Priority Queue in C++ Programming
What is a Priority Queue in C++ ?
A Priority Queue in C++ programming is a advanced data structure, which is one step ahead of a normal queue. In priority queue we work with the data depending upon the priority of the data. Like, if we want to delete an element from the queue, the data with the highest priority will be deleted first, in the similar way if we are inserting some data in the queue, it will be arranged in the queue depending upon its priority. Let’s see how a priority queue in C++ works.
More About Priority Queue in C++ Programming
A priority queue is a special type of queue in which each element is associated with a priority, and elements with higher priority are served before elements with lower priority. It is different from a regular queue where elements are served on a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) basis.
- As we’ve discussed above, Priority Queue is a special type of Queue, in which the data is arranges on the basis of its priority.
- There are two types of Priority Queue
- Minimum Priority Queue.
- Maximum Priority Queue
- Operations of enqueue(insertion) and dequeue(deletion) are performed on the basis of the priority of the data.
- A Priority Queue can be implemented using various different data structures like
- Using Arrays
- Using Linked List
- Using Heap, etc
What is a Priority Queue in C++ Programming?
A priority queue is an abstract data type that operates similar to a normal queue, but with the following difference:
- In a normal queue, the first inserted element is the first to be removed (FIFO).
- In a priority queue, the element with the highest priority is removed first.
By default, C++ implements a max-heap priority queue, which means the largest element has the highest priority.
Syntax of Priority Queue in C++
#include <queue>
std::priority_queue<datatype> pq;
To create a min-heap:
std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>> minHeap;
Example: Priority Queue Code with Output and Explanation
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
priority_queue pq;
pq.push(30);
pq.push(10);
pq.push(20);
while (!pq.empty()) {
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
return 0;
}
Output :
30 20 10
Explanation:
- Elements are arranged in descending order (max-heap).
- pq.top() gives the largest element.
- Each time we pop, the next highest element appears on the top.
Operations on Priority Queue
Operation can be perform on the Priority Queue:
- Enqueue()
- Dequeue()
- Print()
- isEmpty()
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
1.Enqueue()
- When we have to insert an element in Queue we use Enqueue() operation.
- Enqueue() operation is similar to that of a insertion operation in a data structure
- The difference between a normal insertion and enqueue operation in a Priority Queue is that in Priority Queue, data is inserted depending upon the priority of the data.
2.Dequeue()
- When we have to remove an element from the Queue we use Dequeue() operation.
- Dequeue() operation similar to that of a deletion operation in a data structure.
- The difference between a normal deletion and dequeue operation in a Priority Queue is that in Priority Queue, data is deleted depending upon the priority of the data.
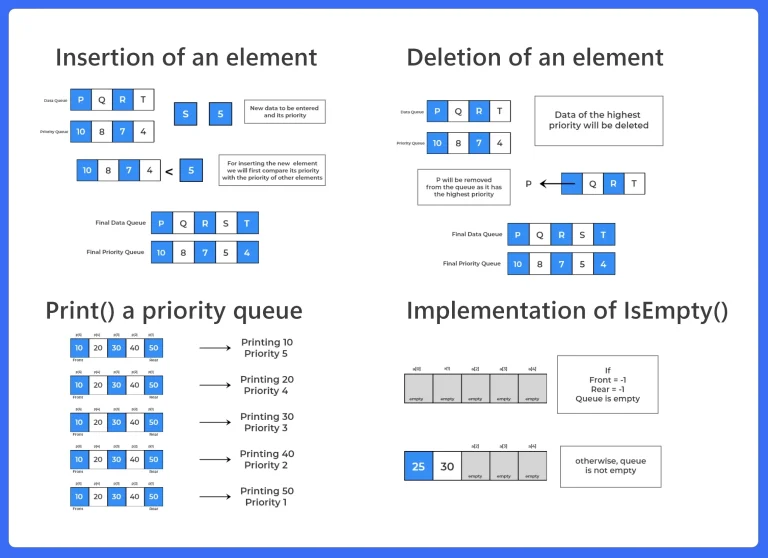
3.Print()
- Print() Is use to print or show the data and its priority of a Queue.
4.IsEmpty()
- isEmpty() function is use to check,Queue is empty or not.
Applications of Priority Queue
There is following applications of Priority Queue:
- Dijktra’s shortest path algorithm.
- Prim’s Algorithm
- Data Compression->Huffman Code
- Heap Sort
- Operating System: Local Balancing, Interrupt Handling.
Internal Working of Priority Queue (Binary Heap)
Internally, the priority_queue in C++ is implemented using a binary heap:
- Max Heap (default): The largest element is at the root.
- Min Heap: The smallest element is at the root (by using greater comparator).
A binary heap is a complete binary tree that follows the heap property:
- Max Heap: parent ≥ children
- Min Heap: parent ≤ children
Declaration and Initialization Examples – Priority Queue in C++
In C++, priority_queue is a part of the Standard Template Library (STL), and you can initialize it in different ways depending on your use case.
Let’s explore the three most commonly used ways:
1. Default Declaration (Max Heap)
By default, the priority_queue in C++ works as a Max Heap, where the largest element has the highest priority.
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
priority_queue maxHeap;
maxHeap.push(50);
maxHeap.push(10);
maxHeap.push(30);
while (!maxHeap.empty()) {
cout << maxHeap.top() << " ";
maxHeap.pop();
}
return 0;
}
Output:
50 30 10
Explanation:
- The largest element 50 is placed at the top.
- On each pop(), the next highest element is displayed.
- This is the default behavior, max heap.
2. Min Heap using greater<> Comparator
To convert the default max heap into a min heap, we need to pass three arguments to priority_queue:
priority_queue<datatype, vector<datatype>, greater<datatype>> minHeap;
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
priority_queue<int, vector, greater> minHeap;
minHeap.push(50);
minHeap.push(10);
minHeap.push(30);
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
cout << minHeap.top() << " ";
minHeap.pop();
}
return 0;
}
Output:
10 30 50
Explanation:
- The smallest element (10) is given highest priority.
- Min heap is useful in algorithms like Dijkstra’s shortest path, A algorithm*, etc
Basic Operations in Priority Queue – C++ STL
A priority queue allows us to manage a collection of elements where the highest priority element is always on top (by default in C++, this means the largest number).
Let’s go through each basic operation one by one:
1. Inserting Elements – push()
- This function is used to insert a new element into the priority queue. It automatically places the element in the correct position based on priority (max or min heap).
Syntax:
pq.push(value);
Code:
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(10);
pq.push(50);
pq.push(30);
Result: The queue becomes: 50 10 30 (internally stored as a max-heap, but not visible to us).
2. Accessing Top Element – top()
This returns the element with the highest priority, i.e., the element at the top of the heap.
Syntax:
pq.top();
Code:
cout << pq.top(); // Output: 50
Explanation: Since it’s a max-heap by default, the largest value (50) is at the top.
3. Deleting the Top Element – pop()
Removes the element with the highest priority (top of the heap).
Syntax:
pq.pop();
Code:
pq.pop(); // Removes 50
cout << pq.top(); // Output: 30
4. Pseudo Traversal (No Iterators)
priority_queue does not allow direct traversal using iterators, so to “see” the contents, you have to copy and pop.
Code:
priority_queue<int> temp = pq;
while (!temp.empty()) {
cout << temp.top() << " ";
temp.pop();
}
5. Changing Priority Order (Min Heap)
By default, C++ creates a max heap. To create a min heap, use:
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> minHeap;
Now the smallest element will be given the highest priority.
Time Complexity of Each Operation
| Operation | Time Complexity |
| push() | O(log n) |
| pop() | O(log n) |
| top() | O(1) |
| size() | O(1) |
Priority Queue vs Queue
1. Order of Processing:
- Queue follows First-In-First-Out (FIFO) — the first element added is the first to be removed.
- Priority Queue serves elements based on priority, not insertion order.
2. Element Access:
- Queue removes elements in the exact order they were inserted.
- Priority Queue always removes the element with the highest (or lowest) priority.
3. Underlying Structure:
- Queue is usually implemented using arrays or linked lists.
- Priority Queue is typically implemented using a binary heap.
4. Use Cases:
- Queue is used in scenarios like task scheduling, buffer handling, or order queues.
- Priority Queue is used in pathfinding algorithms (like Dijkstra’s), CPU scheduling, or real-time systems where tasks have different levels of importance.
5. C++ STL Behavior:
- In C++ STL, queue maintains FIFO.
- priority_queue uses a max-heap by default, but can be turned into a min-heap using a comparator.
6. Insertion and Removal Time Complexity:
- Queue operations like enqueue and dequeue take O(1) time.
- Priority Queue operations like push and pop take O(log n) time due to heap adjustments.
7. Sorting:
- Queue does not sort elements.
- Priority Queue maintains a sorted order internally based on priority.
Conclusion
The priority_queue in C++ STL is a powerful container used to solve problems where elements must be processed based on priority. It is widely used in algorithms like Dijkstra’s, A*, and task scheduling problems.
Using binary heaps under the hood, it provides efficient O(log n) operations for insertions and deletions.
FAQs - Priority Queue in C++ Programming
FAQs - Priority Queue in C++ Programming
Yes, by using:
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> minHeap;
Yes, using a custom comparator with a struct or lambda function.
Internally, it maintains the heap property, not fully sorted. Only the top (max/min) element is guaranteed.
No direct iteration. You can simulate traversal by copying and popping.
emplace() constructs in-place and is slightly faster than push().
Use it when order of processing depends on priority, like in:
- CPU Scheduling
- Pathfinding (Dijkstra’s)
- Event Handling Systems
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment