Deletion in a Queue in Java
Deletion in a Queue in Java
Deletion in a Queue in Java refers to removing an element from a queue data structure. Since queues follow the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle, the element that was inserted first will be removed first. This deletion operation is also known as dequeue.
In this article, we will cover all major ways to delete an element from a queue in Java, including clear algorithms, working example programs, example input/output, time and space complexity, and common edge cases.

What is Deletion in a Queue?
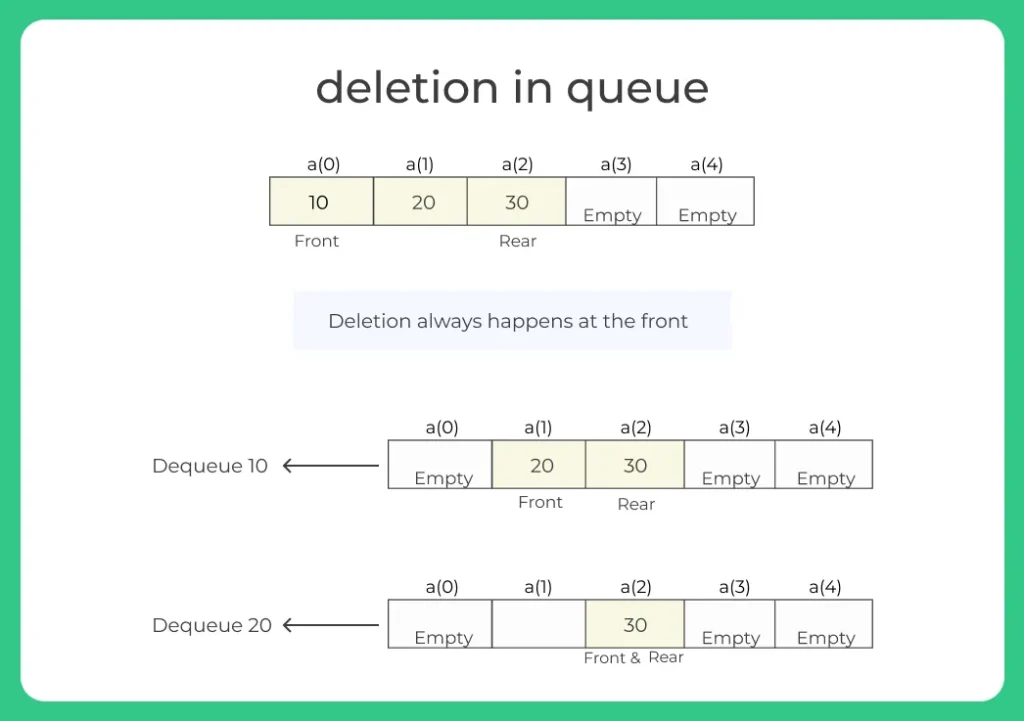
Queue is an abstract data type where:
- Insertion happens at the rear (enqueue)
- Deletion happens at the front (dequeue)
Note: Dequeue operation removes the front element and advances the front pointer. If the queue is empty, deletion can’t proceed, this is known as underflow.
Example:
1. Before deletion:
10 20 30 40
2. After one deletion:
20 30 40
1. Process scheduling (OS)
2. Task queues
3. BFS graph traversal
4. Print job management
5. Rate limiting systems
Methods of Deletion in a Queue in Java
Here we will study about 4 methods for Deletion in a Queue in Java:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods of Deletion in a Queue in Java Code
Method 1: Linear Queue Using Array
Linear queue uses a fixed size array. Deletions always happen at the front.
- After a deletion, the front pointer moves right.
- If the front pointer moves past the rear pointer, the queue is empty.
Algorithm:
- If front == -1 or front > rear
- → Underflow/Queue empty
- Otherwise:
- front = front + 1
Java Code for Deletion in a Queue
class LinearQueueDeletion {
int[] queue;
int front, rear, capacity;
LinearQueueDeletion(int size) {
capacity = size;
queue = new int[capacity];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
void enqueue(int value) {
if (rear == capacity - 1) {
System.out.println("Overflow");
return;
}
if (front == -1) front = 0;
queue[++rear] = value;
}
void dequeue() {
if (front == -1 || front > rear) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty (Underflow)");
return;
}
System.out.println(queue[front] + " removed");
front++;
}
void display() {
if (front == -1 || front > rear) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i <= rear; i++)
System.out.print(queue[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinearQueueDeletion q = new LinearQueueDeletion(5);
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
q.display();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.display();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue(); // underflow
}
}
Example Input & Output:
Queue elements: 10 20 30 10 removed 20 removed Queue elements: 30 30 removed Queue is empty (Underflow)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method of Deletion in a Queue in Java
Method 2: Circular Queue Using Array
Circular queue allows reuse of array space by wrapping the front and rear pointers using modulo. Deletions are still from the front, but the front index wraps around.
Algorithm:
- If size == 0
- → Underflow
- value = queue[front]
- front = (front + 1) % capacity
- size = size – 1
- If size == 0
- front = rear = -1
Java Code
class CircularQueueDeletion {
int[] queue;
int front, rear, size, capacity;
CircularQueueDeletion(int cap) {
capacity = cap;
queue = new int[capacity];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
size = 0;
}
void enqueue(int value) {
if (size == capacity) {
System.out.println("Overflow");
return;
}
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
queue[rear] = value;
size++;
if (front == -1) front = rear;
}
void dequeue() {
if (size == 0) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty (Underflow)");
return;
}
System.out.println(queue[front] + " removed");
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
size--;
if (size == 0) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
}
void display() {
if (size == 0) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return;
}
int count = size, idx = front;
while (count-- > 0) {
System.out.print(queue[idx] + " ");
idx = (idx + 1) % capacity;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularQueueDeletion q = new CircularQueueDeletion(4);
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
q.display();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.display();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue(); // underflow
}
}
Example Input & Output:
Queue: 10 20 30 10 removed 20 removed Queue: 30 30 removed Queue is empty (Underflow)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method 3: Queue Using Linked List
Linked list queue uses nodes with pointers. The deletion (dequeue) removes the front node and moves the front pointer to the next node.
Algorithm:
- If front == null
- → Queue is empty
- value = front.data
- front = front.next
- If front == null
- rear = null
- Return value
Java Code
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedListQueueDeletion {
Node front, rear;
void enqueue(int value) {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (rear == null) {
front = rear = newNode;
} else {
rear.next = newNode;
rear = newNode;
}
}
void dequeue() {
if (front == null) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty (Underflow)");
return;
}
System.out.println(front.data + " removed");
front = front.next;
if (front == null) rear = null;
}
void display() {
if (front == null) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = front;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListQueueDeletion q = new LinkedListQueueDeletion();
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
q.display();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.display();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue(); // underflow
}
}
Example Input & Output:
10 20 30 10 removed 20 removed 30 30 removed Queue is empty (Underflow)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method 4: Using Java Built In Queue Interface
Java’s Queue interface provides the remove() or poll() methods to delete elements from the front. remove() throws an exception if the queue is empty; poll() returns null.
Algorithm:
- Create Queue object
- Call queue.remove() or queue.poll()
Java Code
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class BuiltInQueueDeletion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(10);
queue.offer(20);
queue.offer(30);
System.out.println("Queue before deletion: " + queue);
int removed1 = queue.remove(); // head removed
System.out.println("Removed: " + removed1);
int removed2 = queue.poll(); // also removes
System.out.println("Removed: " + removed2);
System.out.println("Queue after deletion: " + queue);
}
}
Example Input & Output:
Queue before deletion: [10, 20, 30] Removed: 10 Removed: 20 Queue after deletion: [30]
Space Complexity: O(n)
Comparison of All Methods
| Method | Structure | Overflow | Time (Per Dequeue) | Space |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Queue (Array) | Fixed Array | Yes | O(1) | O(n) |
| Circular Queue (Array) | Fixed Circular | Yes | O(1) | O(n) |
| Linked List Queue | Nodes | No | O(1) | O(n) |
| Built In Queue Interface | Collection | No | O(1) | O(n) |
Before deleting, always check:
- Queue is not empty (front beyond rear or size 0)
- For built in queues, use poll() to avoid exceptions on empty queues
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer:
Deletion in a queue in Java is the process of removing the element from the front of the queue, also called dequeue.
Answer:
Deletion takes O(1) time in all standard queue implementations.
Answer:
Underflow is when you try to delete from an empty queue.
Answer:
Use queue.remove() or queue.poll() to remove the head element.
Answer:
For real applications, the built in Queue interface is best; for learning internals, linked list or circular queue is preferred.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment