Deletion in Singly Linked List in C++
What is deletion in singly linked list in C++?
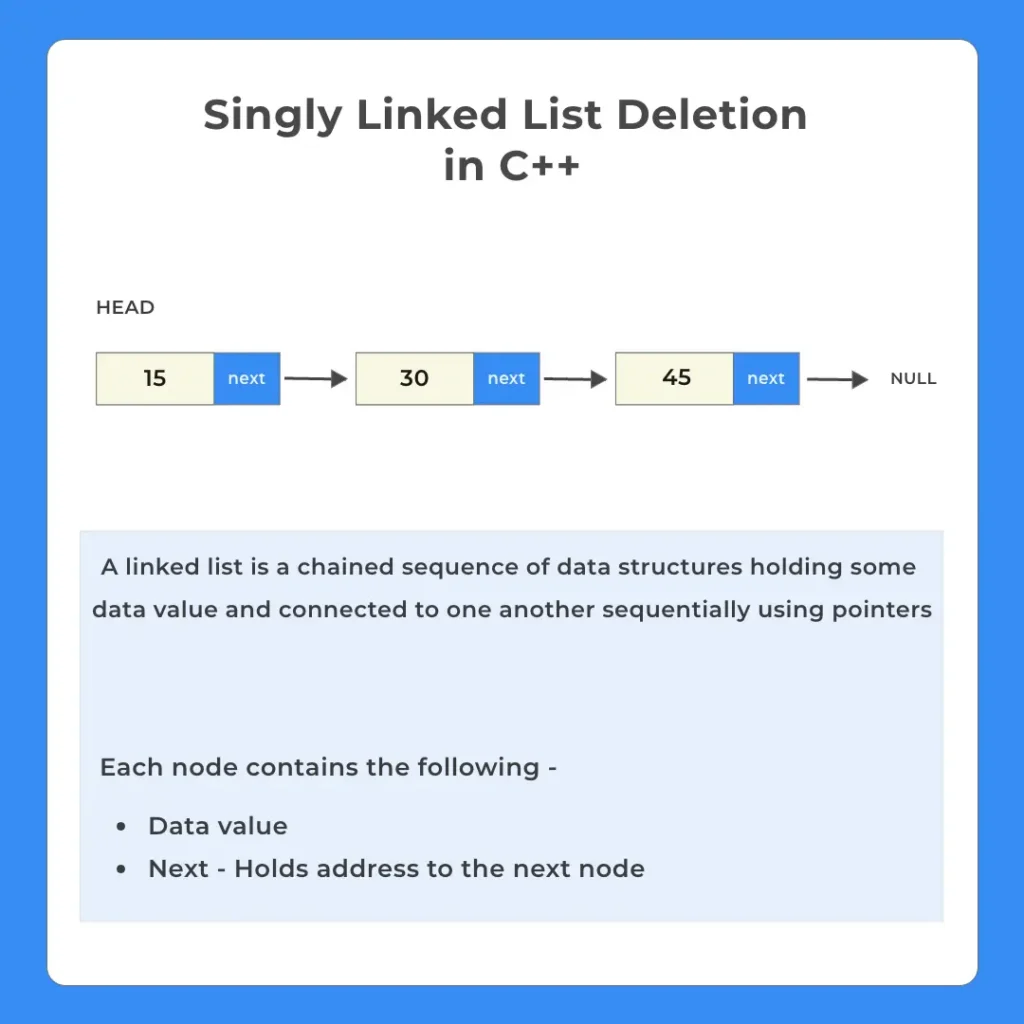
Deletion in singly linked in C++ can be simplified as deleting a node from an already constructed linked list. We can perform three different types of deletion operations on a singly linked-
- Deleting the beginning
- Deletion from a specific position
- Deletion from end

Types of deletion in singly linked list
There can be two different approaches for deletion –
- Deletion for position
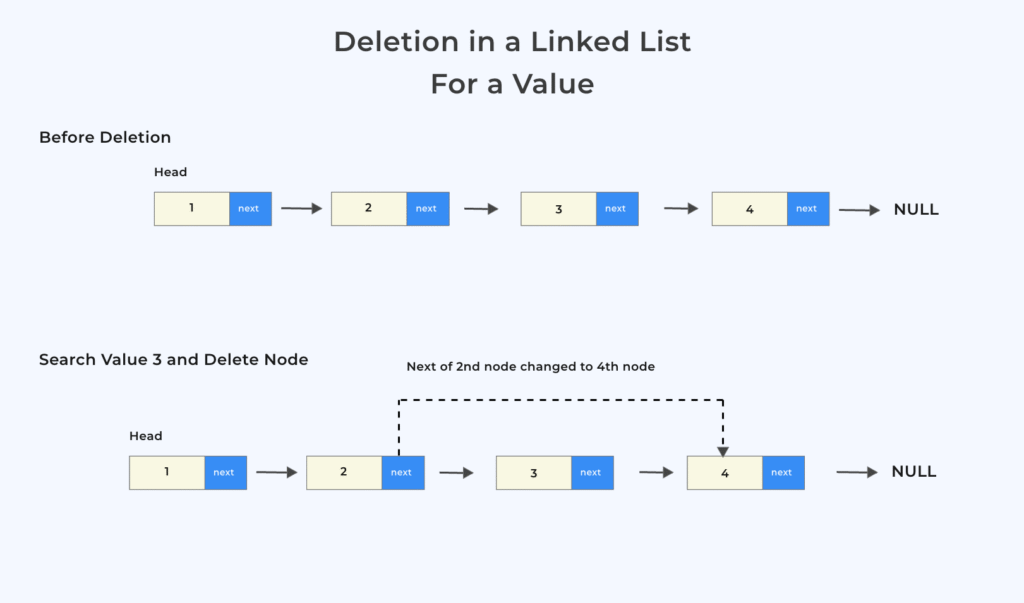
- Deletion for a Value
We will look at both of them in this page and understand how to code them.
Deletion in a Singly Linked List for a Value
Let’s have a look at the program
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void insert(Node** head, int data){
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
void deleteNode(Node** head, int delVal)
{
Node* temp = *head;
Node* previous;
if(temp == NULL){
cout << "Can't delete Linked List empty" << endl;
return;
}
// Case when there is only 1 node in the list
if(temp->next==NULL)
{
*head = NULL;
free(temp);
cout << "Deleted: " << delVal << endl;
return;
} // if the head node itself needs to be deleted
if(temp->data==delVal)
{
*head = temp->next; //changing head to next in the list
cout << "Deleted: " << temp->data << endl;
free(temp);
return;
}
// traverse until we find the value to be deleted or LL ends
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != delVal)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// if value is not present then
// temp will have traversed to last node NULL
if(temp==NULL)
{
cout << "Value not found" << endl;
return;
}
// for node to be deleted : temp lets call it nth node
// assign (n-1)th node's next to (n+1)th node
previous->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
cout << "Deleted: " << delVal << endl;
}
void display(Node* node){
cout << "\nLinked List : " ;
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL){
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
Node* head = NULL;
insert(&head, 1);
insert(&head, 2);
insert(&head, 3);
insert(&head, 4);
insert(&head, 5);
insert(&head, 6);
display(head);
deleteNode(&head, 4);
display(head);
deleteNode(&head, 10);
deleteNode(&head, 1);
deleteNode(&head, 5);
deleteNode(&head, 6);
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deleted: 4 Linked List : 6 5 3 2 1 Value not found Deleted: 1 Deleted: 5 Deleted: 6 Linked List : 3 2
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
LinkedList() { // constructor
head = NULL;
}
void insert(int data);
void display();
void deleteNode(int data);
};
void LinkedList::insert(int data){
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = head;
head = new_node;
}
void LinkedList::deleteNode(int delVal)
{
Node* temp = head;
Node* previous;
if(temp == NULL){
cout << "Can't delete Linked List empty" << endl;
return;
} // Case when there is only 1 node in the list
if(temp->next==NULL)
{
head = NULL;
free(temp);
cout << "Deleted: " << delVal << endl;
return;
} // if the head node itself needs to be deleted
if(temp->data==delVal)
{
head = temp->next; //changing head to next in the list
cout << "Deleted: " << temp->data << endl;
free(temp);
return;
} // traverse until we find the value to be deleted or LL ends
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != delVal)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// if value is not present then
// temp will have traversed to last node NULL
if(temp==NULL)
{
cout << "Value not found" << endl;
return;
} // for node to be deleted : temp lets call it nth node // assign (n-1)th node's next to (n+1)th node
previous->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
cout << "Deleted: " << delVal << endl;
}
void LinkedList::display(){
Node* node = new Node();
node = head;
cout << "\nLinked List : " ;
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL){
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
LinkedList* list = new LinkedList();
list->insert(1);
list->insert(2);
list->insert(3);
list->insert(4);
list->insert(5);
list->insert(6);
list->display();
list->deleteNode(4);
list->display();
list->deleteNode(10);
list->deleteNode(1);
list->deleteNode(5);
list->deleteNode(6);
list->display();
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deleted: 4 Linked List : 6 5 3 2 1 Value not found Deleted: 1 Deleted: 5 Deleted: 6 Linked List : 3 2
Time and space complexity table:
| Operation | Function-based | Class-based | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insert at Beginning | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Delete Node (Best Case) | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Delete Node (Worst Case) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display Linked List | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) |
Deletion in a Singly Linked List in C++ (For a Position)
Deletion can be performed at the following positions –
Below we will write a program that will handle all the above cases in a single function, however, if you wish to write individual functions for each you can check the pages hyperlinked above.
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void insert (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
int calcSize (Node * node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void deletepos (Node ** head, int pos)
{
Node *temp = *head;
Node *previous;
int size = calcSize (*head);
if (pos < 1 || pos > size)
{
printf ("Enter valid position\n");
return;
}
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
if (pos == 1)
{
//changing head to next in the list
*head = temp->next;
cout << "Deleted Item: " << temp->data << endl;
free (temp);
return;
}//run until we find the value to be deleted in the list
while (--pos) { // store previous link node as we need to
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// (pos-1)th node's next assigned to (pos+1)nth node
previous->next = temp->next;
cout << "Deleted Item: " << temp->data << endl;
free (temp);
}
void display (Node * node)
{
cout << "\nLinked List : ";
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Node *head = NULL;
/*Need & i.e. address as we
need to change head address
*/
insert (&head, 10);
insert (&head, 20);
insert (&head, 30);
insert (&head, 40);
insert (&head, 50);
insert (&head, 60);
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not
need to change head address
*/
display (head);
deletepos(&head, 1);
display (head);
deletepos(&head, 3);
display(head);
deletepos(&head, 4);
display(head);
deletepos(&head, -2); // not valid as pos negative
deletepos(&head, 10); // not valid as breaches size of Linked List
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 60 50 40 30 20 10 Deleted Item: 60 Linked List : 50 40 30 20 10 Deleted Item: 30 Linked List : 50 40 20 10 Deleted Item: 10 Linked List : 50 40 20 Enter valid position Enter valid position
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node * head;
public:
LinkedList ()
{ // constructor
head = NULL;
}
void insert (int data);
void display ();
void deleteNode (int data);
int calcSize ();
void deletepos (int pos);
};
void LinkedList::insert (int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = head;
head = new_node;
}
int LinkedList::calcSize ()
{
int size = 0;
Node *node = head;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void LinkedList::deletepos (int pos)
{
Node *temp = head;
Node *previous;
int size = calcSize ();
if (pos < 1 || pos > size)
{
printf ("Enter valid position\n");
return;
}
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
if (pos == 1)
{
//changing head to next in the list
head = temp->next;
cout << "Deleted Item: " << temp->data << endl;
free (temp);
return; //run until we find the value to be deleted in the list
}
while (--pos) { // store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// (pos-1)th node's next assigned to (pos+1)nth node
previous->next = temp->next;
cout << "Deleted Item: " << temp->data << endl;
free (temp);
}
void LinkedList::display ()
{
Node *node = new Node ();
node = head;
cout << "\nLinked List : ";
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main () {
LinkedList *list = new LinkedList ();
list->insert (1);
list->insert (2);
list->insert (3);
list->insert (4);
list->insert (5);
list->insert (6);
list->display ();
list->deletepos (1);
list->display ();
list->deletepos (3);
list->display ();
list->deletepos (4);
list->display ();
list->deletepos (-2); // not valid as pos negative
list->deletepos (10); // not valid as breaches size of Linked List
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 6 5 4 3 2 1 Deleted Item: 6 Linked List : 5 4 3 2 1 Deleted Item: 3 Linked List : 5 4 2 1 Deleted Item: 1 Linked List : 5 4 2 Enter valid position Enter valid position
Time and space complexity table:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insert at Beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Delete at Position | O(n) — due to traversal and size calculation | O(1) |
| Calculate Size | O(n) — traverses entire list | O(1) |
| Display Linked List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
It covers various deletion scenarios, including removing nodes from the beginning, middle, and end of the list. The guide emphasizes the importance of pointer manipulation to maintain the integrity of the list structure during deletion operations.
By understanding these deletion techniques, developers can efficiently manage dynamic data structures in their applications. The article also highlights common challenges and best practices to ensure robust and error free implementation of deletion operations in singly linked lists.

FAQs
To delete the first node, move the head pointer to the second node and free the memory of the original head to avoid memory leaks. This operation has O(1) time complexity.
Traverse the list to the node just before the target position, adjust its next pointer to skip the node, and then delete the target node to free memory.
Traverse the list to reach the second-last node, set its next pointer to NULL, and delete the last node to remove it safely.
Attempting to delete in an empty list does nothing but should be checked to avoid segmentation faults, as the head pointer is NULL.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment