Insert a Node at specific Position in a Singly Linked List in C++
C++ Program to Insert a node at a given position in a Singly Linked List
Here we will learn to write a program to insert a node at a specific position in a Singly Linked List in C++. A linked list is a collection of nodes which stores data and a pointer pointing towards the next node.
This program helps in efficiently adding elements anywhere in the list without shifting existing elements, unlike arrays. Understanding this insertion technique is crucial for dynamic data manipulation and forms the basis for more advanced data structures.

Insert a Node at Specific Position in a Singly Linked List in C++
Singly Linked Lists (SLL) are one of the fundamental data structures in C++ programming. Unlike arrays, SLLs store elements in nodes that contain data and a pointer to the next node. This allows for efficient memory usage and dynamic resizing. One common operation in linked lists is inserting a node at a specific position, which is slightly more complex than inserting at the beginning or end.
Steps to Insert
- Take the user input n, for the position where the new node has to be inserted
- Create the memory the new node and assign its data value
- Traverse till the (n-1)th node and change its next pointer to the new Node created
- Change the next pointer of this new node and assign it to the address of (n+1)th node.
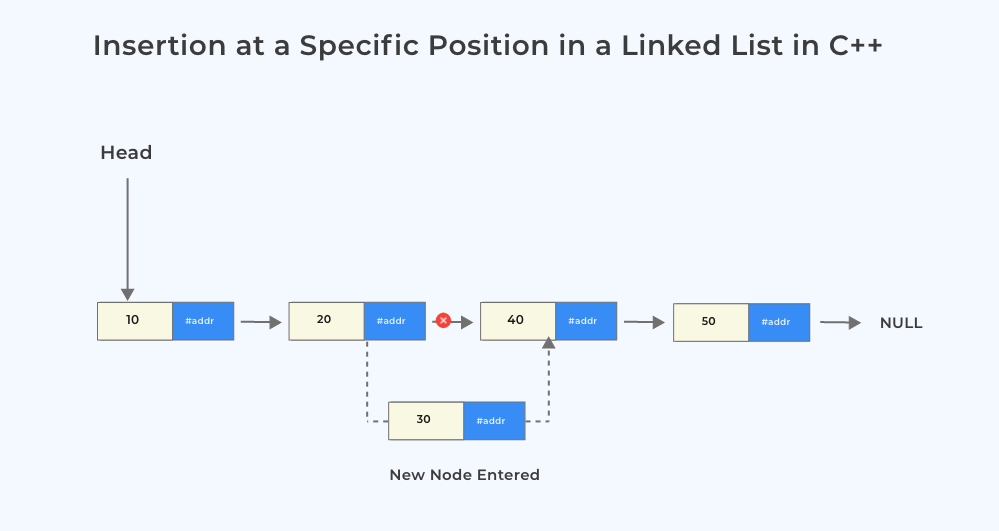
- Always check if the position is valid; inserting at a non-existent position can lead to runtime errors.
- For empty lists, inserting at position 1 is valid, but any other position should be rejected.
- Traversal is required to reach the correct position, which makes inserting at the middle or end an O(n) operation.
C++ Program to Insert a node at a given position in a Singly Linked List
In C++, inserting a node at a specific position in a singly linked list allows you to place data exactly where it’s needed, rather than just at the beginning or end. This operation involves traversing the list to the desired position and adjusting the pointers to include the new node seamlessly. It’s a fundamental technique for dynamic data management in linked lists.
// Linked List Insertion at a specific position in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
// Create a global variable for the size of the Linked List
int listSize = 0; // Rename the global size variable
void insert(Node **head, int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
listSize++; // Update the global size variable
}
// Method to insert at a given position
void insertPosition(int pos, int data, Node **head)
{
Node *new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = nullptr;
// Invalid positions
if (pos < 1 || pos > listSize + 1) // Use listSize instead of size
{
cout << "Invalid" << endl;
return;
}
// Inserting as the first node
if (pos == 1)
{
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
listSize++; // Update the global size variable
}
else
{
Node *temp = *head;
// Traverse to the current (pos-1)th node
while (--pos > 1)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
new_node->next = temp->next;
temp->next = new_node;
listSize++; // Update the global size variable
}
}
void display(Node *node)
{
cout << "Linked List: ";
while (node != nullptr)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Node *head = nullptr;
insert(&head, 140);
insert(&head, 120);
insert(&head, 80);
insert(&head, 60);
insert(&head, 20);
display(head);
insertPosition(2, 40, &head);
insertPosition(5, 100, &head);
insertPosition(8, 160, &head);
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 20 60 80 120 140 Linked List : 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Code Type | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insert at Beginning | Function-based (using Node** head) | O(1) — Directly inserts new node at head without traversal | O(1) — Constant extra space (excluding new node memory) |
| Insert at Specific Position | Function-based (insertPosition function) | O(n) — Traverses up to (pos−1) nodes in worst case | O(1) — Constant auxiliary space (excluding node memory) |
| Display List | Function-based (display function) | O(n) — Traverses the entire list to print nodes | O(1) — No extra space used apart from traversal pointer |
To Wrap It Up:
The article clearly explains how to insert a node at any given position in a singly linked list, covering both boundary conditions and general cases. The use of a size counter ensures that every insertion happens safely and efficiently.
This implementation provides a clear understanding of pointer manipulation and traversal logic in linked lists. Once you grasp these steps, modifying or extending the program for your own needs becomes an easy and practical task.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs
Inserting a node at a specific position allows us to add elements in a desired order, maintaining the logical sequence of data within the linked list.
You traverse the list from the head node and stop at the node just before the desired position, then adjust the pointers to insert the new node.
If the position exceeds the list’s length, insertion is usually not possible unless handled by adding the node at the end or returning an error.
The time complexity is O(n) since traversal is required to reach the given position before performing the insertion.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment