C++ program to find middle of the linked list
Finding the middle element of a Singly Linked List in C++?
Finding middle of anything means to find the center position it. In this article, we will be learning how to code a C++ program to find middle of the linked list. We will take two pointers for the process one pointer will be moving with twice the speed of second pointer.
So when the first pointer will reach the end of the liked list, the second pointer will be at middle of it as it is moving with half the speed of first pointer. In this way center node of the linked list is fetched.
How to define a linked list?
A linked list is a fundamental data structure in C++ and other programming languages, used to store a collection of elements called nodes. Unlike arrays, linked lists do not require contiguous memory, allowing efficient insertion and deletion of elements at any position. Each node in a linked list contains data and a pointer to the next node, forming a chain-like structure.
- A linked list is a dynamic data structure.
- Each node has two parts: data and a pointer to the next node.
- The first node is called the head, and the last node points to NULL.
- Types of linked lists include singly, doubly, and circular linked lists.
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
Steps to write a C++ program for finding middle of a linked list
These steps are used to find middle the linked list in CPP programming
- Start the program and initialize the variables.
- Create a function to create and display list.
- Now create a function to find middle of the list.
- In this function initialize two pointers.
- Traverse one pointer with normal speed.
- Traverse other pointer with double speed.
- When the pointer moving with double speed reaches end of the list other pointer will be at middle.
- Print data at the address of this pointer.
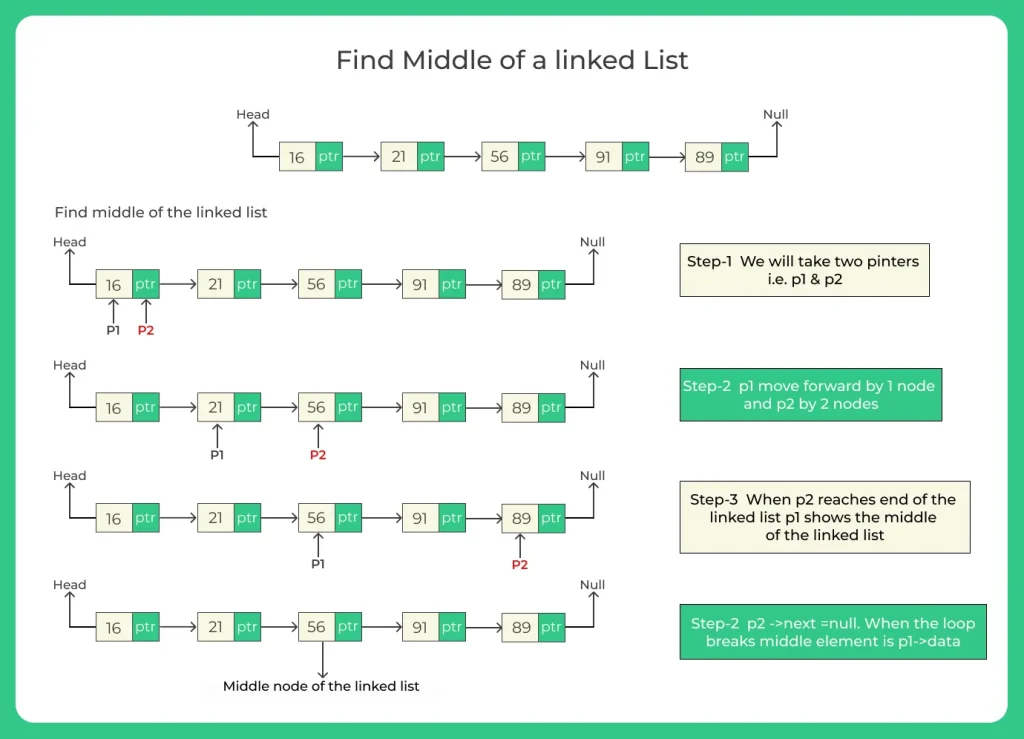
Algorithm for finding the middle of a linked list
Algorithm to find middle of the linked list in CPP programming is given below
- SINGLE_PTR=STNODE
- TWICE_PTR=STNODE
- IF(STNODE!=NULL)
- WHILE(TWICE_PTR!=NULL&&TWICE_PTR->NEXTPTR!=NULL
- TWICE_PTR=TWICE_PTR->NEXTPTR->NEXTPTR
- SINGLE_PTR=SINGLE_PTR->NEXTPTR
- PRINT SINGLE_PTR->NUM
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ Program to find middle of linked list
A C++ program to find the middle of a linked list identifies the central node efficiently using techniques like the slow and fast pointer method, without altering the list.
#include < iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int num;
node* nextptr;
} *stnode; // node constructed
void make(int n);
void printMiddle(struct node* stnode);
void display();
int main() // Main method
{
int n;
cout << "Enter the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
make(n);
cout << "\nLinked list data: \n";
display();
printMiddle(stnode);
return 0;
}
void make(int n) // Function to create a linked list
{
struct node* frntNode, *tmp;
int num, i;
stnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << "Memory cannot be allocated";
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node 1: "; cin >> num;
stnode->num = num;
stnode->nextptr = NULL; // Links the address field to NULL
tmp = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
frntNode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (frntNode == NULL)
{
cout << "Memory cannot be allocated";
break;
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node " << i << ": "; cin >> num;
frntNode->num = num;
frntNode->nextptr = NULL;
tmp->nextptr = frntNode;
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
}
void display() // Function to display the linked list
{
struct node* tmp;
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << "List is empty";
}
else
{
tmp = stnode;
cout << "Linked List: ";
while (tmp != NULL)
{
cout << tmp->num << " \t "; tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
void printMiddle(struct node* stnode) // Function to print the middle node of the list
{
struct node* single_ptr = stnode;
struct node* twice_ptr = stnode;
if (stnode != NULL)
{
while (twice_ptr != NULL && twice_ptr->nextptr != NULL)
{
twice_ptr = twice_ptr->nextptr->nextptr; // Moving with twice speed.
single_ptr = single_ptr->nextptr;
}
cout << "The middle element is " << single_ptr->num << endl;
}
}
Output:
Enter the number of nodes: 5 Enter the data for node 1: 5 Enter the data for node 2: 9 Enter the data for node 3: 8 Enter the data for node 4: 4 Enter the data for node 5: 6 Linked list data: Linked List 5 9 8 4 6 The middle element is 8
Explanation:
- The program creates a singly linked list where each node stores a number and a pointer to the next node.
- The make() function dynamically allocates memory for each node and links them together sequentially.
- The display() function traverses the linked list and prints all elements in order.
- The printMiddle() function uses two pointers — one moves one step (single_ptr), and the other moves two steps (twice_ptr) — to efficiently find the middle node in a single traversal.
- When the faster pointer reaches the end, the slower pointer points to the middle element, which is then displayed as output.
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time | Space | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
make() | O(n) | O(n) | Creates and links all nodes. |
display() | O(n) | O(1) | Traverses list to print elements. |
printMiddle() | O(n) | O(1) | Finds middle using two pointers. |
| Overall | O(n) | O(n) | Linear time and space usage. |
To wrap it up:
Finding the middle of a linked list in C++ becomes simple and efficient when you apply the two-pointer approach explained above. This method not only saves time but also enhances your understanding of pointer manipulation in data structures.
By mastering this logic, you’ll strengthen your grasp of linked lists and be better prepared for coding interviews and competitive programming challenges.
FAQs
You can find the middle by using two pointers: a slow pointer that moves one node at a time and a fast pointer that moves two nodes at a time. When the fast pointer reaches the end, the slow pointer will be at the middle node. This approach works in a single traversal.
The time complexity is O(n) because the list is traversed only once, where n is the number of nodes. The space complexity is O(1) since no extra data structures are used.
Yes, for an even-length list, you can choose either the first or the second of the two middle nodes. The standard slow-fast pointer method usually returns the second middle node.
Yes, the slow and fast pointer technique does not require knowing the size of the list beforehand. The pointers automatically ensure that the slow pointer points to the middle when the fast pointer reaches the end.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment