JAVA Program for Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List
Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List in Java is one of the core operations in linked list manipulation. A doubly linked list allows movement in both directions through prev and next pointers, making deletion at the end straightforward and efficient.
This operation is commonly used in applications such as undo redo systems, browser navigation, media playlists, and memory management modules where the last element must be removed dynamically.

Java Program for Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List
What is Deletion from End in a Doubly Linked List?
A doubly linked list node contains:
- prev pointer (link to previous node)
- next pointer (link to next node)
Deletion from end means removing the last node and updating the second last node to become the new end of the list.
Example:
Before deletion:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
After deleting the last node:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30
Node 40 is removed, and 30 becomes the new tail node.
Understanding Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List using Java helps students and interview candidates learn:
- How to adjust bidirectional node links
- How to correctly detach the tail node
- Difference between singly and doubly linked list operations
- Handling edge cases (empty list, one-node list)
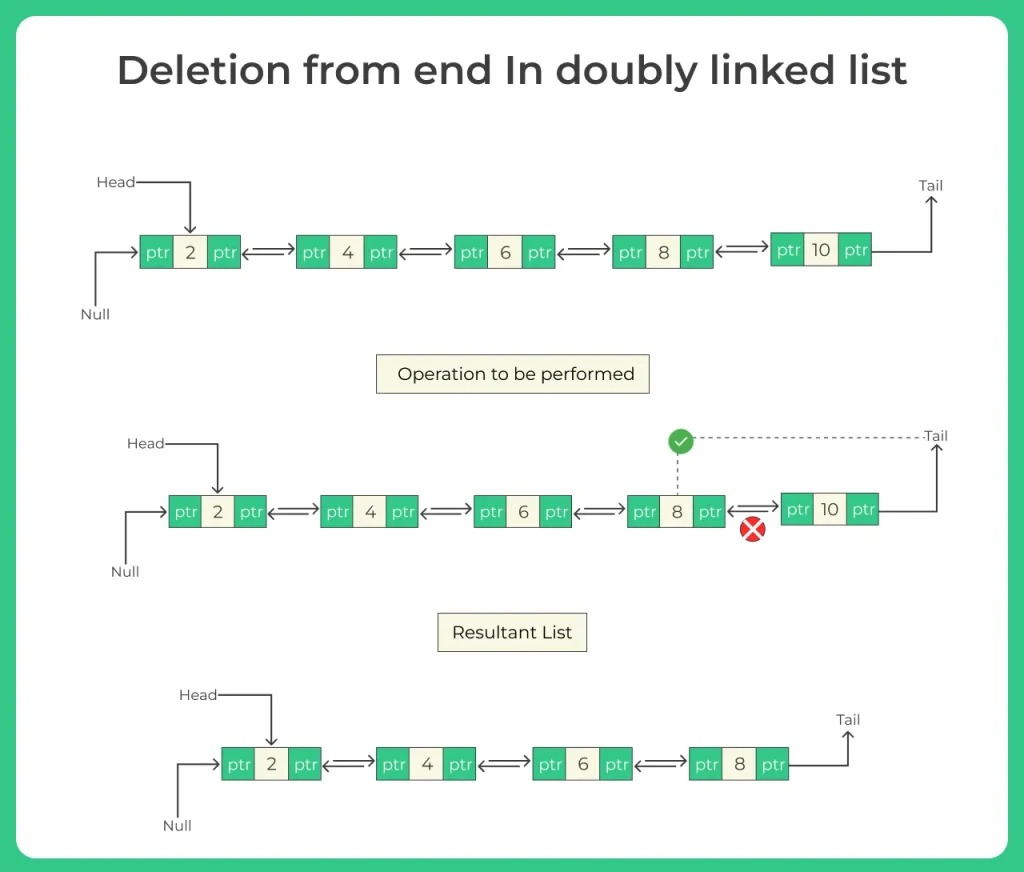
To delete the last node in a doubly linked list:
- If the list is empty → nothing to delete
- If there is only one node:
- Delete it → list becomes empty
- Otherwise:
Traverse to the last node
Update the previous node’s next pointer to null
Set last node’s prev pointer to null (disconnect fully)
Note: Java’s garbage collector clears the removed node automatically.
Methods for Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Basically we can perform Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java:
Each method will have Step by step algorithm, Java code, Time and space complexity.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method for Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 1: Simple Traversal to Last Node
Algorithm:
- If head == null, return null (empty list).
- If head.next == null, return null (only one node).
- Create pointer temp = head.
- Traverse until temp.next == null (last node).
- Set temp.prev.next = null.
- Disconnect last node by setting temp.prev = null.
- Return head.
Java Code:
class DeleteEndDLL {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev, next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static Node deleteFromEnd(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node temp = head;
// Move to last node
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.prev.next = null;
temp.prev = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node t = head;
while (t != null) {
System.out.print(t.data + " ");
t = t.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
Node second = new Node(15);
Node third = new Node(25);
head.next = second;
second.prev = head;
second.next = third;
third.prev = second;
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteFromEnd(head);
System.out.println("After deleting from end:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
5 ⇆ 15 ⇆ 25
Output:
5 ⇆ 15
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method for Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 2: Using a Doubly Linked List Class
Algorithm:
- If list empty → do nothing
- If list has 1 node → head becomes null
- Traverse to tail.
- Remove tail by linking:
- tail.prev.next = null
- Clear tail’s prev.
Java Code:
class DoublyLinkedList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev, next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node head;
// Insert at end (helper)
public void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = temp;
}
public void deleteFromEnd() {
if (head == null) return;
if (head.next == null) {
head = null;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.prev.next = null;
temp.prev = null;
}
public void printList() {
Node t = head;
while (t != null) {
System.out.print(t.data + " ");
t = t.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
list.insert(11);
list.insert(22);
list.insert(33);
list.insert(44);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
list.printList();
list.deleteFromEnd();
System.out.println("After deleting last node:");
list.printList();
}
}
Input:
5 ⇆ 15 ⇆ 25
Output:
5 ⇆ 15
Space Complexity: O(1)
Conclusion:
Deletion from the end of a doubly linked list highlights how bidirectional linking simplifies list manipulation.
- While traversal to the final node takes linear time, the deletion itself is completed with constant time pointer adjustments.
- Doubly linked structures allow safe removal without losing access to previous nodes, making them ideal for dynamic systems requiring flexible insertions and deletions.
Learning Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List in Java builds a solid understanding of pointer operations essential for advanced linked list algorithms.
FAQ's for Deletion from End of a Doubly Linked List
Answer:
It is the operation of removing the last node and updating the second-last node’s next pointer to null.
Answer:
The time complexity is O(n) because traversal is needed to reach the last node.
Answer:
Traverse to the final node, update its previous node’s next link, and disconnect the last node.
Answer:
If empty, nothing is deleted. If one node exists, deletion makes the list empty.
Answer:
Because it maintains both backward (prev) and forward (next) links, making pointer updates clear and reliable.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment