0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Representation of a Stack as a Linked List in Java .
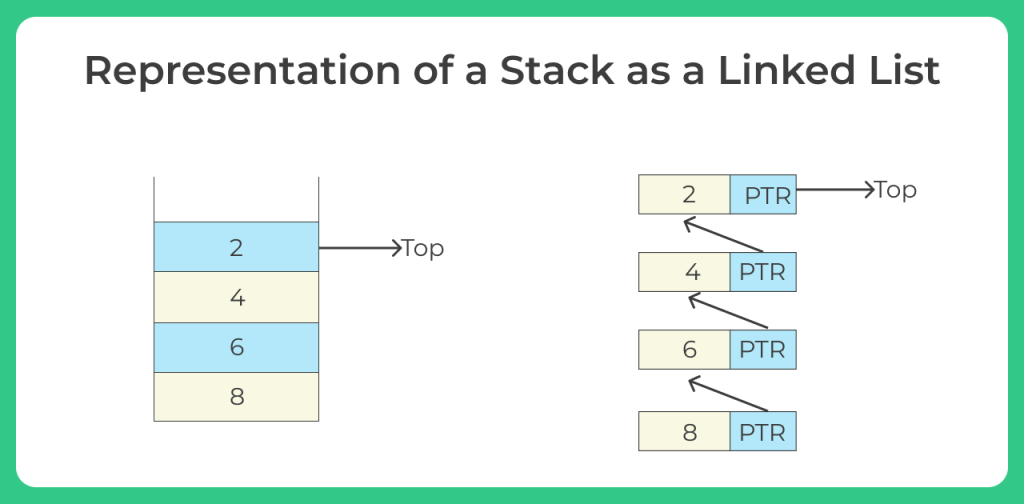
Representation of a Stack as a Linked List.
A Stack is a linear data structure that follows the principle of (Last-In-First-Out) LIFO . In Stack there is one end through which insertion and deletion takes place. Whenever an element is added in the stack, it is added on the top of the stack, and the element can be deleted only from the stack. In other words, a stack can be defined as a container in which insertion and deletion can be done from the one end known as the top of the stack.
On this page we will discuss about representation of a stack as a linked list in Java.
Representation of a Stack as a Linked List.
Stack can also be represented by using a linked list. We know that in the case of arrays we face a limitation , i.e , array is a data structure of limited size. Hence before using an array to represent a stack we will have to consider an enough amount of space to hold the memory required by the stack.
Operation in stack:
Following are common operations implemented on the stack:
- push():When we insert an element in a stack then the operation is known as a push. If the stack is full then the condition is called overflow condition.
- pop(): When we want to delete an element from the stack, the operation is known as a pop. If the stack is empty means there is no element in the stack, this condition is known as an underflow state.
- isEmpty():When we want to determines whether the stack is empty or not.
- isFull(): when we want to determines whether the stack is full or not.’
- peek(): It returns the element at the given position.
Implementation of a Stack using a Linked List:
A push operation is implemented by inserting an element at the beginning of the list.
A pop operation is implemented by deleting the node from the beginning (the header/top node).
Java code for representation of a stack as a Linked List:
import java.lang.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Obj = new Main();
Obj.insert(10);
Obj.insert(20);
Obj.insert(30);
Obj.insert(40);
Obj.insert(50);
Obj.insert(60);
System.out.println("Original List");
Obj.print();
}
class Node{
int element;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int element) {
this.element = element;
}
}
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
int size=0;
public void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev = null;
if (head != null)
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
public void print() {
Node node = head;
Node end = null;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.element + " ");
end = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Original List 60 50 40 30 20 10
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java

 0
0



Login/Signup to comment