Linked List Insertion and Deletion in Java
Singly Linked List Insertion and Deletion in Java
In this post, we will look at all possible ways of insertion and deletion of a node in a Single Linked List in Java. Both insertions and deletion in a Linked List can happen at the following positions-
- At Front
- At End
- In the Middle (After a certain position)

Possible positions to insert/delete in a Linked List
Both insertions and deletion in a Linked List can happen at the following positions-
- At Front
- At End
- In the Middle (After a certain position)
We will look at the program with all three above functions, however, do note that the default nature of a Linked List is to always insert at the front.q
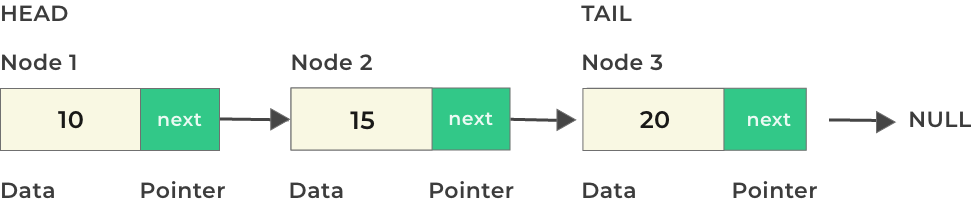
Structure of a Linked List in Java
// Node Class
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}Insertion in Singly Linked List in Java
Let us have a look at the programs below –
import java.lang.*;
class LinkedList {
Node head;
// not using parameterized constructor would by default
// force head instance to become null
// Node head = null; // can also do this, but not required
// Node Class
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
public Node insertStart(int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// assigning this newNode's next as current head node
newNode.next = head;
// re-assigning head to this newNode
head = newNode;
return head;
}
public void insertLast(int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// if Linked List was empty, entering first node
if(head==null)
{
head = newNode;
return;
}
// required to traverse the Linked List
Node temp = head;
// traverse till the last node in Linked List
while(temp.next!=null)
temp = temp.next;
// assigning the current last node's next to this newNode
// thus newNode becomes the last node in Linked List
temp.next = newNode;
}
public void insertPosition(int n,int data)
{
int size = calcSize(head);
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(n < 1 || n > size)
{
System.out.println("Can't insert\n");
}
else
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// required to traverse
Node temp = head;
// traverse to the nth node
while(--n > 0)
temp=temp.next;
// assigning this newNode's next to nth node's next
newNode.next= temp.next;
// assigning the nth node's next to this newNode
temp.next = newNode;
// newNode added after nth node
}
}
public void display()
{
Node node = head;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
while(node!=null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// required for insertPosition() method
public int calcSize(Node node){
int size = 0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while(node!=null){
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList();
ll.insertStart(3);
ll.insertStart(2);
ll.insertStart(1);
ll.display();
ll.insertLast(5);
ll.insertLast(6);
ll.insertLast(7);
ll.insertLast(8);
ll.display();
//Inserts after 3rd position
ll.insertPosition(3,25);
ll.display();
}
}
import java.lang.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class Main
{
static Node insertBeginning(Node head, int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
static Node insertEnd(Node head, int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(head==null) {
head = newNode;
return head;
}
Node temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
return head;
}
static Node insertAt(int pos, int data, Node head) {
int size = calcSize(head);
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(pos < 1 || size < pos) { System.out.println("Can't insert," + pos + " is not a valid position\n"); } else { Node newNode = new Node(data); // required to traverse Node Node temp = head; // traverse to the nth node while (--pos > 0)
temp = temp.next;
newNode.next= temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
return head;
}
static void display(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
static int calcSize(Node node){
int size=0;
while(node!=null)
{
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = insertBeginning(head,15);
head = insertBeginning(head,10);
head = insertBeginning(head,5);
display(head);
head = insertEnd(head,20);
head = insertEnd(head,25);
head = insertEnd(head,30);
head = insertEnd(head,35);
display(head);
//Inserts at 3rd position
head = insertAt(3,100,head);
display(head);
}
}
Output
1 2 3
1 2 3 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 25 5 6 7 8
Deletion in a Linked List in Java
Let us have a look at the programs below –
import java.lang.*;
class LinkedList {
Node head;
// Node Class
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
public void deleteStart()
{
if (head == null){
System.out.println("List is empty, not possible to delete");
return;
}
System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data);
// move head to next node
head = head.next;
}
public Node insert(int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
public void display()
{
Node node = head;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
while(node!=null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
public void deleteLast()
{
if (head == null){
System.out.println("List is empty, not possible to delete");
return;
}
// if LL has only one node
if(head.next == null)
{
System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data);
head = head.next;
}
Node previous = null;
Node temp = head;
// else traverse to the last node
while (temp.next != null)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
System.out.println("Deleted: " + temp.data);
previous.next = null;
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
}
public void deleteNthNode(int n)
{
int len = calcLen(head);
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(n < 1 || n > len)
{
System.out.println("Can't delete\n");
}
else
{
if(n == 1)
{
// head has to be deleted
System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data);
head = head.next;
return;
}
// required to traverse
Node temp = head;
Node previous = null;
// traverse to the nth node
while(--n > 0) {
previous = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// assigned next node of the previous node to nth node's next
previous.next = temp.next;
System.out.println("Deleted: " + temp.data);
}
}
public int calcLen(Node temp){
int len = 0;
while(temp!=null){
temp = temp.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList();
ll.insert(6);
ll.insert(5);
ll.insert(4);
ll.insert(3);
ll.insert(2);
ll.insert(1);
ll.display();
ll.deleteStart();
ll.display();
ll.deleteLast();
ll.display();
ll.deleteNthNode(3);
ll.display();
}
}
import java.lang.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class Main
{
public static Node deleteStart(Node head)
{
if (head == null){
System.out.println("List is empty, not possible to delete");
return head;
}
System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data);
// move head to next node
head = head.next;
return head;
}
static Node deleteLast(Node head) {
if (head == null){
System.out.println("List is empty, not possible to delete");
return head;
}
// if LL has only one node
if(head.next == null)
{
System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data);
head = head.next;
return head;
}
Node previous = null;
Node temp = head;
// else traverse to the last node
while (temp.next != null)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
System.out.println("Deleted: " + temp.data);
previous.next = null;
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
return head;
}
static Node deletePosition(int n, Node head) {
int size = calcSize(head);
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(n < 1 || n > size)
System.out.println("Can't delete\n");
else
{
if(n == 1)
{
// head has to be deleted
System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data);
head = deleteStart(head);
return head;
}
// required to traverse
Node temp = head;
Node previous = null;
// traverse to the nth node
while(--n > 0) {
previous = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// assigned next node of the previous node to nth node's next
previous.next = temp.next;
System.out.println("Deleted: " + temp.data);
}
return head;
}
public static Node insert(Node head, int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// assigning this newNode's next as current head node
newNode.next = head;
// re-assigning head to this newNode
head = newNode;
return head;
}
static void display(Node node) {
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
// required for insertPosition() method
static int calcSize(Node node){
int size=0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while(node!=null)
{
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = insert(head, 6);
head = insert(head, 5);
head = insert(head, 4);
head = insert(head, 3);
head = insert(head, 2);
head = insert(head, 1);
display(head);
head = deleteStart(head);
display(head);
head = deleteLast(head);
display(head);
// deletes 3rd node
head = deletePosition( 3, head);
display(head);
}
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6
Deleted: 1
2 3 4 5 6
Deleted: 6
2 3 4 5
Deleted: 4
2 3 5
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment