Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List in Java
Java Program to Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List
Learning how to Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List in Java is an important step toward mastering linked list manipulation. This operation removes every second node from the list and helps beginners understand pointer adjustments, traversal patterns, and deletion logic in linked lists.
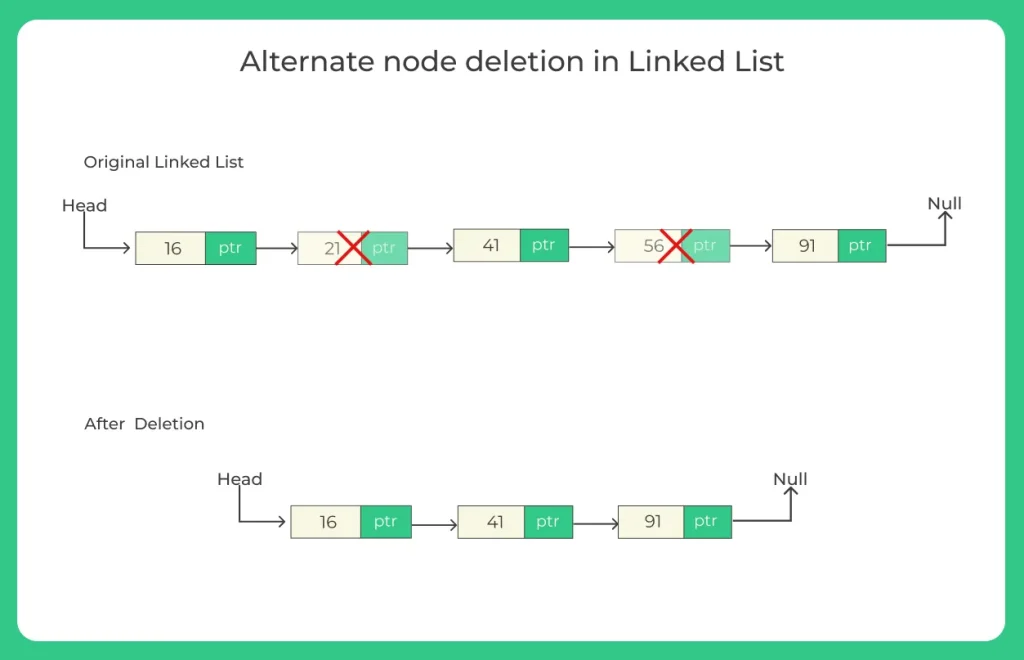
Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List in Java
What Does Deleting Alternate Nodes Mean?
Deleting alternate nodes means removing every second node from the linked list.
This means:
- Keep the 1st node
- Delete the 2nd
- Keep the 3rd
- Delete the 4th
- And so on…
Example:
Input list:
10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 50
After deleting alternate nodes:
10 → 30 → 50
Only the links are changed that is no data shifting is needed. Understanding Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List helps students learn:
- Pointer movement
- How to skip nodes
- How to safely delete nodes
- Edge case handling
This problem is frequently asked in technical interviews to test basic linked list knowledge.
1. Start from the head
2. Use a pointer current initialized at the head
3. Delete current.next
4. Move current to the next remaining node (current = current.next)
Repeat until the end of the list
Methods to Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List in Java
We will use 2 different methods to Delete alternate nodes of a linked list using java:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods to Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List using Java
Method 1: Iterative Pointer Skip Method
Algorithm:
If head is null, return null.
Set current = head.
While current != null and current.next != null:
Let temp = current.next
Set current.next = temp.next
Disconnect temp.next = null
Move current = current.next
- Return head.
Java Code:
class DeleteAlternateNodes {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node deleteAlternate(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node current = head;
while (current != null && current.next != null) {
Node temp = current.next;
current.next = temp.next;
temp.next = null;
current = current.next;
}
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(30);
head.next.next.next = new Node(40);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(50);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteAlternate(head);
System.out.println("After deletion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30 40 50
Output:
10 30 50
Space Complexity: O(1)
Methods to Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List
Method 2: Recursive Deletion Method
Algorithm:
- If list is empty or has one node, return head.
- Remove the second node:
- head.next = head.next.next
- Recursively call for the next remaining node:
- delete(head.next)
- Return head.
Java Code:
class DeleteAlternateNodesRec {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node deleteAlternate(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
head.next = head.next.next;
deleteAlternate(head.next);
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next = new Node(25);
head.next.next.next = new Node(35);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteAlternate(head);
System.out.println("After deletion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
5 15 25 35
Output:
5 25
Space Complexity: O(n)
Conclusion....
Deleting alternate nodes in a singly linked list demonstrates how simple pointer adjustments can modify a list structure efficiently.
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Iterative Pointer Skip | O(n) | O(1) |
| Recursive Method | O(n) | O(n) |
Since linked lists rely on sequential access, removing every second node requires traversing the list while updating next pointers correctly.
The iterative method is the most efficient because it uses constant memory, while recursion provides cleaner logic at the cost of additional stack space.
Mastering how to Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List in Java strengthens your understanding of linked list traversal, memory handling, and structural transformations, which are essential for solving more complex linked list problems.
FAQ's related to Delete Alternate Nodes of a Linked List
Answer:
It means removing every second node from the list starting with deleting the second node.
Answer:
By skipping the next pointer of each node and connecting it to the next-next node.
Answer:
Yes, it works in O(n) time and constant space using the iterative method.
Answer:
When you prefer clean code, but it uses extra space.
Answer:
Yes, node connections change permanently.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







public void deletealternate(){
node pre=head;
int size=size();
if(size==0){
System.out.println(“invalid deletion”);
}
if(size%2!=0){
while(pre.next!=null){
pre.next=pre.next.next;
pre=pre.next;
}
}
else{
while(pre!=null){
pre.next=pre.next.next;
pre=pre.next;
}
}
}