Linked List Insertion and Deletion Program in C
Singly linked list Insertion and Deletion in C
We will look at all possible ways of insertion and deleting a node in a Single Linked List.

Things Discussed in the Post
We will be discussing the following in this post –
- Insertion in a Linked List
- At Start
- At end
- After a given position
- Deletion in a Linked List
- At start
- At end
- After a given position

First Lets understand what a Linked List is?
A linked List as the name suggests is a chain of linked data connected to one another in a sequential format just like a chain. A linked list has the following components in general –
- Data – This contains the data value held in any individual node of the linked list
- Next Pointer – This contains the address to the next node in a Linked List
Following are also some commonly used terminologies with a Linked List –
- Node – Individual component with its data and next pointer value together is called a node
- Head – The first node in the Linked List is called the head node.
- Tail – The last node in the Linked list is called as a tail node. Which points towards a NULL value.
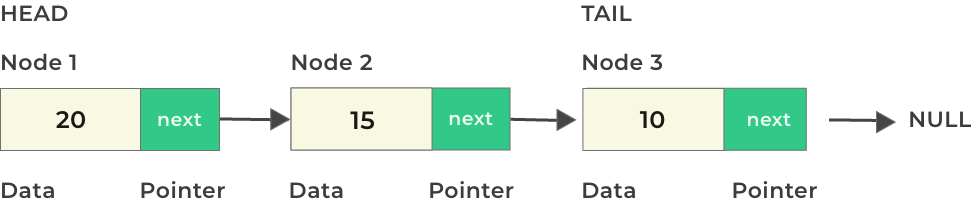
Structure of Linked List
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
Let us first Look at Insertion
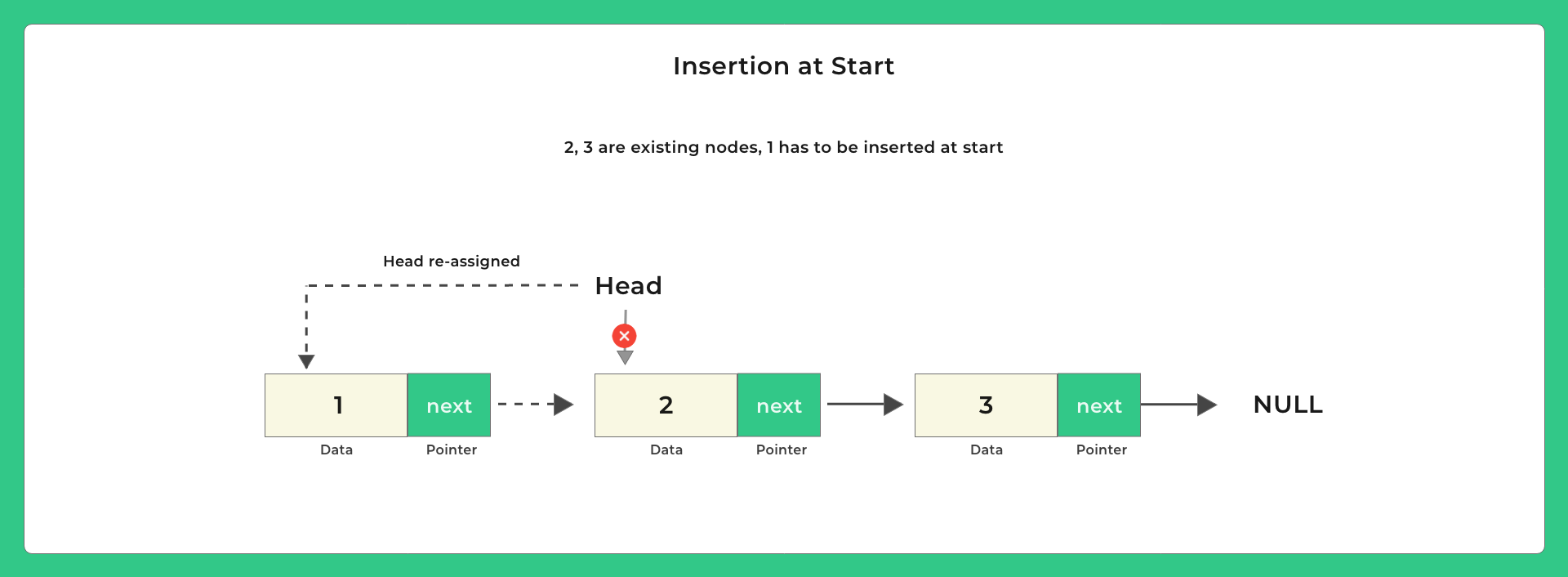
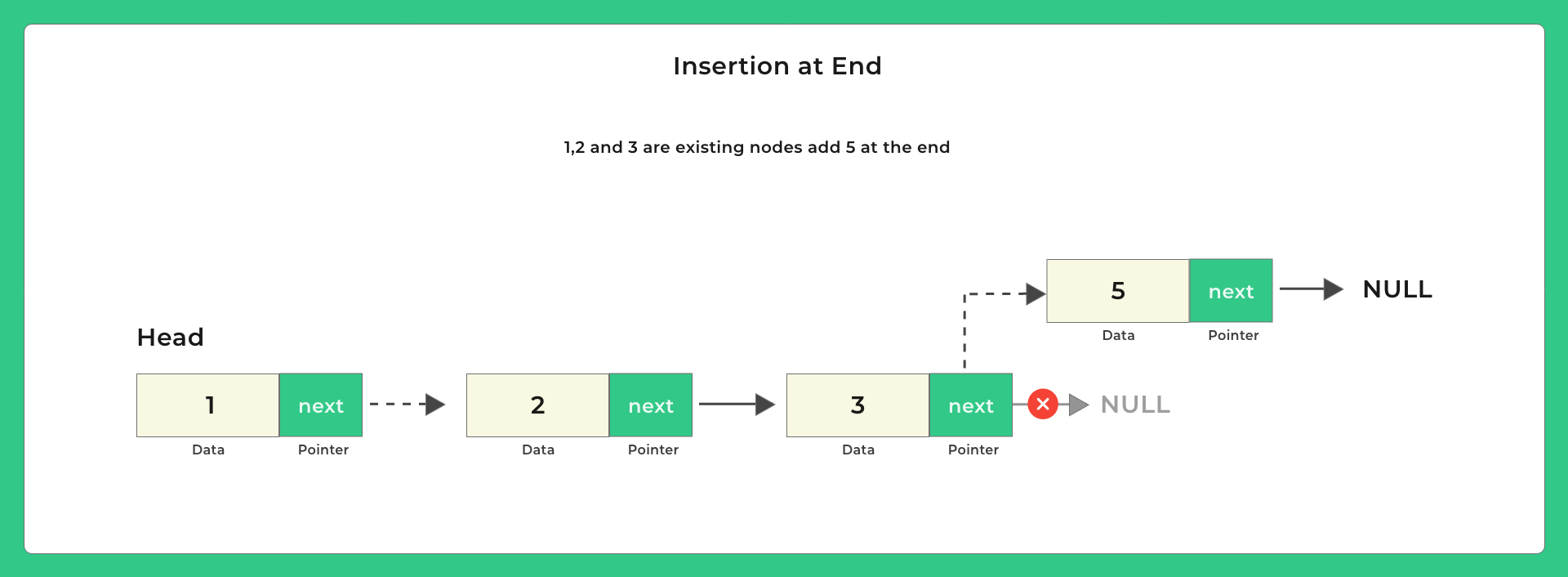
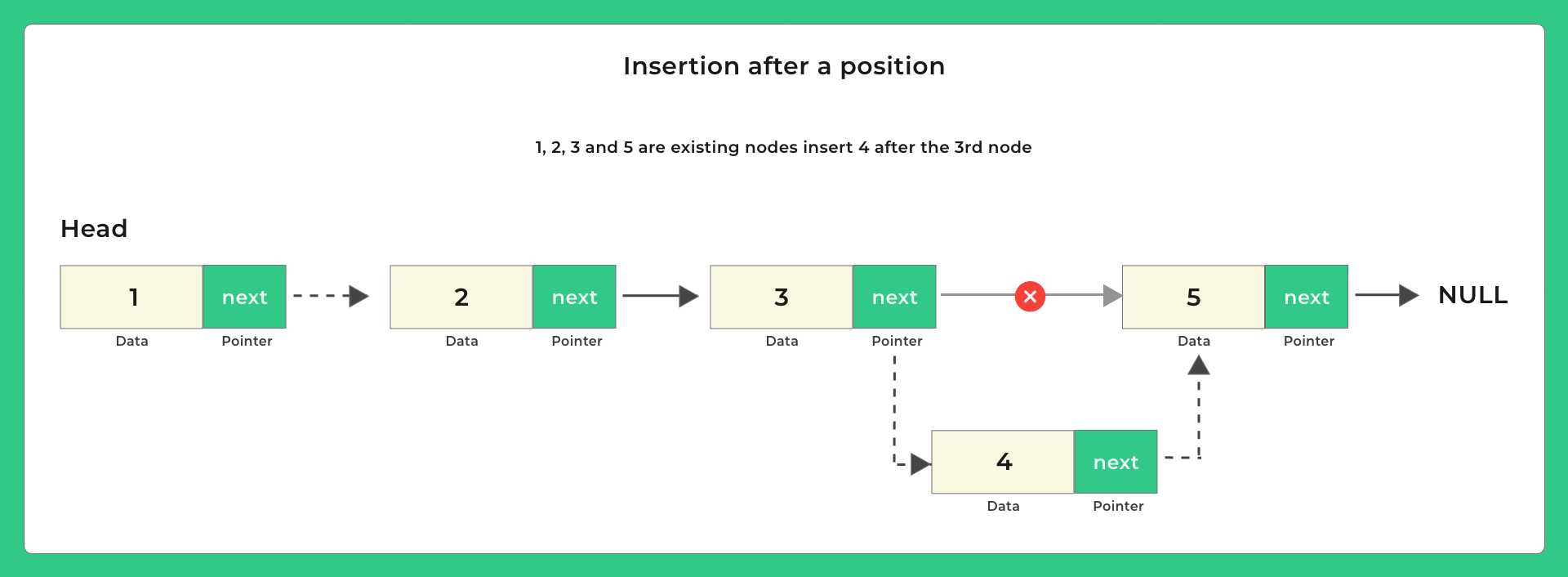
Possible positions to insert –
Lets look at some pictures on how to insert and then we will look at the code –
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void insertEnd (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
// since this will be the last node so it will point to NULL
newNode->next = NULL;
// if the Linked List is empty this is the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
return;
}
// create another variable to traverse the LL
// *head should not be used as we do not want to change head
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse to the last node of Linked List
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// assign last node's next to this newNode
temp->next = newNode;
}
// required for insertAfter
int getCurrSize (struct Node *node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertPosition (int pos, int data, struct Node **head)
{
int size = getCurrSize (*head);
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if (pos < 1 || pos > size)
printf ("Invalid position to insert");
else
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
// temp used to traverse the Linked List
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse till the nth node
while (--pos)
temp = temp->next;
// assign newNode's next to nth node's next
newNode->next = temp->next;
// assign nth node's next to this new node
temp->next = newNode;
// newNode inserted b/w 3rd and 4th node
}
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 1);
// no need for '&' as head need not be changed
// only doing traversal
display (head);
insertEnd (&head, 5);
insertEnd (&head, 6);
insertEnd (&head, 7);
display (head);
//Inserts data: 4 after 3rd position
insertPosition (3, 4, &head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
1 2 3 1 2 3 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Let us Look at Deletion
Possible positions to delete –
Lets look at some pictures on how to delete and then we will look at the code –
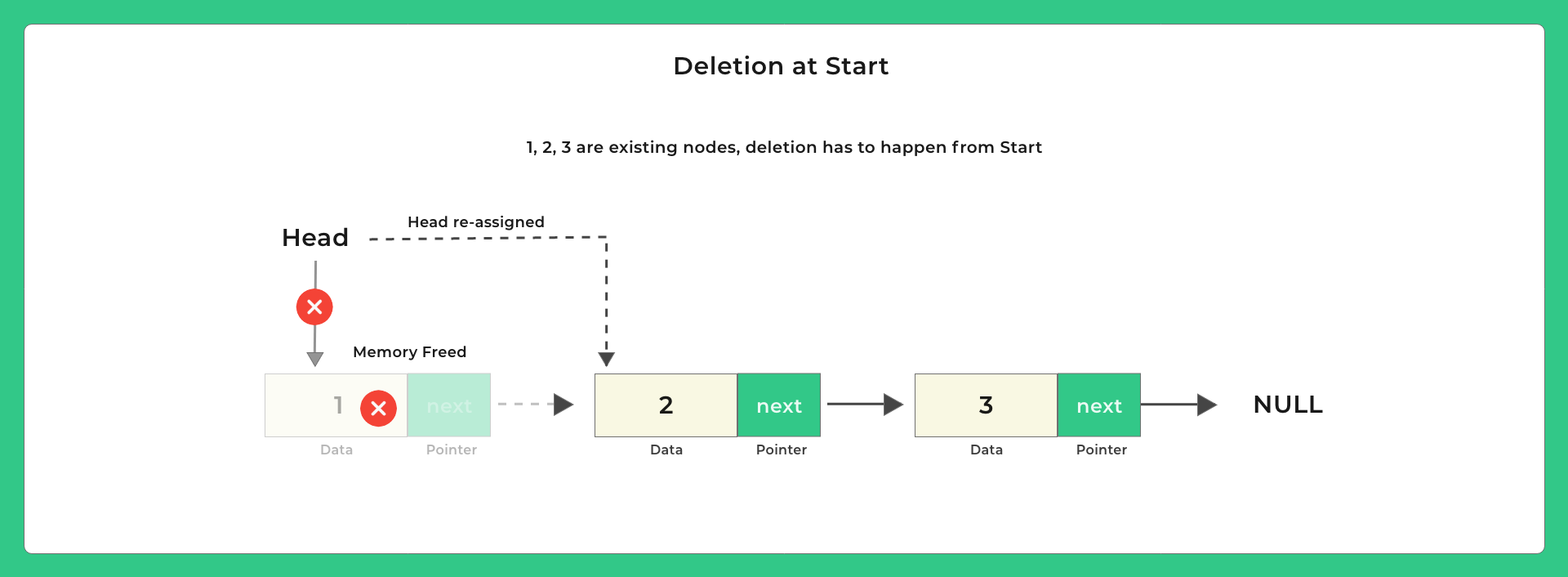
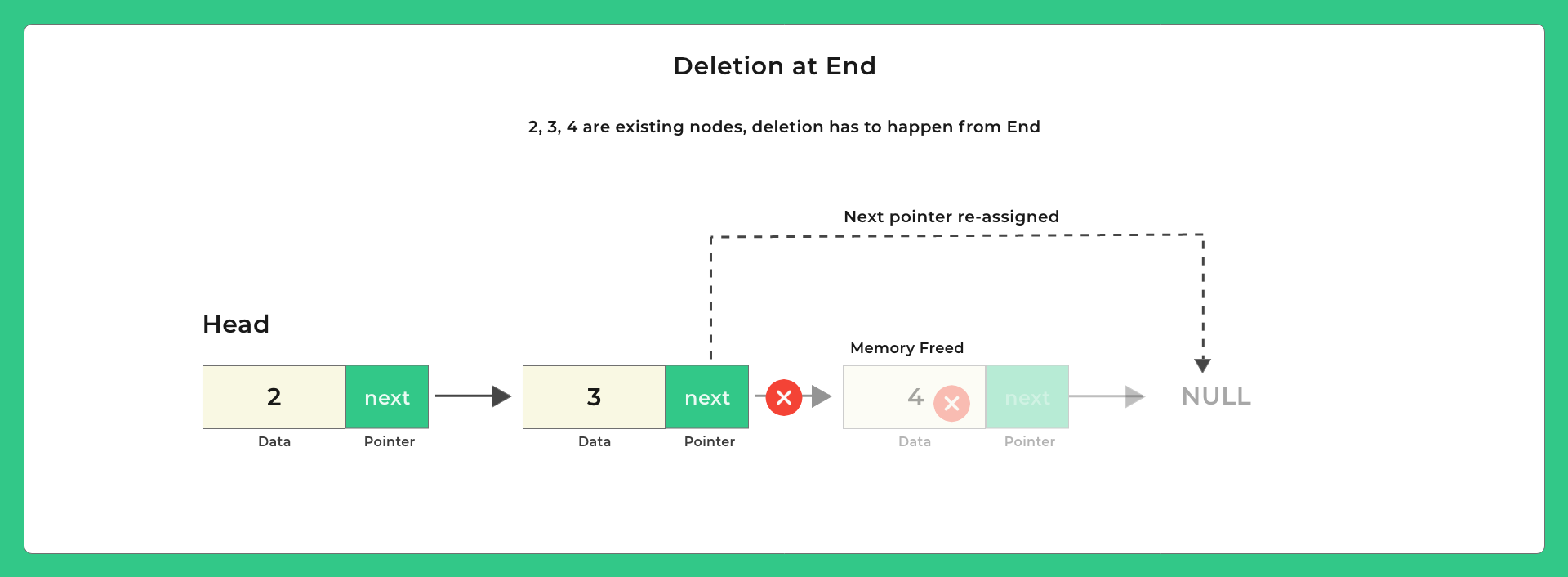
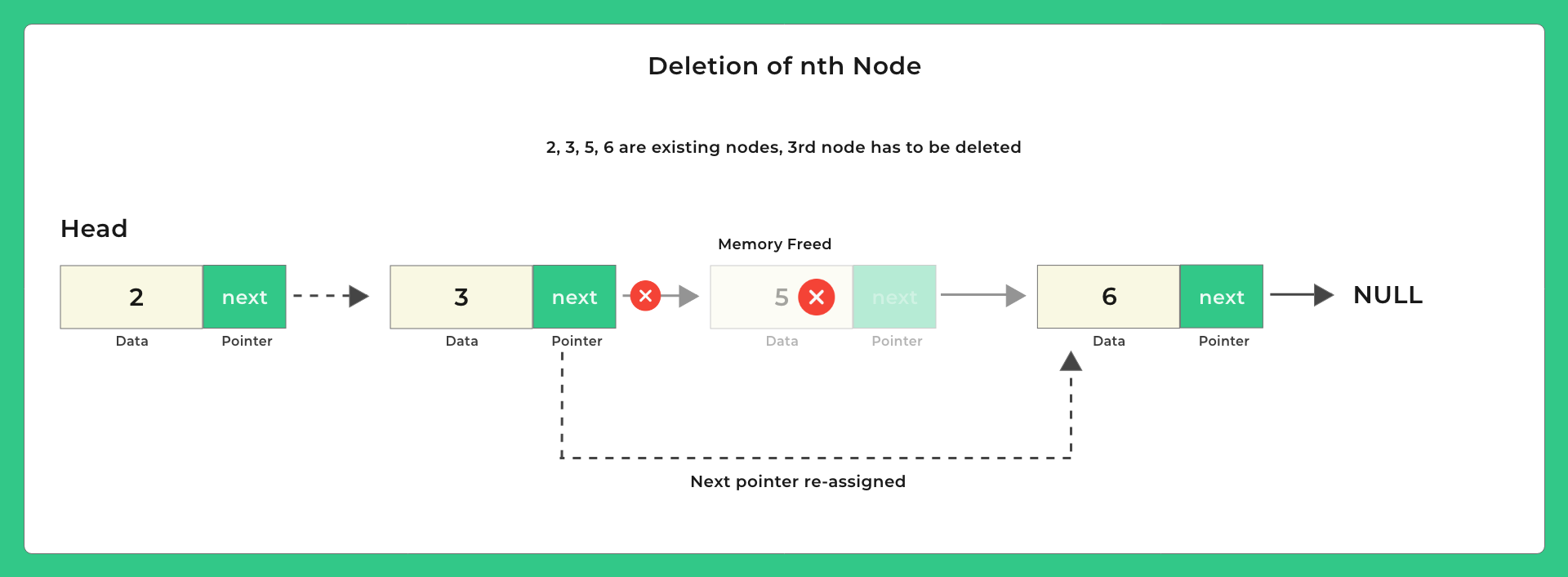
Code for Delete from Start and Delete From End
Run
#include<stdio.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void deleteStart (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
free (temp);
}
void deleteEnd (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *previous;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
previous->next = NULL;
// delete the last node
free (temp);
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
}
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertStart (&head, 6);
insertStart (&head, 5);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 1);
display (head);
deleteStart (&head);
display (head);
deleteEnd (&head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5
Deletion nth Node (A position)
Let us look at the code for deletion of a node at a position that is deletion nth node.
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void deleteStart(struct Node** head);
int getCurrSize(struct Node* node);
// to delete nth node
void deletePosition (struct Node **head, int pos)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *previous;
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
int size = getCurrSize (*head);
// not valid
if (pos < 1 || pos > size)
{
printf ("Enter valid position\n");
return;
}
// delete the first node
if (pos == 1)
{
deleteStart (head);
return;
}
// traverse to the nth node
while (--pos)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// change previous node's next node to nth node's next node
previous->next = temp->next;
// delete this nth node
free (temp);
}
void deleteStart (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
free (temp);
}
// required for deletePosition
int getCurrSize (struct Node *node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertStart (&head, 5);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 1);
display (head);
// delete 3rd node
deletePosition (&head, 3);
display (head);
// delete 1st node
deletePosition (&head, 1);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 4 5 2 4 5



Login/Signup to comment