the beginning, providing a practical way to reorganize data within the list.
By carefully following the explained steps and implementing the provided code, developers can easily modify and optimize linked list structures to meet specific programming requirements.
FAQs
It means taking the last ‘n’ nodes from the end of a linked list and moving them to the start, changing the list’s order without creating a new list.
We first calculate the total length of the list, then traverse to the (length-n)th node to identify and detach the last ‘n’ nodes
The program runs in O(length of linked list) time since it traverses the list a few times to count nodes and adjust pointers.
Yes, the program modifies the existing linked list pointers directly, so no additional memory is required besides a few pointer variables.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment