Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder In C++
Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder in C++
Tree traversal is a fundamental concept in data structures, allowing us to visit every node of a tree in a specific sequence. A tree can be navigated using two major approaches Level Order Traversal and Depth First Traversal. Under depth first traversal, we primarily use three methods: Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder.
Each of these techniques follows a unique visiting pattern and is widely used in various C++ applications such as expression tree evaluation, binary search tree operations, and hierarchical data processing.
In this article, we will explore all three depth first traversals with explanations and examples to help you understand how they work in C++.

More About Preorder Traversal
- Preorder traversal is a depth first algorithm.
- We first print the value of the node,them move to the left subtree and finally to the right subtree.
- If we need to explore more about the node itself before inspecting its leaves, we use preorder traversal.
- Preorder traversal is used to find the prefix expression of an expression tree.
More About Inorder Traversal:
- Inorder Traversal is a depth first algorithm.
- In Inorder Traversal, we first move to the left subtree, then print the node and finally move to the right subtree.
- If you want the orginal sequence or how the tree was made, we use the inorder sequence.
- Inorder Traversal of a binary search tree gives the sequence in non decreasing order.
More About Postorder Traversal:
- Postorder traversal is a depth first algorithm.
- In postorder traversal, we first move to the left subtree then to the right subtree and finally print the node.
- Post order traversal is used when we want to free the nodes of the tree.
- It is also used to find the postfix expression.
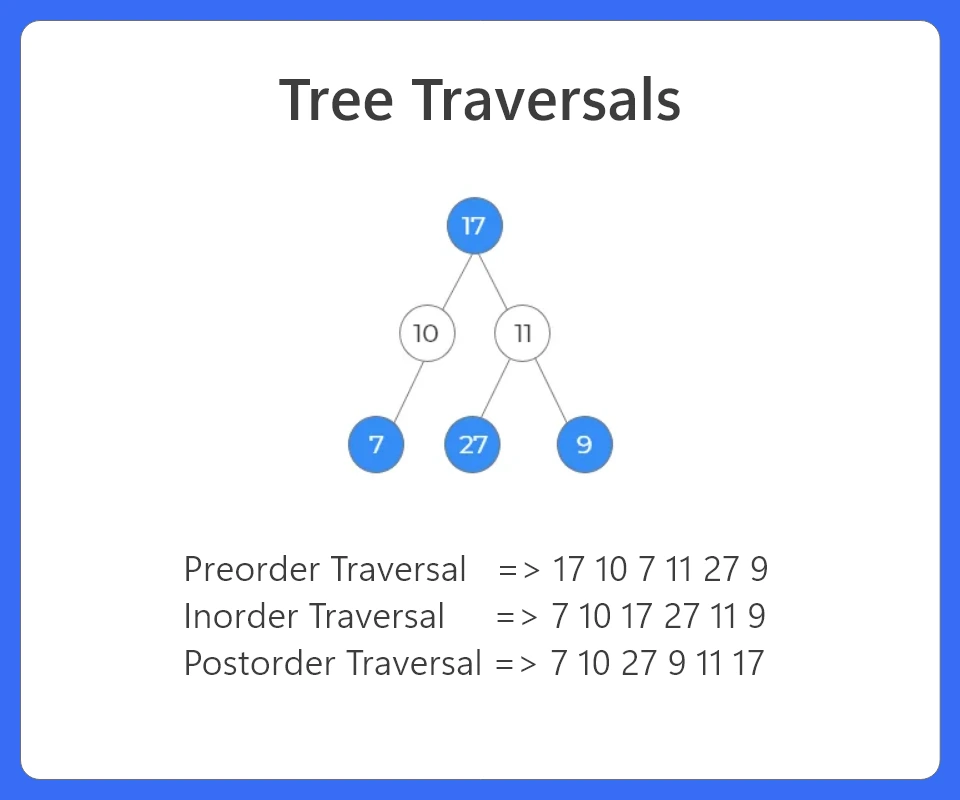
Algorithm To Find Preorder Traversal:
- If root is NULL, return NULL.
- Print the node.
- Visit left subtree.
- Visit right subtree.
Algorithm To Find Inorder Traversal:
- If root is NULL, return NULL.
- Visit the left subtree.
- Print the node.
- Visit right subtree.
Algorithm To Find Postorder Traversal:
- If root is NULL, return NULL.
- Visit the left subtree.
- Visit the right subtree
- Print the data.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code Implementation for various Tree traversals
Code implementation for various tree traversals Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder helps you understand how data is accessed in different depth first patterns. These traversal methods play a crucial role in solving problems related to binary trees, searching, and expression evaluation. In C++, implementing each traversal provides a clear view of how nodes are visited and processed systematically.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
int data;
Tree *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
// Constructor initialised
Tree (int x)
{
data = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void preorder_traversal (Tree * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Print the data
cout << root->data << " "; // Visit Left subtree preorder_traversal (root->left);
// Visit right subtree
preorder_traversal (root->right);
}
void inorder_traversal (Tree * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Visit Left subtree
inorder_traversal (root->left);
// Print the data
cout << root->data << " "; // Visit right subtree inorder_traversal (root->right);
}
void postorder_traversal (Tree * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Visit Left subtree
postorder_traversal (root->left);
// Visit right subtree
postorder_traversal (root->right);
// Print the data
cout << root->data << " "; } int main () { Tree *root = new Tree (17); root->left = new Tree (10);
root->right = new Tree (11);
root->left->left = new Tree (7);
root->right->left = new Tree (27);
root->right->right = new Tree (9);
cout << "Preorder => ";
preorder_traversal (root);
cout << endl;
cout << "Inorder => ";
inorder_traversal (root);
cout << endl;
cout << "Postorder => ";
postorder_traversal (root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Preorder => 17 10 7 11 27 9 Inorder => 7 10 17 27 11 9 Postorder => 7 10 27 9 11 17
Explanation:
- The code creates a Tree class where each node stores data and two child pointers initialized to NULL.
- Traversal functions use recursion, each checking if the current node is NULL before continuing.
- Preorder prints the node first, inorder prints after visiting the left subtree, and postorder prints after both subtrees.
- The main function manually builds a binary tree by linking nodes together as left and right children.
- Each traversal function is called in main, and the visited nodes are printed according to their respective order.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation / Traversal | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Preorder Traversal | O(n) | O(h) |
| Inorder Traversal | O(n) | O(h) |
| Postorder Traversal | O(n) | O(h) |
| Tree Construction | O(n) | O(1) |
To Wrap It Up:
Tree traversals like Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder play a crucial role in understanding how data is accessed and processed in binary trees. These traversal methods help programmers navigate a tree efficiently while preserving different logical sequences based on specific requirements.
By mastering these three depth-first techniques, you can easily handle tasks such as expression evaluation, tree construction, and sorted data extraction. With clear logic and simple implementation in C++, these traversals form a strong foundation for more advanced tree-based algorithms.
FAQs
Choose the traversal based on your requirement inorder for sorted output, preorder for tree construction, and postorder for operations that require child processing first.
Yes, all three traversals can be implemented using stacks, allowing them to work iteratively without relying on recursive calls.
Traversal order determines how data is visited, displayed, or processed, which directly impacts tasks like searching, evaluating expressions, and serialization.
While these specific orders are mainly used for binary trees, similar traversal concepts can be adapted for multi way trees with slight modifications.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment