C++ program to print reverse a linked list without actually reversing
How to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing in CPP programming?
In this article, we will learn to write a C++ program to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing. For doing this we will create a function that will recursively print data from last node till the beginning node without actually reversing it. Further in this article we will see steps and algorithm for the same.
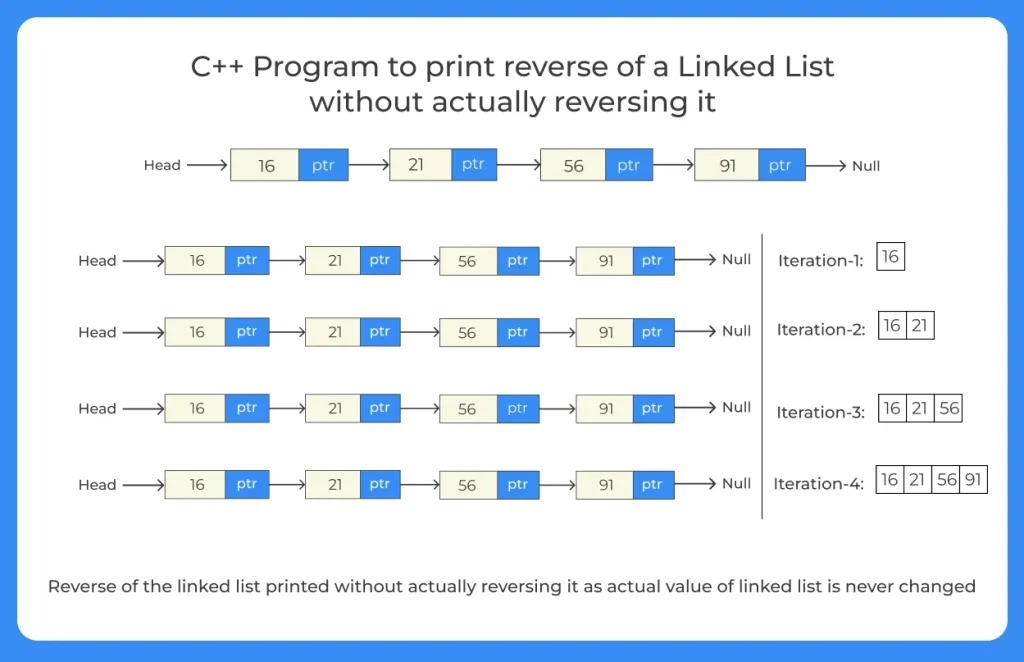
Steps write a C++ program to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing
To print the reverse of a linked list without modifying it, you can traverse the list recursively or use a stack to store node values. By accessing the nodes in reverse order during printing, the original list remains unchanged while displaying its elements backward.
These steps are used to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing in CPP programming
- Start the program and initialize the variables.
- Create function to create list (listBanao).
- The above created function will help us to create linked list.
- Now create another function toto print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing (reverse).
- This function will have our main algorithm to reverse the given linked list.
- This function will help to display the linked list in reverse order without actually reversing it.
Syntax
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
Algorithm to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing in C++
Below is the algorithm used to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing in C++
- VOID REVERSE(NODE *STNODE)
- IF (STNODE == NULL)
- RETURN
- REVERSE(STNODE->NEXTPTR)
- PRINT STNODE->NUM
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing in C++
In C++, you can display a linked list in reverse without changing its structure. This approach lets you access elements from end to start while preserving the original list.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int num;
node *nextptr;
} *stnode; //node constructed
void listBanao (int n);
void reverse (node * stnode);
int main ()
{
int n, num, item;
cout << "Enter the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
listBanao (n);
cout << "After reversing\n";
reverse (stnode);
return 0;
}
void listBanao (int n) //function to create linked list.
{
struct node *frntNode, *tmp;
int num, i;
stnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << "Memory can not be allocated";
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node 1: "; cin >> num;
cout << "\n"; stnode->num = num;
stnode->nextptr = NULL; //Links the address field to NULL
tmp = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
frntNode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (frntNode == NULL) //If frntnode is null no memory cannot be allotted
{
cout << "Memory can not be allocated";
break;
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node " << i << ": "; // Entering data in nodes. cin >> num;
cout << "\n"; frntNode->num = num;
frntNode->nextptr = NULL;
tmp->nextptr = frntNode;
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
}
void reverse (node * stnode) //function to reverse linked list
{
if (stnode == NULL)
return;
reverse (stnode->nextptr);
cout << stnode->num << "\t";
}
Output
Enter the number of nodes: 5
Enter the data for node 1: 1
Enter the data for node 2: 2
Enter the data for node 3: 3
Enter the data for node 4: 4
Enter the data for node 5: 5
After reversing
5 4 3 2 1
Explanation:
- The program uses a node structure to represent each element of a singly linked list, storing a number and a pointer to the next node.
- Using the listBanao function, the linked list is built dynamically, with the user entering data for each node one by one.
- Each node is allocated memory using malloc, and the code ensures memory allocation is successful before proceeding.
- The reverse function leverages recursion to print the elements of the linked list in reverse order without modifying the original links.
- In main, the program first asks for the number of nodes, creates the linked list, and then displays it in reverse by calling the recursive function.
Time and space complexity:
| Function / Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Creating the linked list (`listBanao`) | O(n) — Iterates through n nodes to allocate memory and input values | O(n) — Each node requires memory allocation, so total memory is proportional to n nodes |
| Reversing the linked list (`reverse` function) | O(n) — Recursive function visits each node exactly once | O(n) — Recursion stack stores n function calls for n nodes |
| Main function (`main`) | O(n) — Calls `listBanao` and `reverse`, both O(n) | O(n) — Dominated by linked list memory + recursion stack |
To wrap it up:
This C++ program provides a simple and effective way to display a linked list in reverse without actually modifying the list. By using recursion, it prints elements from the last node to the first, maintaining the original order of the linked list.
This technique is ideal when you want to reverse the output but keep the underlying data intact. It ensures a clean and efficient approach for situations where preserving the original list structure is important.
FAQs
You can use recursion or a stack to traverse the linked list and print nodes in reverse order without modifying the actual links.
Using recursion or a stack, the time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Yes, using recursion or a stack consumes additional memory proportional to the number of nodes, so the space complexity is O(n).
This approach is useful when you need to preserve the original linked list structure while still displaying its elements in reverse order.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment