Linked List Insertion in C++
Insertion in Singly linked in C++
Singly Linked List Insertion in C++, in general words can be understood as insertion of a new node in a singly linked list that is already created. We can perform three different types of insertion operations on a singly linked list –
- Insertion at the head.
- Insertion at tail
- Insertion at the specific position.
Types of insertion in a singly linked list
Insertion at the head:
In this type of insertion in a singly linked list, a new node is added before the head of the list i.e. before the first node of the list.
Insertion at specific position:
Here we insert a new node at a specific position by traversing to the desired position and inserting a new node there.
Insertion at the tail:
We insert a new node after the last node i.e. after the tail node in the insertion at the end singly linked list.
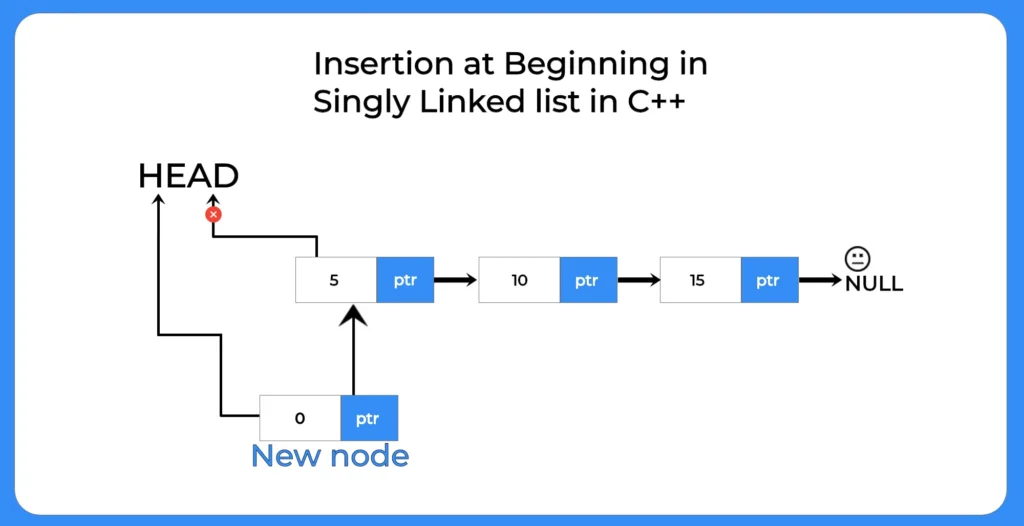
How to perform insertion at beginning in Singly Linked List in C++?
To perform insertion at the beginning in a singly linked list we will use the following steps:-
- Create the memory for new Node
- Assign the data value
- Assign the newNode’s next as the current head
- Change the head to this newNode
If it was the first node in the Linked List then next would null for this newNode
void insertAtBeginning(Node** head, int val){
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
}
void LinkedList:: insertAtBeginning(int val){
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
}
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
How to perform insertion at end in singly linked list?
To perform insertion at the end in the singly linked list we will use the following steps:-
- Create the memory and assign data value call this newNode
- Traverse to the current end node of the list.
- Assign this current end node’s next to newNode
- Since this will be the last node assign next to NULL
void insertAtLast(Node** head, int val){
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->val = val;
// Last node always pointst to NULL
newNode->next = NULL;
// If Linked List was empty
if(*head==NULL){
*head = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
return;
}
Node* tempNode = *head;
// reach to the last node of Linked List
while(tempNode->next!=NULL)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
// assign last node's next to this newNode
tempNode->next = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
}void LinkedList:: insertAtLast(int val){
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->val = val;
// Last node always pointst to NULL
newNode->next = NULL;
// If Linked List was empty
if(head==NULL){
head = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
return;
}
Node* tempNode = head;
// reach to the last node of Linked List
while(tempNode->next!=NULL)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
// assign last node's next to this newNode
tempNode->next = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
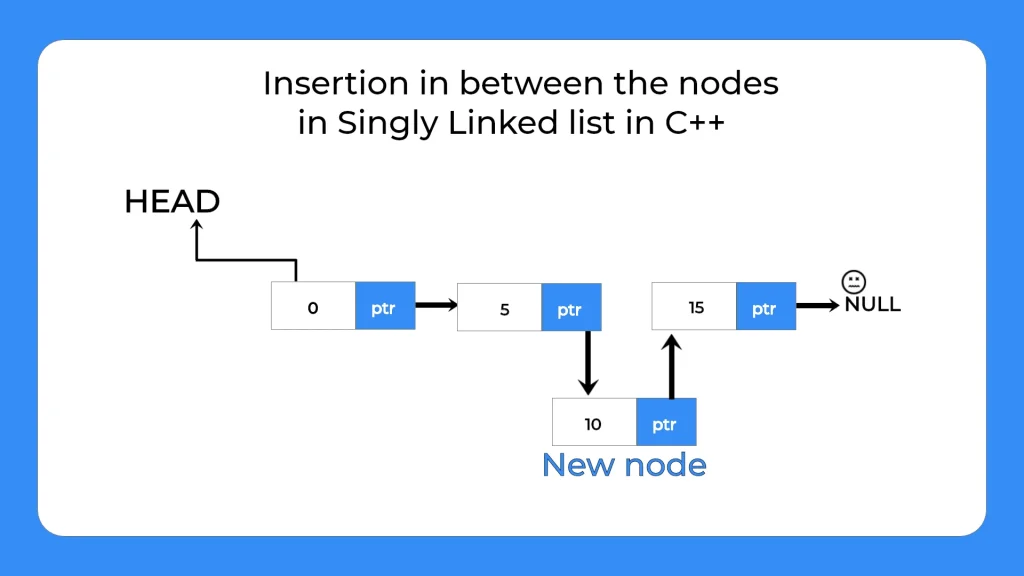
}How to perform insertion After specific position in singly linked list?
To perform insertion after specific position in singly linked list we will use the following steps:-
- Create the memory and assign data value
- Check if the position user asked us to Insert After is valid or not (Should not be negative and should not be greater than size)
- Traverse till the nth node
- Assign this new Node’s next to the nth node’s next that is the (n+1)th node
- Assign nth node’s next to this new Node
// required for insertAfterNthNode
int getCurrSize(Node* node){
int size=0;
while(node!=NULL){
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertAfterNthNode(int n, int val, Node** head)
{
int size = getCurrSize(*head);
// Negative Position Insertions not possible
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(n < 0 || n > size)
cout << "Invalid position to insert";
if(n == 0){
insertAtBeginning(head, val);
}
else {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = NULL;
// tempNode used to traverse the Linked List
Node* tempNode = *head;
// traverse till the nth node
while(--n)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
// assign newNode's next to nth node's next
newNode->next= tempNode->next;
// assign nth node's next to this new node
tempNode->next = newNode;
// newNode inserted
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
}
}
// required for insertAfterNthNode
int LinkedList:: getCurrSize(){
int size=0;
Node* node = new Node();
node = head;
while(node!=NULL){
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void LinkedList:: insertAfterNthNode(int n, int val)
{
int size = getCurrSize();
// Negative Position Insertions not possible
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(n < 0 || n > size)
cout << "Invalid position to insert";
if(n == 0){
insertAtBeginning(val);
} else {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = NULL;
// tempNode used to traverse the Linked List
Node* tempNode = head;
// traverse till the nth node
while(--n)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
// assign newNode's next to nth node's next
newNode->next= tempNode->next;
// assign nth node's next to this new node
tempNode->next = newNode;
// newNode inserted
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
}
}Complete Program for Insertion in a Linked List in C++
Let us have a look at the program –
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int val;
Node *next;
};
void insertAtBeginning (Node ** head, int val)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
}
void insertAtLast (Node ** head, int val) {
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->val = val;
// Last node always pointst to NULL
newNode->next = NULL;
// If Linked List was empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
return;
}
Node *tempNode = *head; // reach to the last node of Linked List
while (tempNode->next != NULL)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
// assign last node's next to this newNode
tempNode->next = newNode;
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
} // required for insertAfterNthNode
int getCurrSize (Node * node) {
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertAfterNthNode (int n, int val, Node ** head)
{
int size = getCurrSize (*head);
// Negative Position Insertions not possible
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if (n < 0 || n > size)
cout << "Invalid position to insert";
if (n == 0)
{
insertAtBeginning(head, val);
}
else
{
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = NULL;
// tempNode used to traverse the Linked List
Node *tempNode = *head;
// traverse till the nth node
while (--n)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
// assign newNode's next to nth node's next
newNode->next = tempNode->next;
// assign nth node's next to this new node
tempNode->next = newNode;
// newNode inserted
cout << newNode->val << " inserted" << endl;
}
}
void display (Node * node)
{
cout << "\n";
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->val << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << "\n" << endl;
}
int main ()
{
Node *head = NULL;
insertAtBeginning (&head, 12);
insertAtBeginning (&head, 11);
insertAtBeginning (&head, 10);
display (head);
insertAtLast (&head, 13);
insertAtLast (&head, 14);
insertAtLast (&head, 16);
display (head);
//Inserts data: 15 after 5th node
insertAfterNthNode (5, 15, &head);
insertAfterNthNode (0, 9, &head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
12 inserted 11 inserted 10 inserted 10 11 12 13 inserted 14 inserted 16 inserted 10 11 12 13 14 16 15 inserted 9 inserted 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
int calcSize (Node * node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertStart (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
void insertLast (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
}
void insertPosition (int pos, int data, Node ** head)
{
int size = calcSize (*head);
//If pos is 1 then should use insertStart method
//If pos is less than or equal to 0 then can't enter at all
//If pos is greater than size then bufferbound issue
if (pos < 1 || size < pos)
{
printf ("Can't insert, %d is not a valid position\n", pos);
}
else
{
Node *temp = *head;
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
while (--pos)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
//(25)->next = 10 as 12->next is 10
newNode->next = temp->next;
// (12)->next = 25
temp->next = newNode;
//new node added in b/w 12 and 10
}
}
void display (Node * node)
{
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
Node *head = NULL;
/*Need & i.e. address as we
need to change head address only needs to traverse
and access items temporarily
*/
insertStart (&head, 12);
insertStart (&head, 16);
insertStart (&head, 20);
insertLast (&head, 10);
insertLast (&head, 14);
insertLast (&head, 18);
insertLast (&head, 11);
//Inserts after 3rd position
insertPosition (3, 25, &head);
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not
need to change head address
*/
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
20 16 12 25 10 14 18 11
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insert at Beginning | O(1) — Directly updates head pointer | O(1) — Only new node allocation |
| Insert at End | O(n) — Must traverse to last node | O(1) — Only new node allocation |
| Insert After Nth Node / Insert at Position | O(n) — Traverse up to nth node | O(1) — Only new node allocation |
| Get/Calculate Size of Linked List | O(n) — Must traverse entire list | O(1) — Only counter variable used |
| Display / Print Linked List | O(n) — Must traverse all nodes | O(1) — Only temporary pointer used |
To Wrap It Up:
Inserting elements into a singly linked list is a fundamental operation in data structures. This process involves creating a new node and adjusting pointers to maintain the list’s integrity. Whether inserting at the beginning, end, or a specific position, each method requires careful pointer manipulation to ensure the list remains properly linked.
Mastering insertion techniques in singly linked lists is crucial for implementing dynamic data structures like stacks, queues, and more complex systems. Efficient insertion operations enable the development of scalable and flexible applications that can handle dynamic data effectively.
FAQs
Linked list insertion can be at the beginning, at the end, or at a specific position. Each type changes pointers differently to maintain the list structure.
If the list is empty, the new node becomes the head, and its next pointer is nullptr. This ensures the list is correctly initialized.
Before inserting, check if the given position exists; otherwise, display an error or insert at the end. This prevents memory corruption or segmentation faults.
Yes, inserting at the beginning is O(1), while inserting at a position or end is O(n) because it may require traversing the list.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment