Deletion from beginning in singly linked list in C++
How to delete element from beginning in Singly Linked List in C++?
Deletion from beginning in singly linked list in C++ is one of the most fundamental operations in linked list manipulation. This operation is typically used when we want to remove the first element (head node) from the list. Understanding how to perform this operation is essential for mastering data structures in C++. We can perform following deletion operation on the linked list:-
- Deleting from beginning of the list
- Deletion from End of the list
- Deleting a specific node

Defining a singly linked list in C++
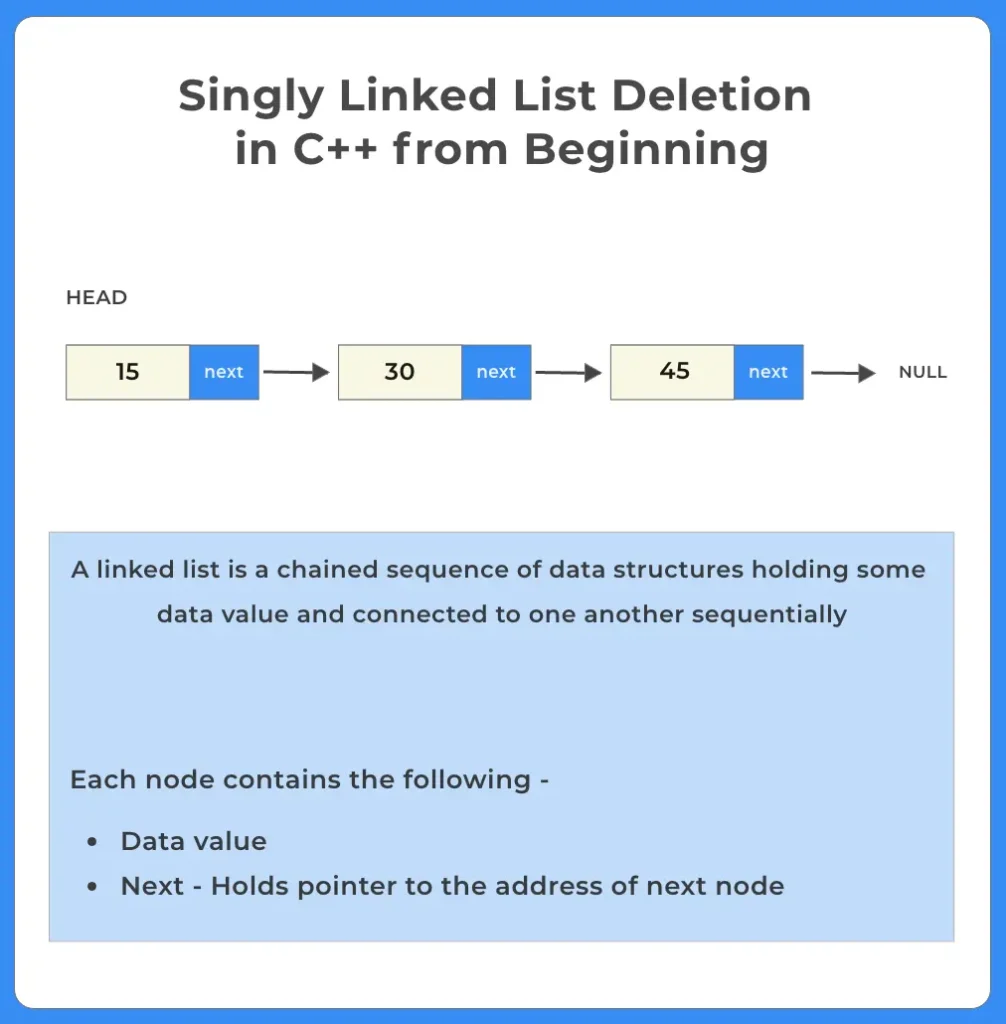
Deletion from beginning in singly linked list in C++ – A singly linked list is a fundamental data structure consisting of nodes where each node contains data and a pointer to the next node in the sequence. Nodes of a singly linked list are created by using the code mentioned alongside. This set of code constructs the linked list by dynamically creating each node and linking them sequentially.
- Nodes of singly linked list is created by using the code mentioned besides.
- This set of code will construct linked list by creating each node of the list.
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
}; 
Program for deleting a node from beginning in singly linked list in C++
- Start with the head pointer of the linked list.
- Check if the list is empty (head == NULL).
- If empty, print a message like “List is empty” and exit.
- If not empty:
- Store the current head node in a temporary pointer (temp = head).
- Move the head pointer to the next node (head = head->next).
- Delete the node pointed by temp using delete temp.
- The node at the beginning is now deleted, and the list starts from the new head.
This method uses non-member class functions and head needs to be passed seperately
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void insertStart(Node** head, int data){
Node* new_node = new Node();
// assign data value
new_node->data = data;
// change the next node of this new_node
// to current head of Linked List
new_node->next = *head;
//changing the new head to this newly entered node
*head = new_node;
}
void display(Node* node){
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL){
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
Node* head = NULL;
insertStart(&head,10);
insertStart(&head,11);
insertStart(&head,12);
insertStart(&head,13);
insertStart(&head,14);
insertStart(&head,15);
insertStart(&head,16);
insertStart(&head,17);
insertStart(&head,18);
display(head);
return 0;
}Output
18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10
This method uses member class functions and head need not to be passed separately as its member variable of class and can be accessed.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
LinkedList() { // constructor
head = NULL;
}
void insertBeginning(int data);
void display();
};
void LinkedList::insertBeginning(int data){
Node* new_node = new Node();
// assign data value
new_node->data = data;
// change the next node of this new_node
// to current head of Linked List
new_node->next = head;
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
head = new_node;
}
void LinkedList::display(){
Node* node = new Node();
node = head;
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL){
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << endl; } int main() { LinkedList* singly_list = new LinkedList(); singly_list->insertBeginning(10);
singly_list->insertBeginning(11);
singly_list->insertBeginning(12);
singly_list->insertBeginning(13);
singly_list->insertBeginning(14);
singly_list->insertBeginning(15);
singly_list->insertBeginning(16);
singly_list->insertBeginning(17);
singly_list->insertBeginning(18);
singly_list->display();
return 0;
}Output
18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Advantages and Disadvantages of deleting a node from the beginning in a singly linked list in C++
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple and easy to implement | Cannot delete a node from the middle or end directly |
| Deletion operation is very fast (O(1)) | If the list is empty, deletion is not possible (needs a check) |
| No need to traverse the list to delete | Only removes the first node, no control over other nodes |
| Efficient for stack-like structures (LIFO) | If head pointer is not updated correctly, list may become corrupted |
| Requires only updating the head pointer | Memory leak risk if the deleted node is not properly deleted (free/delete) |
| Useful when oldest data is at the front | Frequent deletions from beginning can lead to fragmentation or overhead |
Wrap It Up
Deleting from beginning of single linked list in C++, the first node in a singly linked list is a simple yet powerful operation that’s fundamental to understanding how linked lists work. It’s commonly used in data structures like stacks because of how efficient it is requiring just a few steps to execute.
- Fast and efficient: The operation runs in constant time, O(1), which means it’s always quick, no matter the size of the list.
- Update the head pointer: You simply move the head pointer to the next node in the list.
- Memory management matters: Always free the memory of the removed node to avoid memory leaks.
FAQs
If the list is empty (head is NULL), deletion should be skipped after checking, otherwise it may cause a segmentation fault.
Only if nodes are statically allocated, but in most practical cases, dynamic memory is used and delete must be called to free memory.
Once deleted using delete, the memory is freed; restoring it is not possible unless it was stored beforehand.
Always store the current head in a temporary pointer, move the head to the next node, and then delete the temporary node.
No, deleting from the beginning of a singly linked list is not thread-safe in general. If multiple threads access or modify the list concurrently, you should use proper synchronization (like mutexes) to avoid race conditions.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



