Singly Linked List Deletion in Java
Deletion in Singly linked List in Java
In this article, we will learn how to perform deletion in singly linked list in Java, covering different scenarios with clear explanations, algorithms, and full Java code examples.
Linked List is one of the most fundamental data structures in programming especially in Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA). Unlike arrays, linked lists store elements in nodes, where each node contains data and a reference (link) to the next node in the sequence.

What Is Deletion in Singly Linked List in Java?
Deletion means removing an existing node from the linked list.
Depending on the position of the node, there are 3 main cases:
Each case has slightly different logic and time complexity.
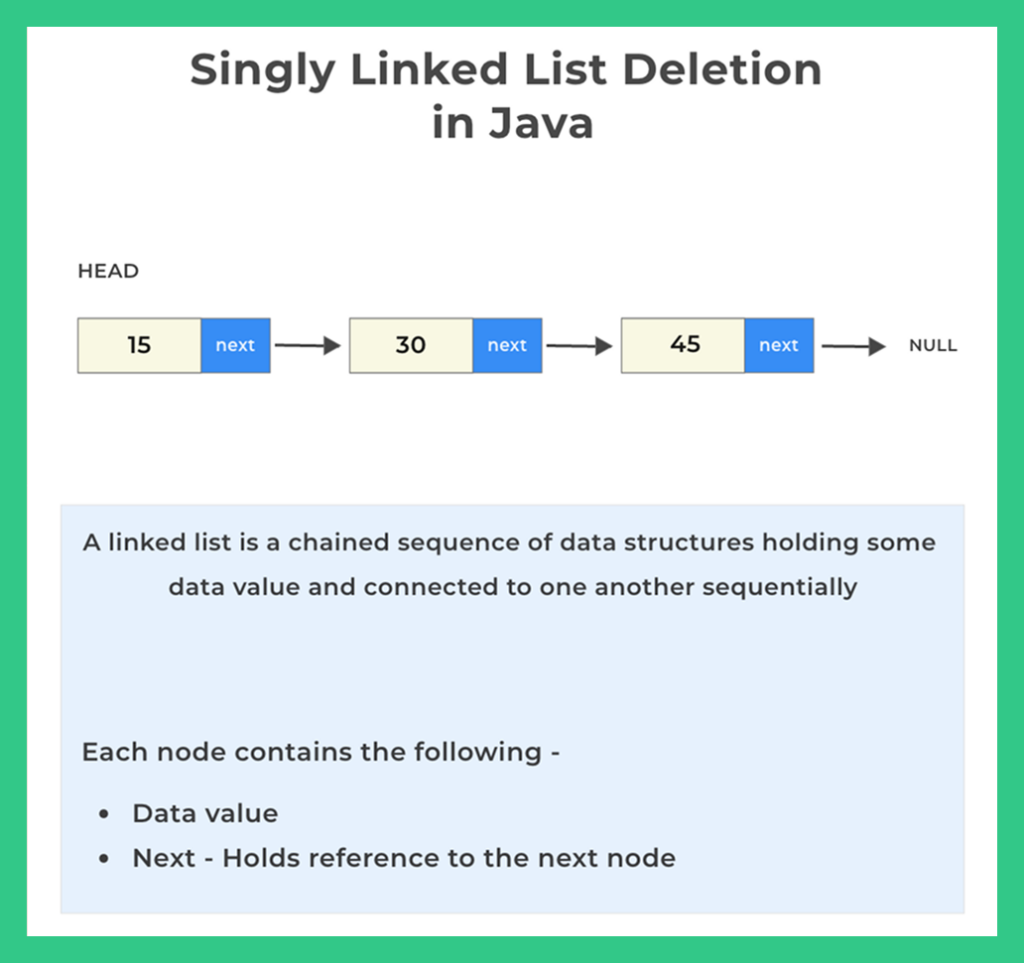
Structure of a Singly Linked List Node:
Before we start, let’s define the Node and LinkedList classes.
Java Code – Node Structure:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
Learn DSA in Java
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
1. Deletion at the Beginning
Algorithm for Deletion in Singly Linked List at the Beginning
- Check if the list is empty (head == null).
- If yes, print “List is empty” and return.
- Move the head pointer to the next node: head = head.next.
- Previous head node will be automatically deleted by Java’s garbage collector.
Code:
class LinkedList {
Node head;
// Insert elements at end (for testing)
void insertEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
// Delete first node
void deleteAtBeginning() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty. Nothing to delete.");
return;
}
head = head.next;
}
// Display list
void display() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.insertEnd(10);
list.insertEnd(20);
list.insertEnd(30);
System.out.println("Before Deletion:");
list.display();
list.deleteAtBeginning();
System.out.println("After Deleting First Node:");
list.display();
}
}
Example Output:
Before Deletion:
10 20 30
After Deleting First Node:
20 30
Space Complexity: O(1): no extra space used.
2. Deletion at the End
Algorithm for Deletion in Singly Linked List at the End
If the list is empty (head == null), print a message and return.
If there is only one node, make head = null.
Otherwise, traverse the list to find the second last node (node before the last).
Set secondLast.next = null.
Code:
class LinkedList {
Node head;
void insertEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
void deleteAtEnd() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty. Nothing to delete.");
return;
}
if (head.next == null) {
head = null;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = null;
}
void display() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.insertEnd(10);
list.insertEnd(20);
list.insertEnd(30);
System.out.println("Before Deletion:");
list.display();
list.deleteAtEnd();
System.out.println("After Deleting Last Node:");
list.display();
}
}
Example Output:
Before Deletion: 10 20 30 After Deleting Last Node: 10 20
Space Complexity: O(1): no extra space used.
3. Deletion at a Given Position
Algorithm for Deletion in Singly Linked List at nth position
If the list is empty, print a message and return.
If the position is 1, delete the first node (same as delete at beginning).
Otherwise, traverse the list to find the node just before the position to be deleted.
- Change the link of the previous node:
- prev.next = prev.next.next
- Handle invalid positions (greater than the length of the list).
Code:
class LinkedList {
Node head;
void insertEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
void deleteAtPosition(int position) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty.");
return;
}
if (position == 1) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < position - 1 && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp == null || temp.next == null) {
System.out.println("Position out of range.");
return;
}
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
void display() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.insertEnd(10);
list.insertEnd(20);
list.insertEnd(30);
list.insertEnd(40);
System.out.println("Before Deletion:");
list.display();
list.deleteAtPosition(3);
System.out.println("After Deleting Node at Position 3:");
list.display();
}
}
Example Output:
Before Deletion: 10 20 30 40 After Deleting Node at Position 3: 10 20 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Comparison of methods for Deletion in Singly Linked list
Here, is the comparison of methods used for Deletion in Singly Linked List in Java:
| Deletion Type | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Delete at Beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Delete at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete at Position | O(n) | O(1) |
Conclusion:
Deletion is one of the key operations in a Singly Linked List, and understanding its logic helps you strengthen your DSA fundamentals.
In Java, linked lists are implemented using objects and references, and the key idea is always to update the links properly without breaking the chain of nodes.
FAQ's related to Deletion in Singly Linked List in Java
Answer:
Deletion in a singly linked list means removing an existing node based on its position or value. It involves adjusting the links (pointers) between nodes to maintain list structure.
Answer:
You simply make head = head.next. This removes the first node and updates the head to point to the next node.
Answer:
- At beginning: O(1)
- At end or by key/position: O(n), since traversal is required.
Answer:
Only if you have access to the node itself (not the head). You can copy the data from the next node and delete the next node, but this trick doesn’t work for the last node.
Answer:
In arrays, elements must be shifted after deletion, taking O(n) time. In linked lists, only pointer adjustments are made, which can take O(1) time (if position is known).
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment