Application of Priority Queue
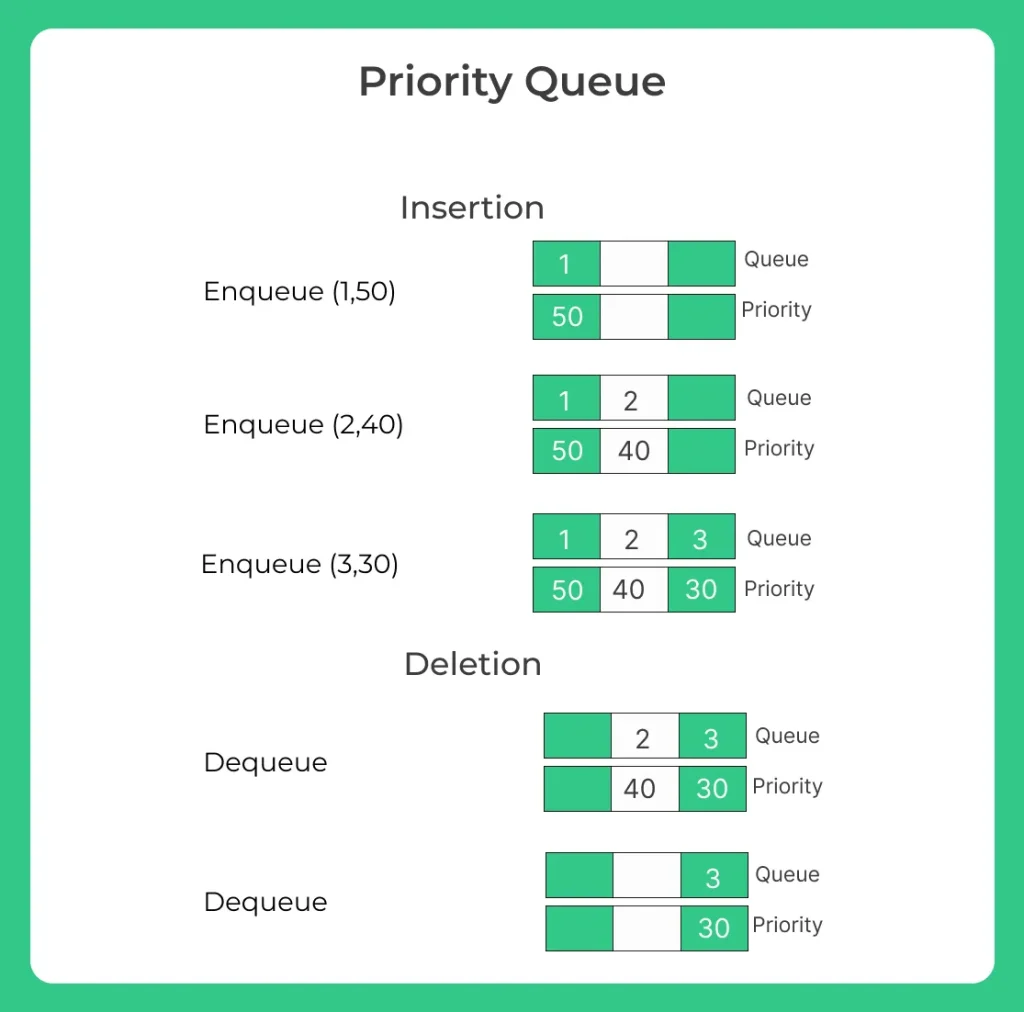
Priority Queue
Normal queue follows a First In First Out (FIFO) order to insert and remove an element. In priority queue we work with the data depending on some priority .For example if we want to delete an element from the queue, the data with the highest priority will be deleted first, in similar way if we are inserting data in the queue, it will be arranged in the queue depending upon its priority. On this page we will discuss about application of Priority Queue.
Priority Queue
Introduction
A priority is basically an extension of the general queue. A major difference is that dequeuing happens based on the priority of each item in the queue.
We have two types of priority queue –
- Max Priority Queue – A larger priority value means higher priority
- Min Priority Queue – A smaller priority value means lower priority
By default, if nothing is mentioned it means that the Priority queue is a min priority queue.
Operations
- enqueue(): To insert a new item at the end of the queue.
- dequeue(): To remove the element with the highest priority from the queue.
- peek()/top(): To get the highest priority element in the queue without dequeuing the item.
Application of Priority Queue
Priority queues have a wide range of applications in computer science, including:
- Operating Systems: In operating systems, priority queues are used to manage processes and threads. The operating system assigns a priority level to each process or thread, and the priority queue ensures that higher priority tasks are executed before lower priority tasks.
- Graph Algorithms: Many graph algorithms, such as Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm and Prim’s minimum spanning tree algorithm, use priority queues to maintain a set of candidate vertices or edges with the minimum distance or weight.
- Data Compression: Huffman coding, a lossless data compression algorithm, uses a priority queue to build a binary tree representing the optimal prefix code for a set of characters based on their frequencies.
- Event-driven Simulation: In event-driven simulation, a priority queue is used to schedule events based on their scheduled time, with the earliest event being processed first.
- Networking: Priority queues are used in Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms in networking to ensure that high-priority traffic, such as voice or video, is given preferential treatment over lower-priority traffic, such as email or file transfers.
- Heapsort: Heapsort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a heap data structure, which is implemented using a priority queue.
Overall, priority queues have a variety of applications in computer science and are a fundamental data structure used in many algorithms and systems.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java





