Insertion in a Queue in Java
Insertion in a Queue in Java
Insertion in a Queue in Java is one of the most fundamental operations in Data Structures. Queue follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle, which means the element inserted first is removed first.
Understanding how insertion works is important for learning stacks and queues, preparing for technical interviews, and building real world systems such as task schedulers, printers, and network buffers.
Here you will learn all major ways to perform queue insertion in Java, including algorithms, implementations, time and space complexity, and practical interview tips.
What is Insertion in a Queue?
Queue is a linear data structure in which:
- Elements are added from the rear
- Elements are removed from the front
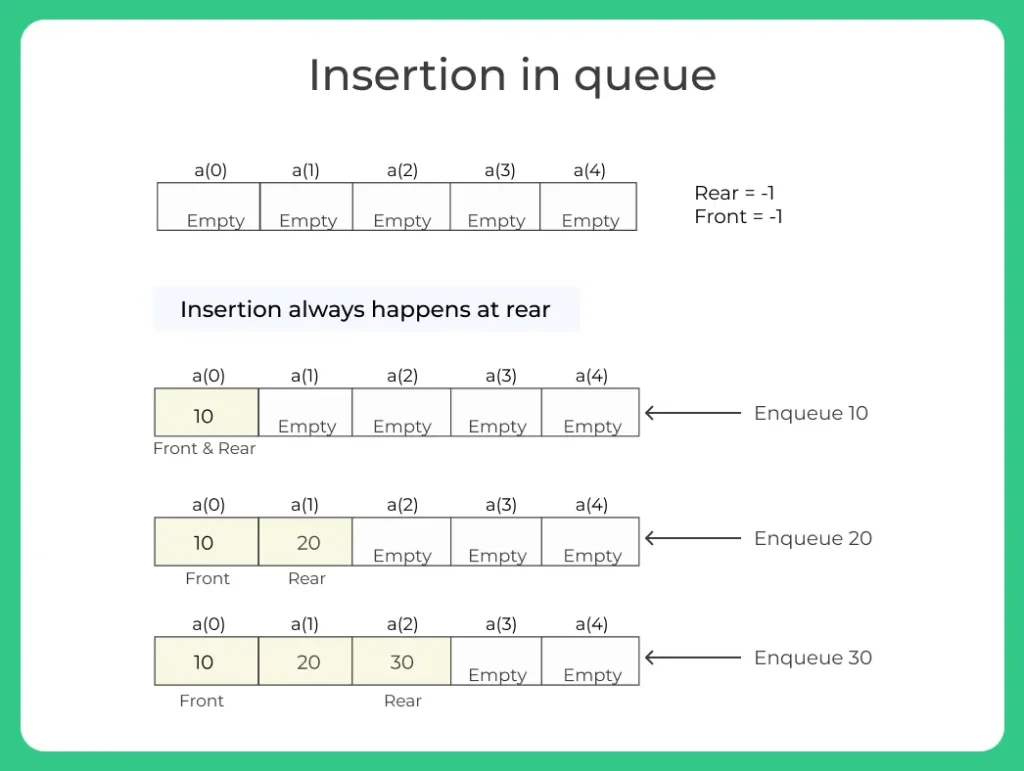
This operation of adding elements is called Enqueue.
Example:
1. Before insertion:
10 20 30
2. After inserting 40:
10 20 30 40
Methods of Insertion in a Queue in Java
Here we will study about 4 methods for Insertion in a Queue in Java:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods of Insertion in a Queue in Java Code
Method 1: Linear Queue Using Array
Algorithm:
- If rear == capacity – 1
- Print “Overflow” and return
- If front == -1
- front = 0
- rear = rear + 1
- queue[rear] = value
Java Code for Insertion in a Queue
class LinearQueue {
int[] queue;
int front, rear, capacity;
LinearQueue(int size) {
capacity = size;
queue = new int[capacity];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
void enqueue(int value) {
if (rear == capacity - 1) {
System.out.println("Queue Overflow");
return;
}
if (front == -1) {
front = 0;
}
queue[++rear] = value;
System.out.println(value + " inserted");
}
void display() {
if (front == -1) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i <= rear; i++) {
System.out.print(queue[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinearQueue q = new LinearQueue(3);
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
q.enqueue(40);
q.display();
}
}
Input
10 20 30 40
Output
10 inserted 20 inserted 30 inserted Queue Overflow 10 20 30
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method of Insertion in a Queue in Java
Method 2: Circular Queue Using Array
Algorithm:
- If size == capacity
- Overflow
- rear = (rear + 1) % capacity
- queue[rear] = value
- size = size + 1
- If front == -1
- front = rear
Java Code
class CircularQueue {
int[] queue;
int front, rear, size, capacity;
CircularQueue(int cap) {
capacity = cap;
queue = new int[capacity];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
size = 0;
}
void enqueue(int value) {
if (size == capacity) {
System.out.println("Queue Overflow");
return;
}
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
queue[rear] = value;
size++;
if (front == -1) {
front = rear;
}
System.out.println(value + " inserted");
}
void display() {
if (size == 0) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return;
}
int i = front;
int count = size;
while (count-- > 0) {
System.out.print(queue[i] + " ");
i = (i + 1) % capacity;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularQueue q = new CircularQueue(3);
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
q.enqueue(40);
q.display();
}
}
Input
10 20 30 40
Output
10 inserted 20 inserted 30 inserted Queue Overflow 10 20 30
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method 3: Queue Using Linked List
Algorithm:
- Create new node
- If rear == null
- front = rear = newNode
- Else:
- rear.next = newNode
- rear = newNode
Java Code
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedListQueue {
Node front, rear;
void enqueue(int value) {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (rear == null) {
front = rear = newNode;
} else {
rear.next = newNode;
rear = newNode;
}
System.out.println(value + " inserted");
}
void display() {
if (front == null) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = front;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListQueue q = new LinkedListQueue();
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
q.display();
}
}
Input
10 20 30
Output
10 inserted 20 inserted 30 inserted 10 20 30
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method 4: Using Java Queue Interface (Built-in)
Algorithm:
- Create Queue object
- Call offer(value)
Java Code
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class BuiltInQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(10);
queue.offer(20);
queue.offer(30);
System.out.println("Queue Elements:");
for (int x : queue) {
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
}
Input
10 20 30
Output
Queue Elements: 10 20 30
Space Complexity: O(n)
Comparison between Methods for Insertion in a Queue in Java Programming:
| Method | Structure | Overflow | Time | Space | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | Array | Yes | O(1) | O(n) | Learning |
| Circular | Array | Yes | O(1) | O(n) | Efficient |
| Linked List | Nodes | No | O(1) | O(n) | Dynamic |
| Built-in | Collection | No | O(1) | O(n) | Real Apps |
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer:
Insertion means adding a new element at the rear using enqueue operation.
Answer:
Built in Queue for projects, Circular Queue for learning.
Answer:
O(1) for all standard implementations.
Answer:
It saves memory by reusing empty space.
Answer:
Use array for fixed size, linked list for dynamic size.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java






