Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list in Java
Java Program to Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List
to the Beginning of the List
In this article, you will learn how to Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List to the Beginning of the List in Java with clear explanations, step by step algorithms, and complete Java code examples.
Appending the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning is a very common interview problem. This problem helps you understand list traversal, pointer movements, and list restructuring.
Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List to the
Beginning of the List in Java
Problem Statement:
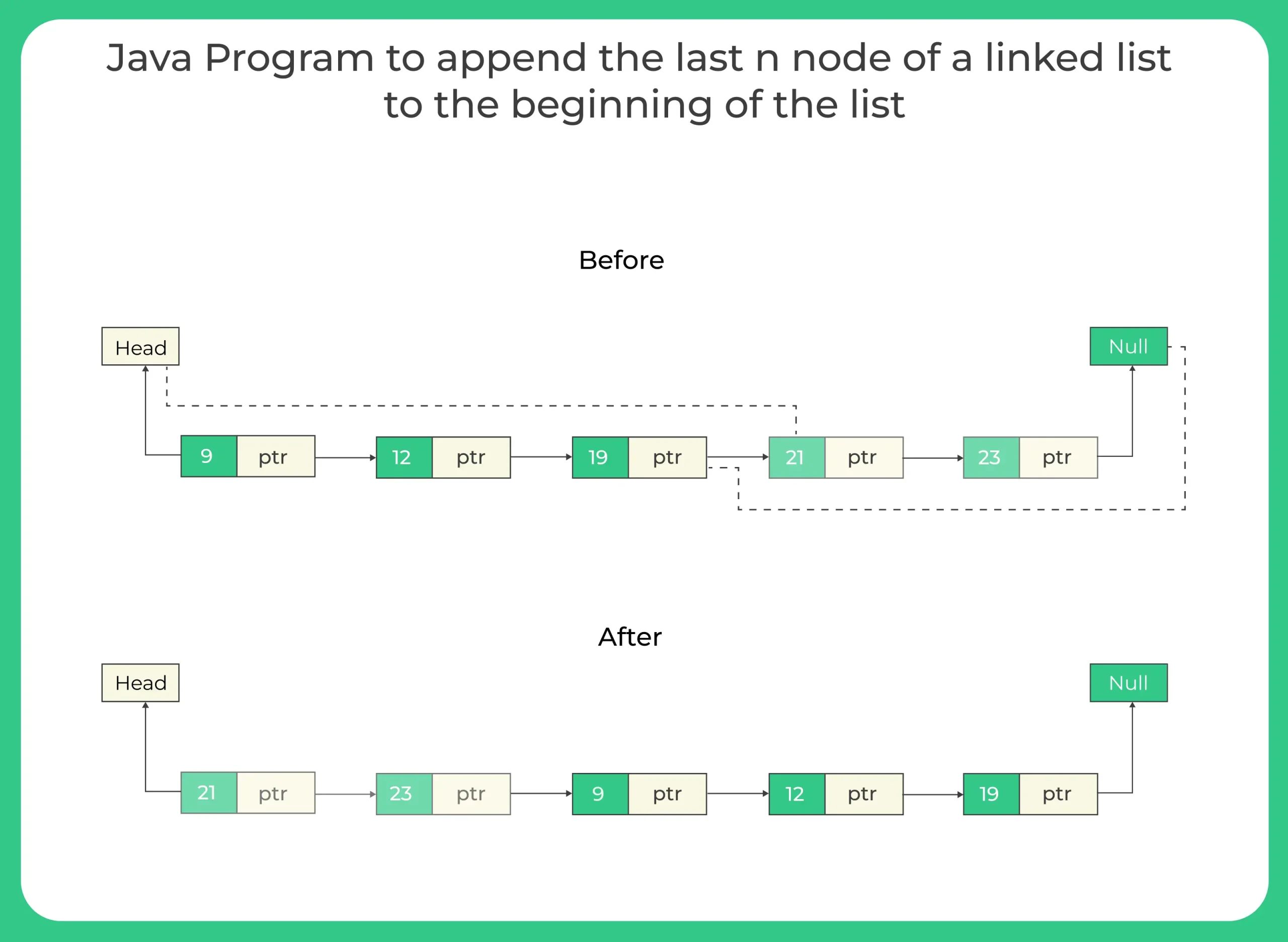
Given a singly linked list and a number n, your task is to cut the last n nodes from the end and attach them to the beginning of the list.
Input List:
1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5 → 6
If n = 2, then we take the last two nodes:
5 → 6
Final List becomes:
5 → 6 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
Explanation:
To solve Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List to the Beginning of the List in Java, you mainly need:
1. Length Calculation:
Find the total number of nodes so you know where to split the list.
2. Identifying the Breaking Point:
If list has size L, then the breaking point is at the node number (L – n).
The last n nodes start from that point.
3. Reconnecting Nodes:
- Detach the last n nodes
- Attach them to the head of the list
- Set the old tail’s next pointer to null
Methods to Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List
to the Beginning of the List in Java
Here, we have mentioned 2 methods to Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list using Java:
Each includes algorithms, full Java code, examples, and complexities.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods to Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List
Method 1: Length + Pointer Movement (Iterative)
Algorithm:
- Let head be the starting node.
- If n == 0, return the original list.
- Traverse the list to calculate total length len.
- Set n = n % len (to handle n > len).
- If n == 0, return original list.
- Find the node just before the breaking position: index (len – n – 1).
- Let newHead be (len – n)th node.
- Traverse to the last node (tail).
- Connect tail.next to original head.
- Set the breaking node’s next to null.
- Return newHead.
Java Code:
class AppendLastNNodes {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node appendLastN(Node head, int n) {
if (head == null || n == 0) return head;
// Find length
int len = 0;
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
temp = temp.next;
len++;
}
n = n % len;
if (n == 0) return head;
int breakPoint = len - n;
Node curr = head;
// Move to (breakPoint - 1)th node
for (int i = 1; i < breakPoint; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
Node newHead = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
Node tail = newHead;
while (tail.next != null) {
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = head;
return newHead;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
System.out.println("Original List:");
printList(head);
head = appendLastN(head, 2);
System.out.println("Modified List:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
1 2 3 4 5 6 n = 2
Output:
5 6 1 2 3 4
Space Complexity: O(1)
Methods to Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List
Method 2: Two Pointer Fast and Slow Method
Algorithm:
Let head be the start of the list.
Use pointer fast and move it forward by n nodes.
Use pointer slow starting at head.
Move both fast and slow until fast reaches the last node.
slow now points to the node before the last n nodes.
Let newHead = slow.next.
Set slow.next = null to break the list.
Move fast to end (if not already there).
Connect fast.next = head.
Return newHead.
Java Code:
class AppendLastNFastSlow {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node appendLastN(Node head, int n) {
if (head == null || n == 0) return head;
Node fast = head;
int count = 0;
while (count < n && fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
count++;
}
if (fast == null) return head;
Node slow = head;
while (fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
Node newHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
fast.next = head;
return newHead;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
System.out.println("Original List:");
printList(head);
head = appendLastN(head, 3);
System.out.println("Modified List:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
1 2 3 4 5 6 n = 3
Output:
4 5 6 1 2 3
Space Complexity: O(1)
What do we got is….
You learned how to Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List to the Beginning of the List in Java using two efficient methods.
- Both techniques run in linear time and constant space.
- Understanding this improves your linked list manipulation skills and prepares you for interview level problems.
FAQ's related to Append the Last n Nodes of a Linked List in Java
Answer:
It means taking the last n nodes of a linked list and moving them to the front while keeping the order of the remaining nodes unchanged.
Answer:
We do this to practice pointer manipulation, linked list traversal, and to solve a common interview question based on list restructuring.
Answer:
Yes, the operation can be done in O(n) time and O(1) space using pointer-based approaches.
Answer:
Recursion is not commonly used for this problem because iterative pointer techniques are simpler and more efficient.
Answer:
We use n % length to handle such cases, ensuring the result remains correct.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java





