Finding the kth Node from End of Linked List
Java Program to Find kth node from end of linked list
In this page of Data Structures we’ll take a look at the solution of a problem, to find where it has been asked to find the kth node from the end of Linked List in Java.
Finding the Kth node from the end of a linked list is a common and important problem in data structures, especially during coding interviews.
In this article, we will explore the problem in detail, understand different ways to solve it, write clean Java code, and analyze the time and space complexity.
Finding the kth Node from end of linked list using java
Example Problem Statement:
Given a singly linked list, your task is to find the Kth node from the end.
For example:
Input: List = [10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 -> 50], K = 2 Output: 40
Because the 2nd node from the end is 40.
The last node in the list points to null.
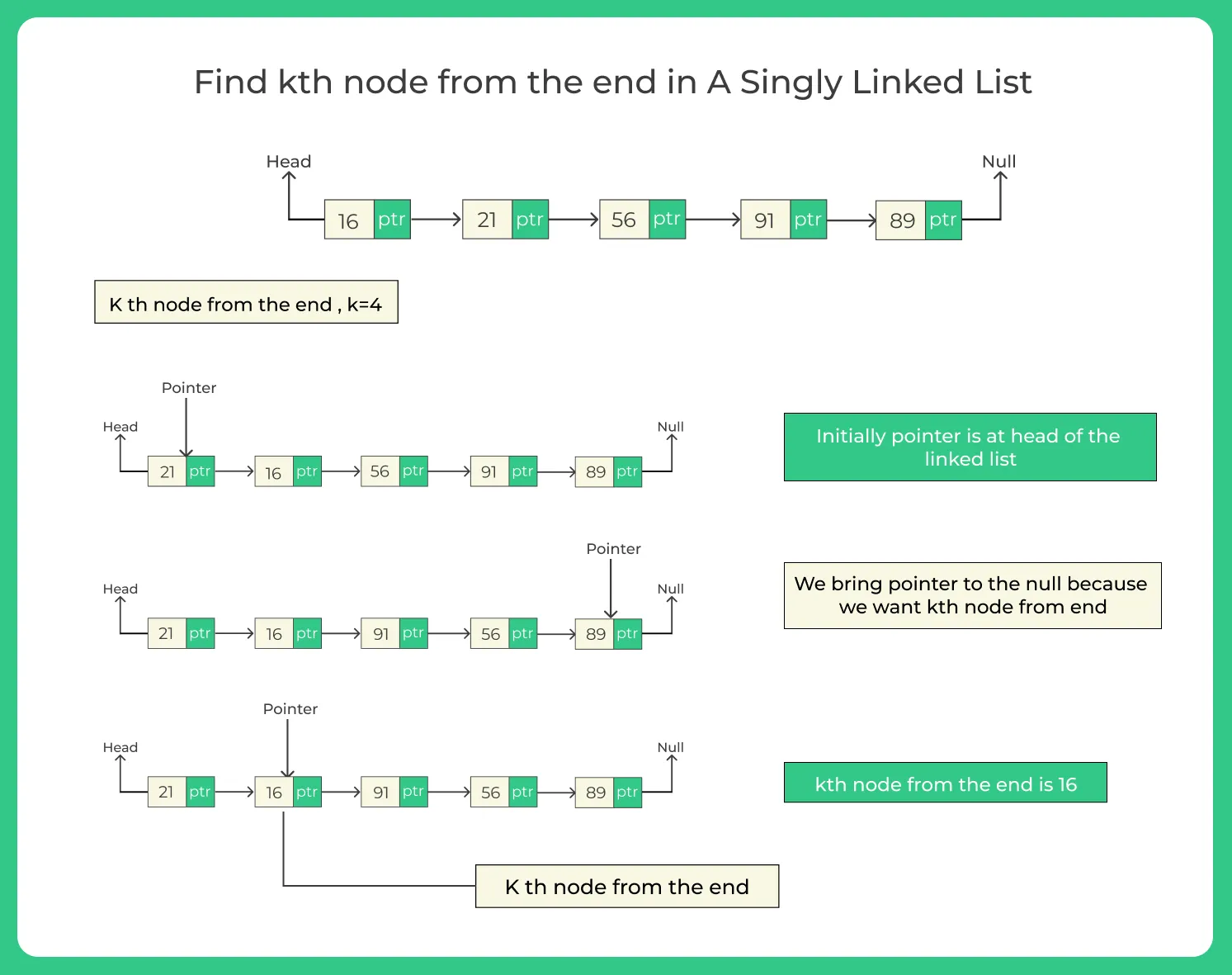
Implementation to find Kth node from end of Linked List in Java
Here, in this article we have solve this problem with 2 approaches. Checkout further on this page to practice more to solve this problem.
- Approach 1: Two Pass Algorithms
- Approach 2: Single pass with two pointer
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Approach 1: Two Pass Algorithm to find Kth node from end.
In the first pass, we find the length of the list. In the second pass, we move length – K steps from the head to find the Kth node from the end.
Algorithm:
- Traverse the linked list to count the total number of nodes.
- If K is greater than the length, return null or an error.
- Traverse again from the head to the (length – K)th node.
- Return the value of that node.
Code in Java Programming Language:
Space Complexity: O(1)
Code:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class KthNodeFromEnd {
public static int findKthFromEnd(Node head, int k) {
int length = 0;
Node temp = head;
// First pass: Count the total number of nodes
while (temp != null) {
length++;
temp = temp.next;
}
// Check if k is valid
if (k > length || k <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid value of k");
}
// Second pass: Move to (length - k)th node
temp = head;
for (int i = 0; i < length - k; i++) { temp = temp.next; } return temp.data; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 -> 50
Node head = new Node(10);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(30);
head.next.next.next = new Node(40);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(50);
int k = 2;
System.out.println("Kth node from end is: " + findKthFromEnd(head, k));
}
}
Output
Kth node from end is: 40
Approach 2: Single Pass with Two Pointers to find the Kth node from the end
This is a more optimized method that uses two pointers (fast and slow). The idea is:
- Move the first pointer k steps ahead
- Then move both pointers one step at a time
- When the first pointer reaches the end, the second pointer will be at the Kth node from the end.
Algorithm:
- Initialize two pointers: first and second.
- Move first pointer k steps forward.
- If first becomes null before reaching k steps, return an error.
- Move both first and second one step at a time until first reaches the end.
- The second pointer now points to the Kth node from the end.
Code in Java Programming Language:
Space Complexity: O(1)
Code:
public class KthNodeFromEndOptimized {
public static int findKthFromEnd(Node head, int k) {
if (head == null || k <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid input");
}
Node first = head;
Node second = head;
// Move first k steps ahead
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (first == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("k is larger than the list size");
}
first = first.next;
}
// Move both pointers until first reaches the end
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
return second.data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 -> 50
Node head = new Node(10);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(30);
head.next.next.next = new Node(40);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(50);
int k = 2;
System.out.println("Kth node from end is: " + findKthFromEnd(head, k));
}
}
Output
Kth node from end is: 40
Conclusion
Finding the Kth node from the end of a linked list is a common problem that tests your understanding of pointers and linked list traversal.
The two pass approach is simple and easy to understand, while the single pass two pointer approach is more efficient and elegant.
By practicing both methods, you’ll improve your confidence in solving linked list problems efficiently.
FAQ's related to Finding the kth Node from end of linked list
Answer:
It means the node that is at the Kth position when counting from the last node of the linked list.
For example, if K = 1, it means the last node; if K = 2, it means the second last node.
Answer:
If K is larger than the number of nodes in the list, it’s an invalid input. In such cases, your program should return an error message or handle it gracefully without crashing.
Answer:
Two pointer approach is considered more efficient because it only scans the list once, which reduces traversal time in long linked lists.
It also avoids the need to store or calculate the total length explicitly, making it more space efficient and better suited for large or dynamic data streams.
Answer:
You could convert the linked list into an array or use extra space like a stack to reverse-traverse the list, but that would increase space complexity. In most cases, modifying the list is not recommended, especially if the list is being used elsewhere or should remain unchanged.
Answer:
Finding the Kth node from the start means starting from the head and moving forward K steps. This is straightforward because the list starts at the head.
In contrast, finding the Kth node from the end requires either knowing the length of the list first or using a strategy like the two pointer approach to reach the correct position without directly accessing elements by index, which is not possible in a singly linked list.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment