Insertion at End in Singly Linked List in C++
How to insert an element at End in Singly Linked List in C++?
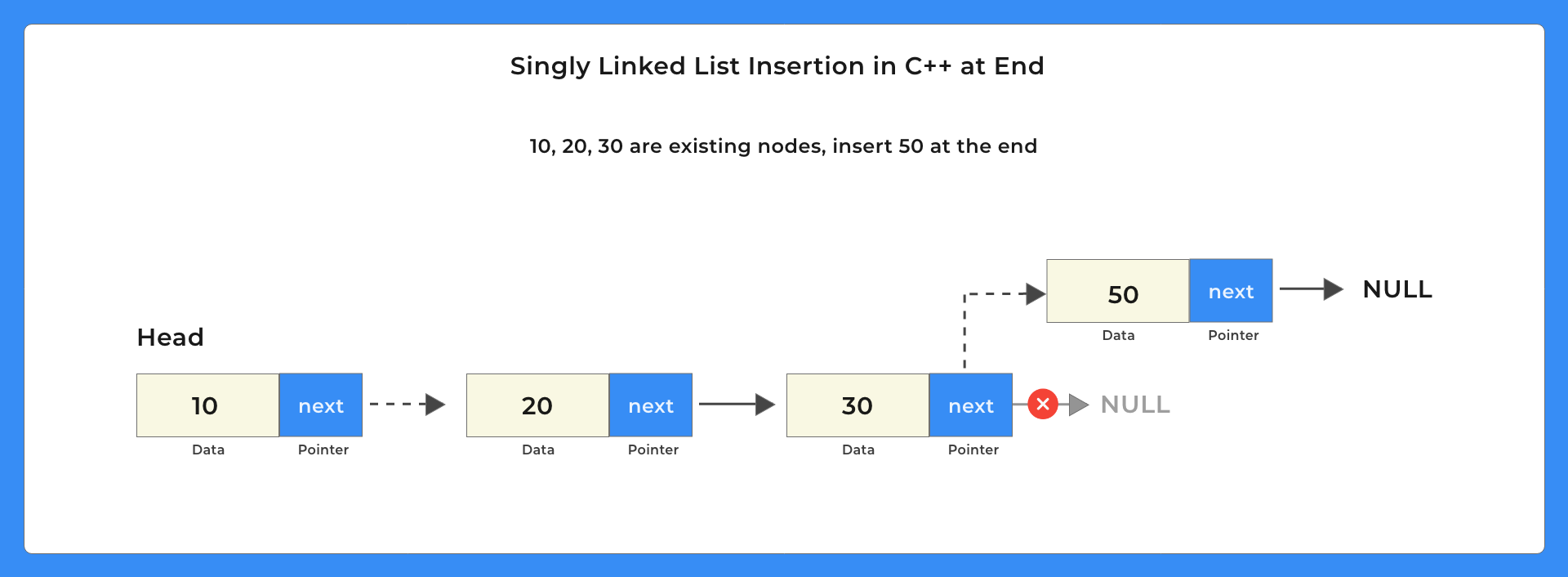
Insertion at End in Singly Linked List in C++ – In this post we will understand how to insert a new node at the end of the singly linked list in C++. Lets go and code Program Insert node at end of linked list in C++. Linked list in C++ is part of a linked list and is a type of linear data structure. Linked list is made up of two parts node and pointer where node contains the data and pointer contains the address of the next node.
This is one of the most commonly used operations while working with linked lists. Whether you’re building a list from scratch or adding new elements, knowing how to insert at the end is essential.
Singly Linked List definition in C++
Nodes of singly linked list is created by using the code mentioned besides.
This set of code will construct linked list by creating each node of the list.
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
}; 
C++ program to insert an element at end of singly linked list
This method uses non member functions and head is passed within function signatures.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void insertEnd(Node** head, int data)
{
Node* freshNode = new Node();
freshNode->data = data;
// since this will be the last node so it will point to NULL
freshNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if(*head==NULL)
{
*head = freshNode;
cout << freshNode->data << " inserted" << endl; return; } struct Node* temp = *head; // traverse to the last node of Linked List while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// assign last node's next to this freshNode
temp->next = freshNode;
cout << freshNode->data << " inserted" << endl;
}
void display(Node* node)
{
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
insertEnd(&head,7);
insertEnd(&head,8);
insertEnd(&head,9);
insertEnd(&head,10);
display(head);
return 0;
}Output
7 inserted 8 inserted 9 inserted 10 inserted 7 8 9 10
This method uses member functions and head the data member of class so it need not be passed with functions signatures.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
LinkedList()
{ // constructor
head = NULL;
}
int calcSize();
void insertLast(int data);
void display();
};
void LinkedList::insertLast(int data)
{
Node* freshNode = new Node();
freshNode->data = data;
// since this will be the last node so it will point to NULL
freshNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if(head==NULL)
{
head = freshNode;
cout << freshNode->data << " inserted" << endl; return; } struct Node* temp = head; // traverse to the last node of Linked List while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// assign last node's next to this freshNode
temp->next = freshNode;
cout << freshNode->data << " inserted" << endl;
}
void LinkedList::display()
{
Node* node = new Node();
node = head;
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << endl; } int main() { LinkedList* mylist = new LinkedList(); mylist->insertLast(7);
mylist->insertLast(8);
mylist->insertLast(9);
mylist->insertLast(10);
mylist->display();
return 0;
}Output
7 inserted 8 inserted 9 inserted 10 inserted 7 8 9 10
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Code Type | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insert at End | Function-based (using Node* head) | O(n) — Traverses the entire list to reach the end | O(1) — Constant extra space used for the new node |
| Insert at End | Class-based (using LinkedList class) | O(n) — Traverses all nodes before appending at the end | O(1) — Constant auxiliary space used |
| Display List | Function-based | O(n) — Visits every node once | O(1) — No extra space except loop variables |
| Display List | Class-based | O(n) — Traverses the complete linked list | O(1) — Constant extra space |
To wrap it up:
The article thoroughly demonstrates how to insert a node at the end of a singly linked list in C++, outlining both a non member function approach and a class based (member function) approach, with complete working code and sample outputs.
It also highlights the time complexity trade off (O(n) traversal unless a tail pointer is maintained) and handles edge cases such as inserting into an empty list thereby giving readers a solid, complete understanding of “insertion at end” in singly linked lists.
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs - Insertion at End in Singly Linked Lists in C++
It means adding a new node as the last node of the linked list. This new node’s next pointer will point to NULL, making it the new tail of the list.
The time complexity is O(n) because we need to traverse the entire list to reach the last node, unless we maintain a tail pointer.
Yes, if we maintain a tail pointer (a reference to the last node), we can insert in O(1) time without traversing the list.
If the list is empty, the new node becomes both the head and tail of the list, as it’s the only node present.
In a singly linked list, NULL indicates the end of the list. It tells us that there is no node after the current one.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment