Java Program to reverse a linked list in groups of given size
Reverse a linked list in groups of given size using Java
In this article, you will learn Java Program to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size. We will explore both recursive and iterative approaches, break down the logic, and provide a full working example.
But what if we’re asked to reverse the linked list in groups of a given size? This problem is not only common in interviews but also an important step toward mastering advanced linked list manipulaton.

What is the Problem?
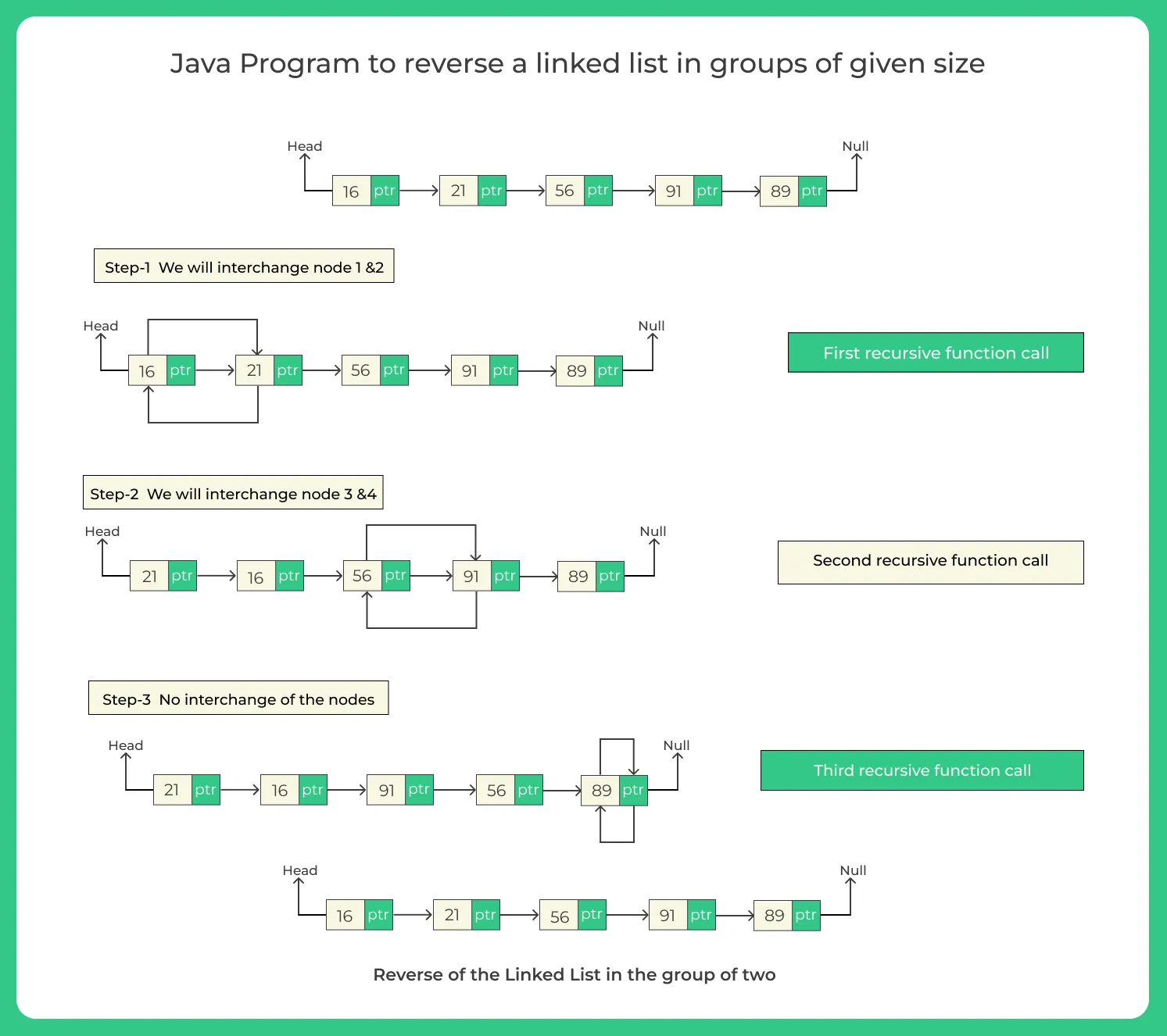
Given a singly linked list, your task is to reverse it in groups of size k. That means for every k nodes in the list, reverse their order.
If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k, the remaining nodes at the end should remain as is (or also reversed, depending on the requirement, we will cover both variations).
Example:
Suppose we have the following linked list:
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8
And k = 3, then the reversed list in groups of 3 will be:
3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 6 -> 5 -> 4 -> 7 -> 8
Methods to reverse a linked list in groups of given size
We can practice 2 approaches to solve the problem to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size:
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Java Program to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size
Method 1: Recursive Approach to Reverse a linked list
Algorithm:
- Initialize three pointers: current, prev, next.
- Reverse the first k nodes using a loop.
- Recursively call for the rest of the list starting from the k+1-th node.
- Connect the k-th node to the result of recursion.
- Return the new head of this segment.
- Time Complexity: O(n) each node is visited once.
- Space Complexity: O(n/k) due to recursive stack space.
Java Code:
public class ReverseKGroupRecursive {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
// Function to reverse in groups of k
public static Node reverseInGroups(Node head, int k) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node current = head;
Node prev = null;
Node next = null;
int count = 0;
// Reverse first k nodes
while (current != null && count < k) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
// Recursively reverse remaining list
if (next != null) {
head.next = reverseInGroups(next, k);
}
return prev; // new head
}
// Print list
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " -> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// Insert node at end
public static Node insert(Node head, int data) {
if (head == null) return new Node(data);
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) current = current.next;
current.next = new Node(data);
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) head = insert(head, i);
System.out.println("Original List:");
printList(head);
int k = 3;
head = reverseInGroups(head, k);
System.out.println("\nReversed in groups of " + k + ":");
printList(head);
}
}
Output:
Original List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> null Reversed in groups of 3: 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 6 -> 5 -> 4 -> 7 -> 8 -> null
Method 2: Iterative Approach to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size
Algorithm:
- Create a dummy node and point it to head.
- Use pointers prevGroupEnd, start, and end to track groups.
- For each group of size k:
Reverse the group.
Connect the reversed group back to the previous part.
- Stop if fewer than k nodes remain.
- Time Complexity: O(n), every node is visited once.
- Space Complexity: O(1), uses constant space.
Java Code:
public class ReverseKGroupIterative {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
// Function to reverse in groups iteratively
public static Node reverseInGroups(Node head, int k) {
if (head == null || k == 1) return head;
Node dummy = new Node(0);
dummy.next = head;
Node prevGroupEnd = dummy;
while (true) {
Node start = prevGroupEnd.next;
Node end = prevGroupEnd;
for (int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i++) end = end.next;
if (end == null) break;
Node nextGroupStart = end.next;
end.next = null;
// Reverse current group
prevGroupEnd.next = reverse(start);
start.next = nextGroupStart;
prevGroupEnd = start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
// Helper to reverse a list
private static Node reverse(Node head) {
Node prev = null;
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
Node next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
// Print list
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " -> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// Insert node
public static Node insert(Node head, int data) {
if (head == null) return new Node(data);
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) current = current.next;
current.next = new Node(data);
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) head = insert(head, i);
System.out.println("Original List:");
printList(head);
int k = 3;
head = reverseInGroups(head, k);
System.out.println("\nReversed in groups of " + k + ":");
printList(head);
}
}
Output:
Original List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> null Reversed in groups of 3: 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 6 -> 5 -> 4 -> 7 -> 8 -> null
Comparison between Space and Time Complexity
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recursive Approach | O(n) | O(n/k) | Due to recursive call stack for each group |
| Iterative Approach | O(n) | O(1) | Preferred for large lists due to constant space usage |
Conclusion….
Reversing a linked list in groups of a given size is a powerful technique that builds your problem solving and pointer manipulation skills.
You now understand both recursive and iterative approaches to solve this problem using Java. Keep practicing similar problems to master linked list operations and enhance your algorithmic thinking.
FAQ's Related to Java Program to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size
Answer:
Time complexity is O(n) for both recursive and iterative approaches.
Answer:
- Recursive: O(n/k) due to call stack
- Iterative: O(1) constant space
Answer:
Yes, it depends on the problem requirements. The above solutions do not reverse the last group if its size is less than k. You can modify the logic to handle that.
Answer:
Iterative approach is preferred in real world applications to avoid stack overflow in large lists.
Answer:
The list remains unchanged if k == 1. If total nodes are less than k, no group is reversed unless the logic is changed to reverse even the final partial group.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment