Circular Queue in C
Circular Queue in C Programming
On this page we will discuss about Circular queue in C . Circular queues are made to overcome the problems faced by normal queues of size reduction whenever Dequeueing any element.
Circular Queues how they work?
Circular queues have the same terminologies and function is queues. The core of the code lies in using remainder operator with size in most operations as given in the code below.
Also enqueue, dequeue, front, rear etc work as queues itself, if you’re unaware of these, we recommend check this page first.
Important to note why Circular Queues?
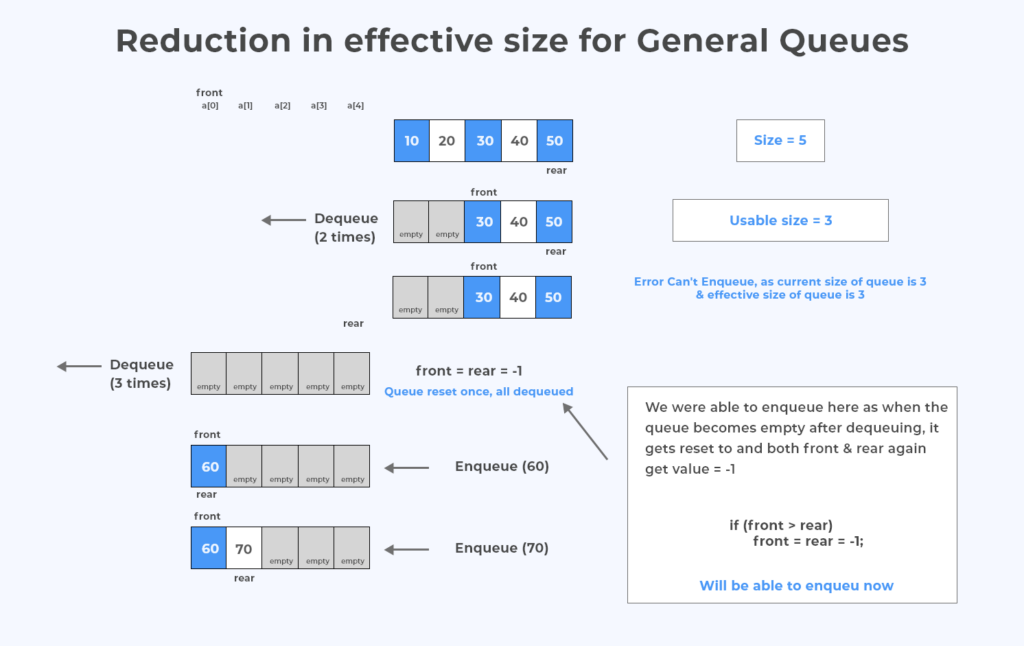
Once the queue becomes full, we can not insert more elements. Even though we dequeue a few of the elements. Because the following code –if (rear == SIZE-1)
printf("Overflow condition");
- After each enqueue, rear value is incremented & once queue is full rear value becomes equal to size – 1
void Enqueue()
{
//Other part of code
rear = rear + 1;
//other part of code
}
- So no more elements can be entered & even if dequeue happens, it only changes the front value & not rear value.
- Thus, with dequeues effective size of queue is reduced

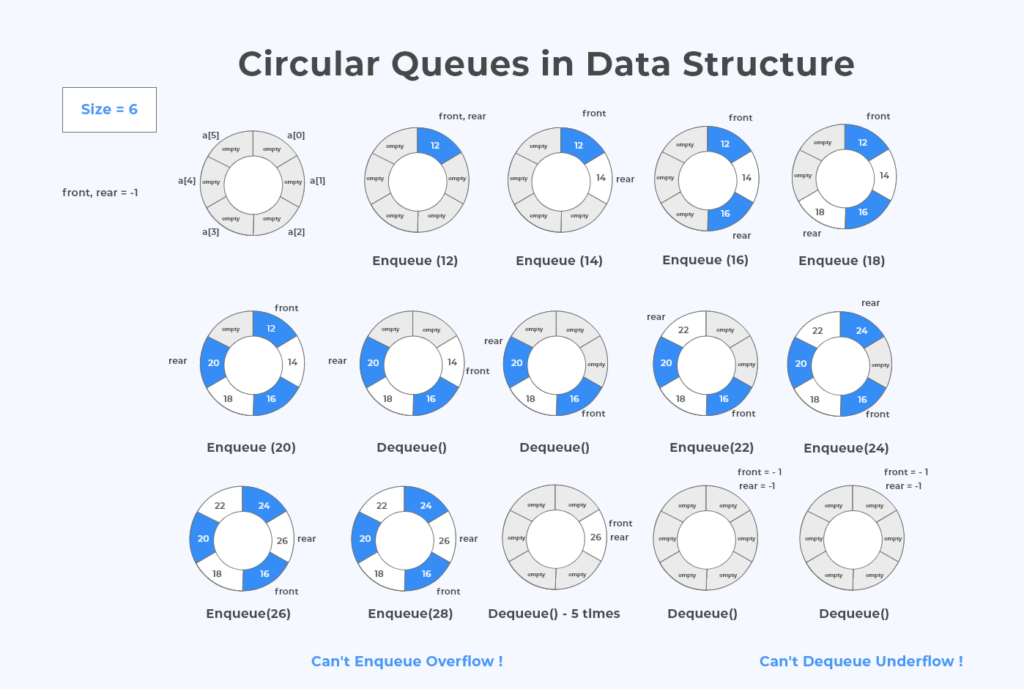
Circular Queues in C Program
Run
Output –
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 6
struct Queue
{
int front, rear, currSize;
unsigned maxSize;
int *a;
};
struct Queue *createQueue (unsigned maxSize)
{
struct Queue *queue = (struct Queue *) malloc (sizeof (struct Queue));
queue->maxSize = maxSize;
queue->front = queue->rear = -1;
queue->a = (int *) malloc (queue->maxSize * sizeof (int));
return queue;
}
// Checking for Overflow condition
int isFull (struct Queue *queue)
{
if ((queue->front == queue->rear + 1) ||
(queue->front == 0 && queue->rear == queue->maxSize - 1))
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Checking for Underflow condition
int isEmpty (struct Queue *queue)
{
if (queue->front == -1)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Function to do enqueue
void enqueue (struct Queue *queue, int value)
{
if (isFull (queue))
printf ("Can't add the queue is full \n");
else
{
if (queue->front == -1)
queue->front = 0;
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % queue->maxSize;
queue->a[queue->rear] = value;
printf ("%d was added\n", value);
}
}
// Function to do dequeue
int dequeue (struct Queue *queue)
{
int item;
if (isEmpty (queue))
{
printf ("Can't add the queue is empty \n");
return (-1);
}
else
{
item = queue->a[queue->front];
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
queue->front = queue->rear = -1;
}
else
{
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % queue->maxSize;
}
printf ("%d dequeued\n", item);
}
}
// Function to print the queue
void print (struct Queue *queue)
{
int i;
if (isEmpty (queue))
printf ("Empty Queue\n");
else
{
printf ("\nThe items in the queue are : \n");
for (i = queue->front; i != queue->rear; i = (i + 1) % queue->maxSize)
{
printf ("%d ", queue->a[i]);
}
printf ("%d \n\n", queue->a[i]);
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Queue *queue = createQueue (6);
dequeue (queue); //Underflow condition
enqueue (queue, 12);
enqueue (queue, 14);
enqueue (queue, 16);
enqueue (queue, 18);
enqueue (queue, 20);
print (queue);
dequeue (queue);
dequeue (queue);
print (queue);
enqueue (queue, 22);
enqueue (queue, 24);
enqueue (queue, 26);
enqueue (queue, 28); //Overflow condition
print (queue);
return 0;
}
Can't add the queue is empty 12 was added 14 was added 16 was added 18 was added 20 was added The items in the queue are : 12 14 16 18 20 12 dequeued 14 dequeued The items in the queue are : 16 18 20 22 was added 24 was added 26 was added Can't add the queue is full The items in the queue are : 16 18 20 22 24 26
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment