Insertion at Beginning in Singly Linked List in C++
How to perform insertion at the beginning in Linked List in C++?
Insertion at Beginning in Linked List in C++ is one of the operations that we can perform on Linked List. linked list in C++ is part of a linked list and is a type of linear data structure. Linked is made up of two parts node and pointer where node contains the data and pointer contains the address of the next node.
If you’re just getting started with linked lists, this is one of the first operations you should know. It’s simple, fast, and forms the base for more complex operations. We’ll explain the logic step by step and provide clear code examples to help you understand how it works.

Linked list definition in C++
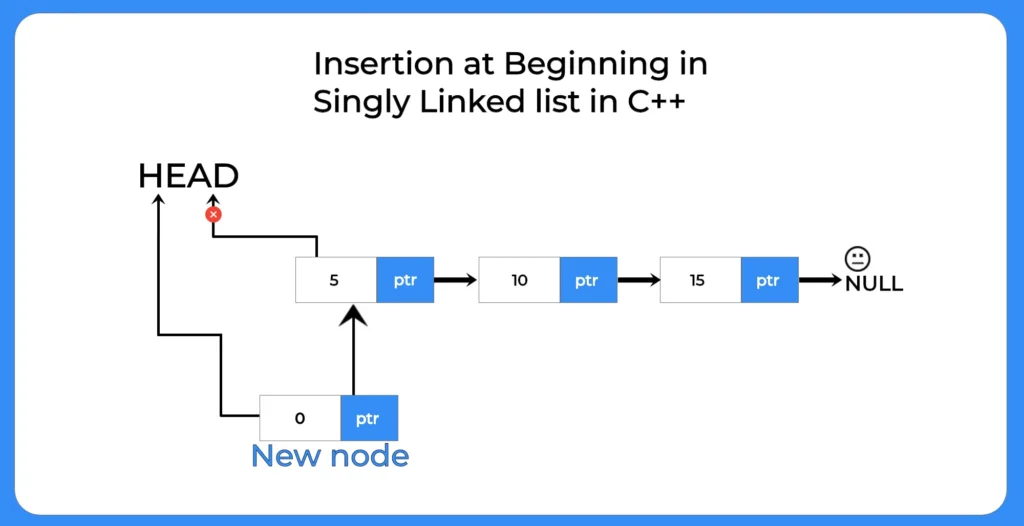
Nodes of a linked list are created by using the code mentioned besides.
This set of codes will construct a linked list by creating each node of the list.
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
}; Steps to insert an element at beginning of linked list
- Allocate space for a new node.
- ptr = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node *));
- In the space created for new node put the data in.
- new_node->data = new_data
- Point the pointer of new node to the head of the linked list
- new_node->ptr = (*head);
- Make new node as head
- (*head) = new_node
C++ program to insert an element at beginning of linked list
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void insertFront(Node** head, int data){
Node* new_node = new Node();
// assign data
new_node->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
new_node->next = *head;
// new_node should become the new head of Linked List
*head = new_node;
cout << "Inserted Item: " << new_node->data << endl;
}
void printList(Node* node){
cout << "\nLinked List : " ;
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL){
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
Node* head = NULL;
insertFront(&head,4);
insertFront(&head,5);
insertFront(&head,6);
insertFront(&head,7);
insertFront(&head,8);
insertFront(&head,9);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output
Inserted Item: 4 Inserted Item: 5 Inserted Item: 6 Inserted Item: 7 Inserted Item: 8 Inserted Item: 9 Linked List : 9 8 7 6 5 4
Using member functions and using head member variable
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
LinkedList() { // constructor
head = NULL;
}
void insertFront(int data);
void printList();
};
void LinkedList::insertFront(int data){
Node* new_node = new Node();
// assign data value
new_node->data = data;
// change the next node of this new_node
// to current head of Linked List
new_node->next = head;
// new_node should become the new head of Linked List
head = new_node;
cout << "Inserted Item: " << new_node->data << endl;
}
void LinkedList::printList(){
Node* node = new Node();
node = head;
cout << "\nLinked List : " ;
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL){
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << endl; } int main() { LinkedList* new_list = new LinkedList(); new_list->insertFront(4);
new_list->insertFront(5);
new_list->insertFront(6);
new_list->insertFront(7);
new_list->insertFront(8);
new_list->insertFront(9);
new_list->printList();
return 0;
}Output
Inserted Item: 4 Inserted Item: 5 Inserted Item: 6 Inserted Item: 7 Inserted Item: 8 Inserted Item: 9 Linked List : 9 8 7 6 5 4
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Code Type | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insert at Front | Function-based (using Node* head) | O(1) — Constant time as insertion is at the head | O(1) extra space per insertion (excluding node memory) |
| Insert at Front | Class-based (LinkedList class) | O(1) — Constant time as insertion is at the head | O(1) extra space per insertion (excluding node memory) |
| Print List | Function-based | O(n) — Traverses all nodes | O(1) extra space |
| Print List | Class-based | O(n) — Traverses all nodes | O(1) extra space |
| Total Memory Usage | Both | — | O(n) — Each node takes memory dynamically (n = number of nodes) |
To Wrap It Up:
Inserting a node at the beginning of a singly linked list allows for quick addition of elements without traversing the list. This method updates the head pointer to the new node, making it the first element efficiently.
Using the C++ implementation, we can clearly see how dynamic memory allocation and pointer adjustments work together to maintain the list structure. This example serves as a practical guide for beginners to understand and implement linked list insertions effectively.
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs
Insertion at the beginning means adding a new node before the current head of the linked list. The new node becomes the new head, pointing to the previous head.
You create a new node dynamically, assign its data, set its next pointer to the current head, and then update the head to this new node.
The time complexity is O(1) because the operation involves updating only a few pointers, regardless of the list size.
Yes, if the list is empty, the new node simply becomes the head, and its next pointer is set to nullptr.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment