Postorder Tree Traversal In Binary Tree In C++
Postorder Tree Traversal
Postorder tree traversal is a widely used depth-first search technique where nodes are visited in the order of left subtree → right subtree → root node. It is one of the three primary tree traversal methods, alongside Preorder and Inorder, and is especially useful in applications like deleting trees or evaluating expressions.
In this article, the postorder traversal process is clearly explained with the help of recursion, making it easier to understand how each node is processed after exploring all its children.
More About Postorder Traversal:
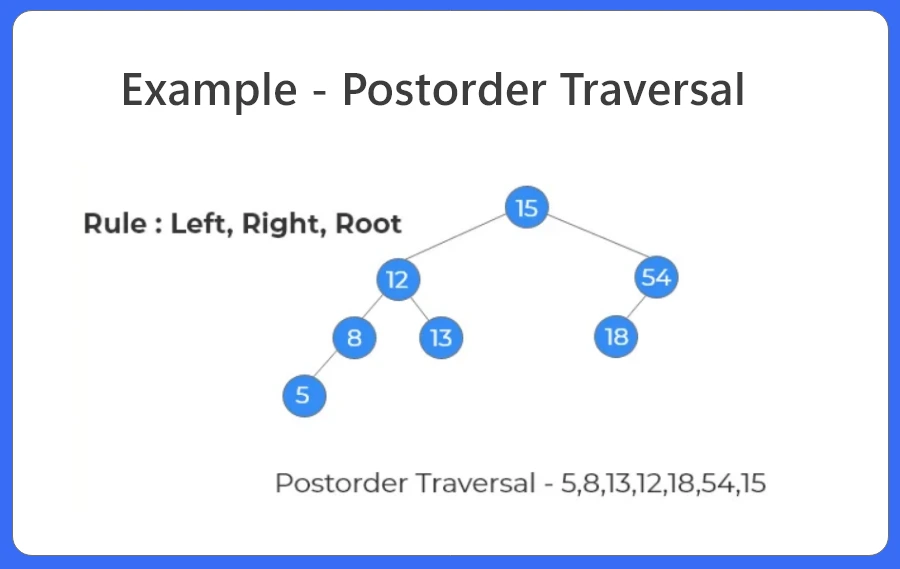
- In postorder traversal, we first move to the left subtree then to the right subtree and finally print the node.
- Used when we want to free the nodes of the tree.
- It is also used to find the postfix expression.
Steps To Find Postorder Traversal:
- Traverse the left subtree. Print the leftmost node ie 5.
- Move back, traverse the right subtree.
- Since there is no right subtree, 8 is printed.
- 13 is printed and the parent node is printed which is 12.
- Finally move, to the right subtree.
- 18 and 54 are printed.
- Print the root.
Algorithm To Find Postorder Traversal:
- If root is NULL, return.
- Visit the left subtree.
- Visit the right subtree.
- Print the node.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code Implementation for Preorder Tree traversal
The Preorder Tree Traversal algorithm visits nodes in the sequence: root, left subtree, and then right subtree, making it ideal for creating prefix expressions or copying trees. Implementing preorder traversal in code helps developers efficiently explore tree structures and understand hierarchical relationships. This approach is widely used in applications like expression evaluation and structured data processing.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
int data;
Tree *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
// Constructor initialised
Tree (int x)
{
data = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void postorder_traversal (Tree * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Visit Left subtree
postorder_traversal (root->left);
// Visit right subtree
postorder_traversal (root->right);
// Print the data
cout << root->data << " "; } int main () { Tree *root = new Tree (15); root->left = new Tree (12);
root->right = new Tree (54);
root->left->left = new Tree (8);
root->left->right = new Tree (13);
root->left->left->left = new Tree (5);
root->right->left = new Tree (18);
postorder_traversal (root);
return 0;
}
Output:
5 8 13 12 18 54 15
Explanation:
- The code defines a Tree class containing an integer data value along with left and right child pointers, and the constructor initializes each node with the given value.
- The postorder_traversal() function performs a Left → Right → Root traversal by recursively visiting the left subtree, then the right subtree, and finally printing the current node’s data.
- In the main() function, a binary tree is manually constructed by creating nodes and linking them to form the required hierarchical structure.
- The traversal function is called with the root node, and recursion ensures that each subtree is fully processed before printing the parent node.
- The final output represents the correct postorder sequence of the tree, printed as: 5 8 13 12 18 54 15.
Time & Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Postorder Traversal | O(n) | O(h) |
| Tree Node Creation | O(1) per node | O(1) |
| Total Program Execution | O(n) | O(h) |
To Wrap It Up:
Postorder tree traversal is an essential technique in binary trees, allowing you to visit and process nodes only after exploring their left and right subtrees. This method ensures that child nodes are handled before the parent, making it ideal for operations that depend on complete subtree processing.
Overall, mastering postorder traversal strengthens your understanding of depth-first search and helps you implement tasks like tree deletion, expression evaluation, and memory cleanup efficiently. Its recursive nature makes it simple to understand while offering powerful real-world applications.
FAQs
In postorder traversal, the algorithm visits the left subtree first, then the right subtree, and finally processes the root node. This ensures children are handled before their parent.
It is helpful in scenarios where nodes must be processed after their subtrees, such as deleting a tree or generating postfix expressions.
The time complexity is O(n) since every node in the tree is visited exactly once. It remains efficient regardless of the tree’s structure.
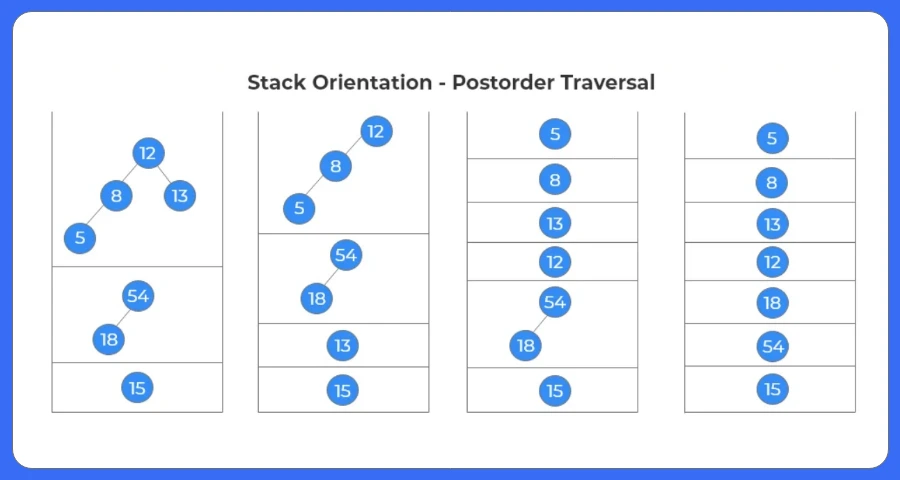
Yes, it can be performed using a stack based iterative method. This approach mimics recursive behavior and is useful when recursion depth may cause stack overflow.
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment