Java program to find middle of a linked list
How to Find the Middle of a Linked List?
In this article, we’ll explore a Java program to find the middle of a linked list using an efficient and easy to understand approach. Before diving into the code, it’s important to understand how the position of the middle node is determined based on whether the total number of nodes in the linked list is even or odd.
Common and effective method to solve this problem involves using two pointers, often referred to as slow and fast. Slow pointer moves one node at a time, while the fast pointer moves two nodes at a time. By the time the fast pointer reaches the end of the list, the slow pointer will be pointing exactly to the middle node. This technique helps us find the middle element without needing to count the total number of nodes beforehand.

Each node consists of two parts:
1. Data: stores the actual value.
2. Next: a pointer/reference to the next node.
Linked lists are dynamic in nature and ideal for scenarios where frequent insertions/deletions are required.
Problem Statement To Find Middle of a Linked List
Given: Singly linked list
- Task: Find the middle node of the list.
- Output: Return the data (or reference) of the middle node.
If the number of nodes is even, you can return the second middle node (common approach).
Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Output: 3
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Example 2:
Input: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 -> 50 -> 60
Output: 40
Approaches to Solve the Problem:
There are primarily two efficient methods to find the middle of a linked list:
- Count Nodes (Two pass approach)
- Tortoise and Hare Algorithm (One pass approach)
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Java Program To Find Middle Of A Linked List
Method 1: Two Pass Algorithm (Length Count Method)
Idea:
- Traverse the list to count the number of nodes.
- Traverse again to reach the middle.
Algorithm:
- Initialize a count to 0.
- Traverse the list once to get the total number of nodes.
- Calculate mid = count / 2.
- Traverse again to the mid-th node.
- Return the node’s value.
Space Complexity: O(1)
Code:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedListMiddle {
Node head;
void append(int data) {
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(data);
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(data);
}
void findMiddle() {
int count = 0;
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
int mid = count / 2;
temp = head;
for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++)
temp = temp.next;
System.out.println("Middle element is: " + temp.data);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListMiddle list = new LinkedListMiddle();
list.append(10);
list.append(20);
list.append(30);
list.append(40);
list.append(50);
list.findMiddle();
// Output: 30
}
}
Java Program To Find Middle Of A Linked List
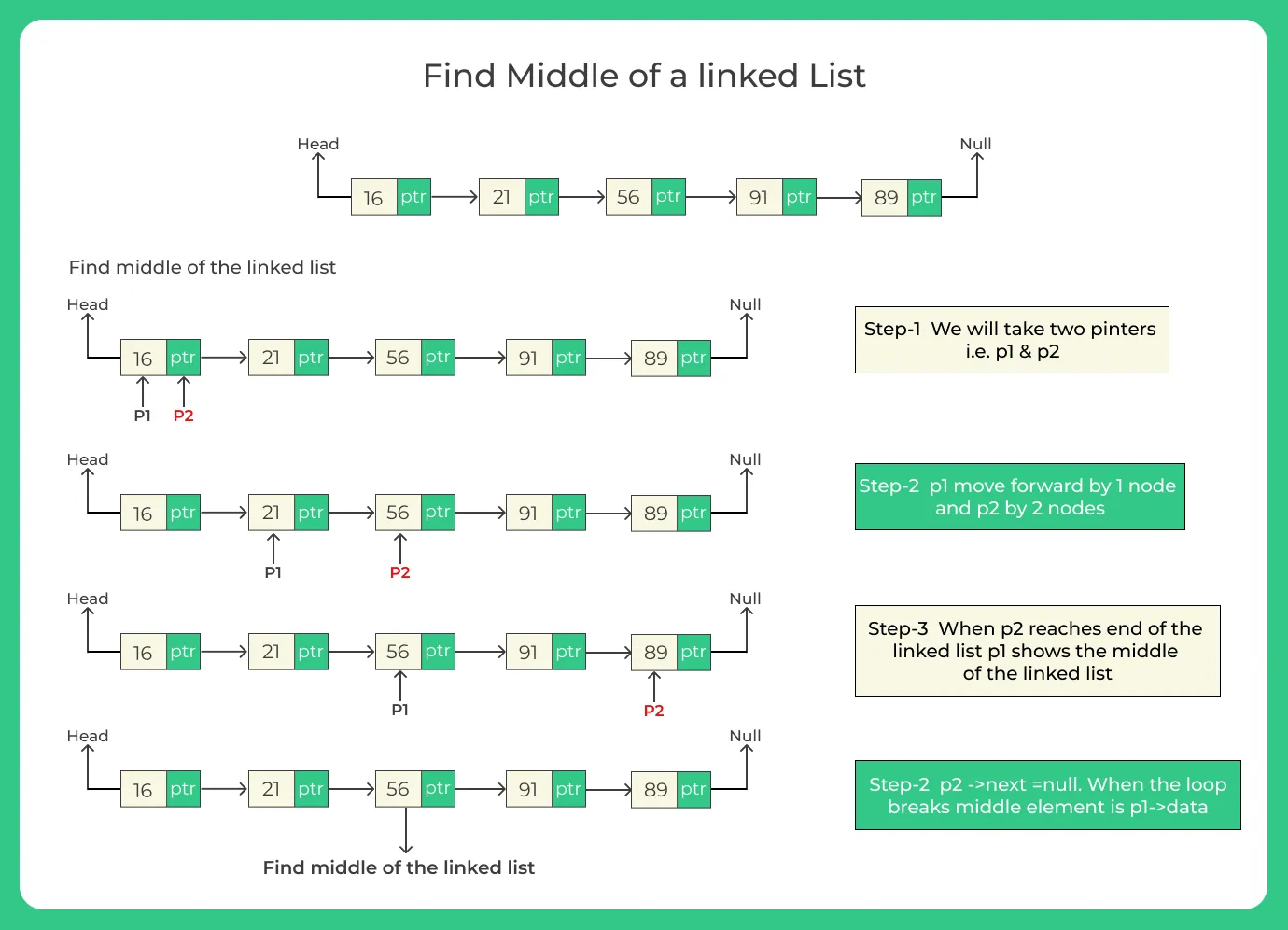
Method 2: Tortoise and Hare Algorithm (Fast and Slow Pointer)
Idea:
Use two pointers:
- Slow pointer: moves one node at a time.
- Fast pointer: moves two nodes at a time.
When the fast pointer reaches the end, the slow pointer will be at the middle.
Algorithm:
Initialize two pointers slow and fast at the head.
Move fast by 2 nodes and slow by 1 node.
When fast is null or fast.next is null, return slow.
Space Complexity: O(1)
Code:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class MiddleOfList {
Node head;
void append(int data) {
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(data);
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null)
current = current.next;
current.next = new Node(data);
}
void findMiddle() {
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
System.out.println("Middle element is: " + slow.data);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MiddleOfList list = new MiddleOfList();
list.append(5);
list.append(15);
list.append(25);
list.append(35);
list.append(45);
list.findMiddle(); // Output: 25
}
}
Comparison of both method to find middle of a linked list
| Feature | Two-Pass (Length Count) | Tortoise and Hare |
|---|---|---|
| Passes through list | 2 | 1 |
| Time Complexity | O(n) | O(n) |
| Space Complexity | O(1) | O(1) |
| Simplicity | Easy to implement | More optimal |
| Performance | Slightly slower | Faster in practice |
Handling Edge Cases
- Empty List: Return a message like “List is empty”.
- Single Node List: Return the data of that single node.
- Even Number of Nodes:
- Standard approach is to return the second middle (as shown above).
- Optional: Modify code to return both if required.
Real World Applications
- Data stream processing (e.g., find the median on the fly)
- Splitting linked lists (e.g., Merge Sort)
- Memory efficient navigation in large datasets
- Cycle detection algorithms (modification of fast/slow pointer)
Tips and Best Practices
- Always check for null pointers to avoid NullPointerException.
- For singly linked lists, avoid using array or index-based logic.
- Use the Tortoise and Hare method for efficiency.
- Consider using generics if you want the linked list to store multiple data types.
Final Thoughts on Finding Middle of a linked list
Finding the middle of a linked list is a fundamental problem in computer science that tests your grasp of pointer manipulation, algorithm design, and optimization.
- Mastering both the count based and pointer based techniques equips you to handle similar problems like cycle detection, palindrome checks, and splitting lists for merge sort.
- Whether you’re preparing for interviews or enhancing your algorithm toolkit, this problem is a must-know, and now you have all the tools to solve it efficiently in Java.
FAQ's related to Find Middle in a linked list
Answer:
Most efficient method is using the Tortoise and Hare algorithm (also known as the slow and fast pointer approach). It traverses the list only once and requires constant space, making it optimal in terms of both time and memory usage.
Answer:
Yes, but it’s not recommended for large lists. A recursive solution may lead to a StackOverflowError due to deep recursive calls. Iterative approaches like the fast and slow pointer method are more efficient and safer.
Answer:
In the two pass method, you first count the total number of nodes, then traverse again up to the count/2 position to find the middle. It’s simple to implement but requires traversing the list twice.
Answer:
In Java, for even length linked lists, the standard approach is to return the second middle node. However, you can modify the logic to return both middle nodes if required, depending on your use case.
Answer:
This operation is frequently used in advanced algorithms like Merge Sort on Linked Lists, palindrome checks, and cycle detection algorithms.
Knowing how to efficiently find the middle improves your problem solving and interview performance.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







public node findmid(){
int mid=(size()%2)+(size()/2);
node temp=head;
while(mid–>1){
temp=temp.next;
d=temp.data;
}
return temp;
}