Delete nth node in Linked List in C++
C+++ Program to delete nth Node from a Singly Linked List
On this article will learn to write a program to delete the nth node from a singly Linked List in C++.
Linked List in C++ is data structures and alternative to arrays, where every node of the linked list is made up of two parts data and pointer.

Delete a Linked List node at a given position in C++
Following are the steps –
- Insert the initial items in the linked list
- Calculate the current size of the linked list
- Ask the user for nth position he wants to delete
- if(n < 1 || n > size) then say invalid
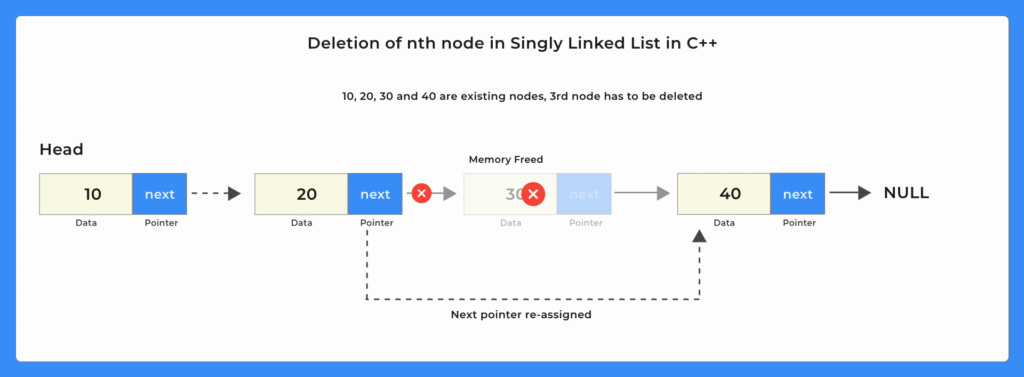
- If deleting the first node, just change the head to the next item in Linked List
- Else traverse to the nth node to delete
- Change the next of (n-1)th node to (n+1)th node
- Free the memory for th nth node
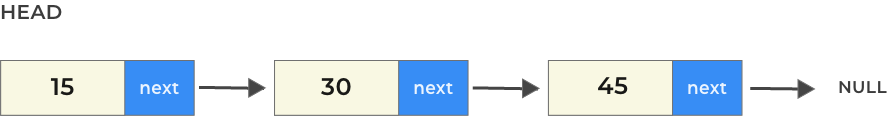
Constructing a singly linked list in C++
Nodes of singly linked list is defined by using the set of code given below. Whole linked list will be build by each set of nodes using this code.
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
}; 
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program for deleting nth Node from Linked List
// deletion of th nth node in a Linked List in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
int calcLen (Node * node)
{
int len = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
void insert (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
void deleteNthNode (int n, Node ** head)
{
Node *temp = *head;
Node *prevNode;
int len = calcLen (*head);
if (n < 1 || n > len)
{
cout << "Invalid" << endl;
return;
}
// delete the 1st node
if (n == 1)
{
*head = (*head)->next;
cout << temp->data << " deleted" << endl;
delete (temp);
return;
}
// traverse to the n'th node
while (--n)
{
prevNode = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// change prevNode node's next node to nth node's next node
prevNode->next = temp->next;
// delete this nth node
cout << temp->data << " deleted" << endl;;
delete (temp);
}
void display (Node * temp)
{
cout << "Linked List : ";
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 25);
insert (&head, 24);
insert (&head, 23);
insert (&head, 22);
insert (&head, 21);
insert (&head, 20);
display (head);
deleteNthNode (2, &head);
deleteNthNode (4, &head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 20 21 22 23 24 25 21 deleted 24 deleted Linked List : 20 22 23 25
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node * head;
public:
LinkedList ()
{ // constructor
head = NULL;
}
int calcSize ();
void deleteStart ();
void deleteEnd ();
void deleteNthNode (int n);
void display ();
void insert (int data);
};
void LinkedList::deleteNthNode (int n)
{
Node *temp = head;
Node *previous;
int size = calcSize ();
if (n < 1 || n > size)
{
cout << "\nEnter valid position\n";
return;
}
// if first node has to be deleted
if (n == 1)
{
head = head->next;
cout << "\nValue deleted: " << temp->data << endl;
delete (temp);
return;
}
//traverse till the nth node
while (--n)
{
// store previous link as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// previous node's next changed to nth node's next
previous->next = temp->next;
cout << "Value deleted: " << temp->data << endl;
delete (temp);
}
int LinkedList::calcSize ()
{
Node *node = new Node ();
node = head;
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void LinkedList::insert (int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = head;
// assigned head to newNode
head = newNode;
}
void LinkedList::display ()
{
Node *temp = new Node ();
temp = head;
cout << "Linked List : ";
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
LinkedList *list = new LinkedList ();
list->insert (25);
list->insert (24);
list->insert (24);
list->insert (22);
list->insert (21);
list->insert (20);
list->display ();
list->deleteNthNode (2);
list->deleteNthNode (4);
list->display ();
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 20 21 22 24 24 25 Value deleted: 21 Value deleted: 24 Linked List : 20 22 24 25
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Calculate Length (calcLen) | O(n) — Traverses entire linked list once | O(1) — Only a counter variable is used |
| Insert at Beginning (insert) | O(1) — Direct insertion at head | O(1) — Only one new node is created |
| Delete nth Node (deleteNthNode) | O(n) — In worst case, traverses up to nth node + O(n) for length calculation → overall O(n) | O(1) — Only a few pointer variables used |
| Display Linked List (display) | O(n) — Traverses entire list | O(1) — Only temporary pointer used |
To wrap it up:
The article explains how to delete a node from a specific position in a singly linked list using C++, covering both function-based and class-based methods. It highlights how to handle different cases like deleting the first node or dealing with invalid positions while ensuring proper link management.
Understanding deletion from a specific location strengthens your grasp of linked list operations and memory handling. It also helps you write cleaner and more efficient programs using both procedural and object-oriented approaches.
FAQs
To delete the nth node, first traverse the list to reach the (n-1)th node, then adjust its next pointer to skip the nth node and finally free the memory of the deleted node.
If the given position exceeds the list size, the operation should be aborted or an error message displayed to prevent segmentation faults.
The time complexity is O(n) since traversal up to the nth node is required before deletion.
To delete the first node, simply move the head pointer to the second node and free the memory of the original head — this takes O(1) time.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment