Implementation of Queues using Linked List in Java

Let us see how to Implement Queue using linked list in java ?
As we know that array implementation can not be used for the many large values where the queues are implemented. So that’s why as an alternative array implementation of queue is replaced by implementation of queues using Linked List.
Implementing queues using link list will increase the efficiency of the program .
Basic Operations of Queue
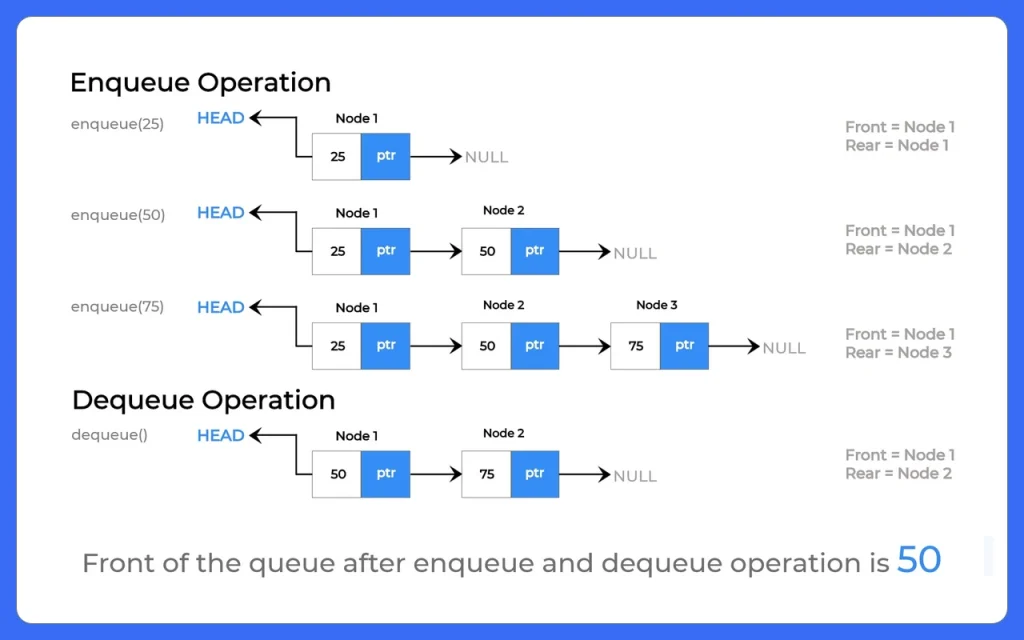
- Enqueue: When we want to add an element to the end of the queue
- Dequeue: when we want to Remove an element from the front of the queue
- IsEmpty: Check if the queue is empty
- IsFull: Check if the queue is full
- Peek: Get the value of the front of the queue without removing it
ALGORITHMS:
- ENQUEUE:
public void enqueue(int data)
{
Node old = rear;
rear = new Node();
rear.data = data;
rear.next = null;
if (isEmpty())
{
front = rear;
}
else
{
old.next = rear;
}
s++;
System.out.println(data+ ” added to the queue”);
}
- DEQUEUE:
public int dequeue()
{
int data = front.data;
front = front.next;
if (isEmpty())
{
rear = null;
}
s–;
System.out.println(data+ ” removed from the queue”);
return data;
}
JAVA CODE TO IMPLEMENT QUEUE USING LINK LIST .
Run
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
private Node front, rear;
private int s; // number of items
//class to define linked node
private class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
}
public Main ()
{
front = null;
rear = null;
s = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty ()
{
return (s == 0);
}
public void disp ()
{
if (s == 0)
{
System.out.println ("queue is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = front;
while (temp != null)
{
System.out.print (" " + temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//to Remove item
public void dequeue ()
{
int data = front.data;
front = front.next;
if (isEmpty ())
{
rear = null;
}
s--;
}
//to Add data .
public void enqueue (int data)
{
Node old = rear;
rear = new Node ();
rear.data = data;
rear.next = null;
if (isEmpty ())
{
front = rear;
}
else
{
old.next = rear;
}
s++;
System.out.println (data + " added to the queue");
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
Main queue = new Main ();
queue.enqueue (1);
queue.enqueue (2);
queue.enqueue (3);
queue.enqueue (4);
System.out.println ("Original queue :");
queue.disp ();
System.out.println ();
queue.dequeue ();
queue.dequeue ();
System.out.println ("Queue after dequeue");
queue.disp ();
}
}
OUTPUT:
1 added to the queue 2 added to the queue 3 added to the queue 4 added to the queue Original queue : 1 2 3 4 Queue after dequeue 3 4
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment