Insertion in Doubly Linked List in C Program
Doubly Linked List C Program
On this article we will discuss about Insertion in Doubly Linked List in C language .We know that in Singly list node has only one pointer but here doubly linked list, each node contains two-pointers which is to help to find previous and next node.
| Insertion Time Complexity (AVG) | Θ(1) |
| Insertion Time Complexity (Worst) | O(1) |
| Space Complexity | O(1) |
Insertion in a Doubly Linked-list
For each insertion operation, we need to consider the three cases. These three cases also need to be considered when removing data from the doubly linked list.
- Insertion at the beginning
- Insertion after nth Node
- Insertion at last
Doubly linked List Definition
struct Node
{
int Data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
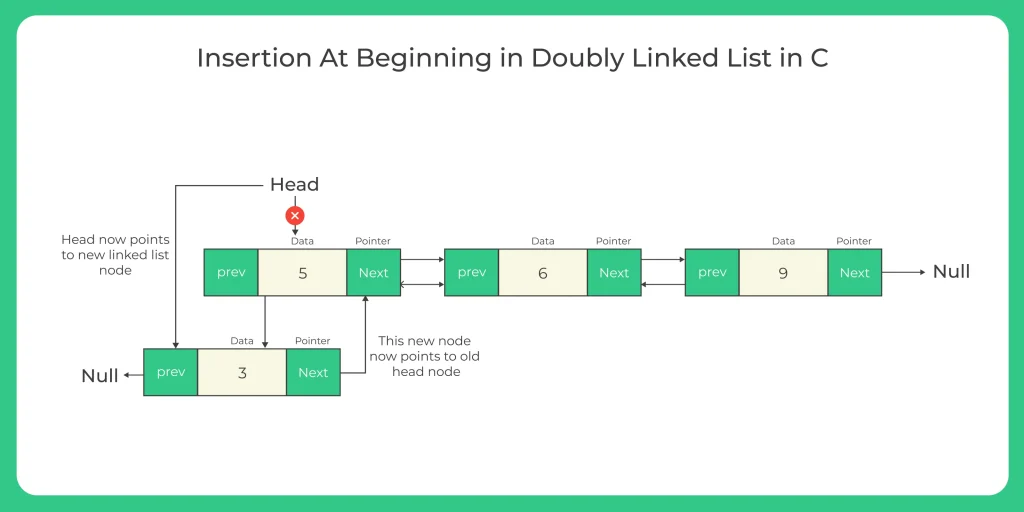
Insertion at Beginning
In the doubly linked list, we would use the following steps to insert a new node at the beginning of the doubly linked list.
- Create a new node
- Assign its data value
- Assign newly created node’s next ptr to current head reference. So, it points to the previous start node of the linked list address
- Change the head reference to the new node’s address.
- Change the next node’s previous pointer to new node’s address (head reference)
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
// changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
Code (Insertion at the beginning)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
//If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// *head->prev = newNode; would not work it has (*head) must be used
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
// function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("List in Forward direction: ");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nList in backward direction: ");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
/*Need & i.e. address as we
need to change head address only needs to traverse
and access items temporarily
*/
insertStart (&head, 12);
insertStart (&head, 16);
insertStart (&head, 20);
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not
need to change head address
*/
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
List in Forward direction: 20 16 12 List in backward direction: 12 16 20
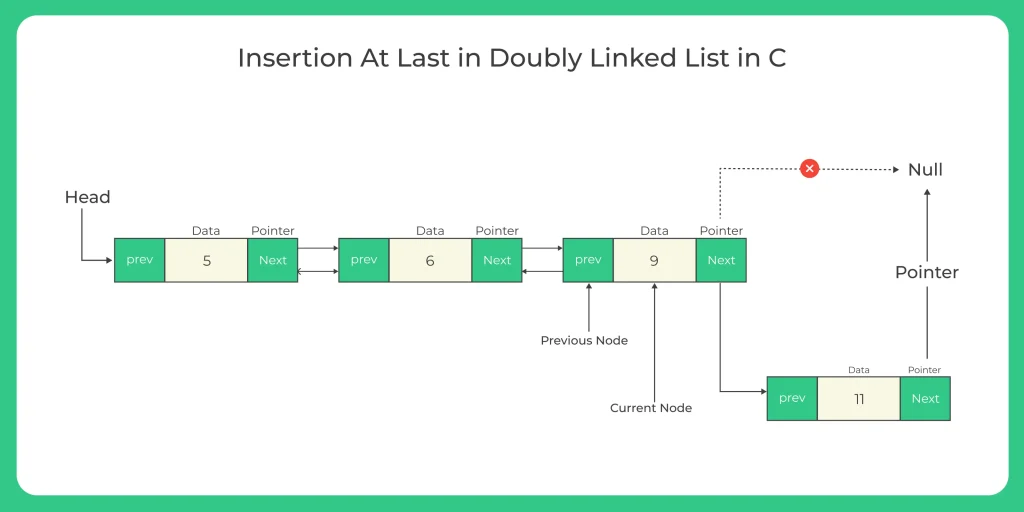
Insertion at last
In insertion, at the last node, we would use the following steps to insert a new Node at the last of the doubly linked list.
- Create a new node
- Assign its data value
- Assign its next node to NULL as this will be the last(tail) node
- Check if the list is empty
- Change the head node to this node
- If it is empty then just assign the previous node as NULL and return
- If not then traverse till the last node
- Assign the last node’s next pointer to this new node
- Assing this new node’s previous to the last node in the list
- Now, the new node has become the last node.
Code (Insertion at Last)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = temp;
}
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
//If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// *head->prev = newNode; would not work it has (*head) must be used
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
// function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("List in Forward direction: ");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nList in backward direction: ");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
/*Need & i.e. address as we
need to change head address only needs to traverse
and access items temporarily
*/
insertStart (&head, 12);
insertStart (&head, 16);
insertStart (&head, 20);
insertLast (&head, 10);
insertLast (&head, 14);
insertLast (&head, 18);
insertLast (&head, 11);
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not
need to change head address
*/
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
List in Forward direction: 20 16 12 10 14 18 11 List in backward direction: 11 18 14 10 12 16 20
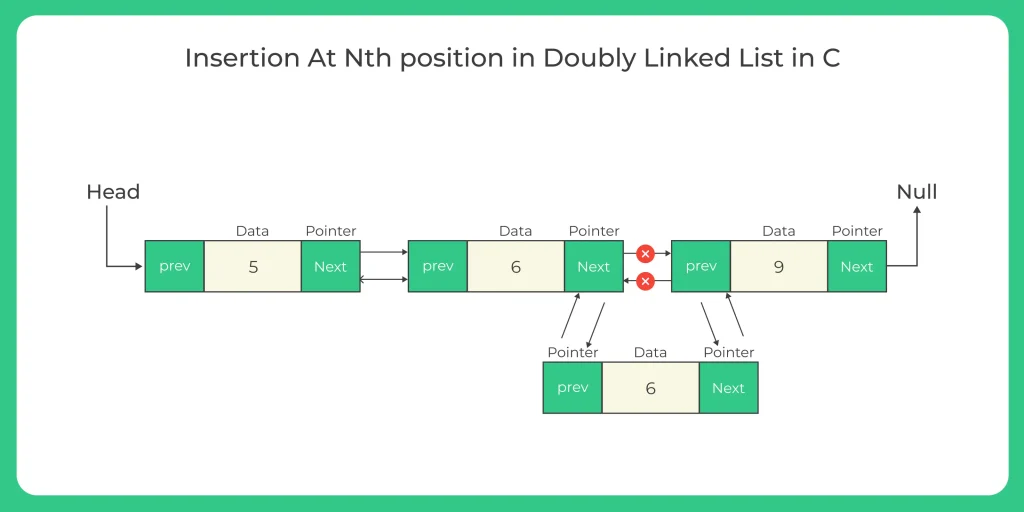
Insertion at After nth Node
- Calculate the size of the node
- If the position you want to enter is less than 1
- Invalid position But, if 0 then use insertAtStart method
- If the position you want to enter is greater than size then
- Invalid position, but if the position is equal to size then use insertLast method
- else create a temp node and assign it the address of the head
- Create a new node and assign it the data value
- Iterate to the position you want to enter after in the linked list
- Assign this new node’s next and previous nodes
- Assign previous node’s next to this new node
- Assign next node’s previous to this new node
Insertion after a position
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data);
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data);
// helper function for insertion after position
int calcSize (struct Node *node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertPosition (int pos, int data, struct Node **head)
{
int size = calcSize (*head);
//If pos is 0 then should use insertStart method
//If pos is less than or equal to 0 then can't enter at all
//If size is lesser than pos then bufferbound issue
if (pos < 0 || size < pos)
{
printf ("Can't insert, %d is not a valid position\n", pos);
return;
}
// Insert after 0th position would mean insert at start
if (pos == 0)
insertStart (head, data);
// insert after size'th position would mean insert at the last
else if (pos == size)
insertLast (head, data);
else
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
while (--pos)
temp = temp->next; //temp2 = 10 as 12->next is 10
struct Node *temp2 = temp->next; //(25)->next = 10 as 12->next is 10
newNode->next = temp->next; //(25)->prev = 12
newNode->prev = temp; // (12)->next = 25
temp->next = newNode; // (10)->prev = 25
temp2->prev = newNode; //new node added in b/w 12 and 10
}
}
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = temp;
}
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL; //If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// *head->prev = newNode; would not work it has (*head) must be used
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
// function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("List in Forward direction: ");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nList in backward direction: ");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
/*Need & i.e. address as we need to change head address */
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 12);
insertStart (&head, 16);
insertStart (&head, 20);
insertLast (&head, 10);
insertLast (&head, 14);
insertLast (&head, 18);
insertLast (&head, 11);
//Inserts after 3rd position
printf ("linked before insertion at specific position\n");
display (head);
printf ("\n\nlinked after insertion at specific position\n");
insertPosition (3, 25, &head);
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not need to change head address */
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
linked before insertion at specific position List in Forward direction: 20 16 12 10 14 18 11 List in backward direction: 11 18 14 10 12 16 20 linked after insertion at specific position List in Forward direction: 20 16 12 25 10 14 18 11 List in backward direction: 11 18 14 10 25 12 16 20

Question 1. What does the following function do for a given Linked List with first node as head?
void myFunction(struct node* head)
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
myFunction(head->next);
printf("%d ", head->data);
}- Prints all nodes of linked lists
- Prints alternate nodes of Linked List
- Prints all nodes of linked lists
- Prints all nodes of linked list in reverse order
(Samsung/Adobe- CoCubes Test)
myFunction() prints the given Linked List in reverse manner. For Linked List 1->2->3->4->5, myFunction() prints 5->4->3->2->1
Ans. Option D




Login/Signup to comment