Java Program for Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List
Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
In this article, we will understand Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java with clear theory, step by step logic, and complete Java code.
Deleting a node from a specific position is one of the core operations in linked list manipulation. Doubly linked lists make this deletion easier because each node has links in both directions, allowing smooth pointer adjustment.

Java Program for Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List
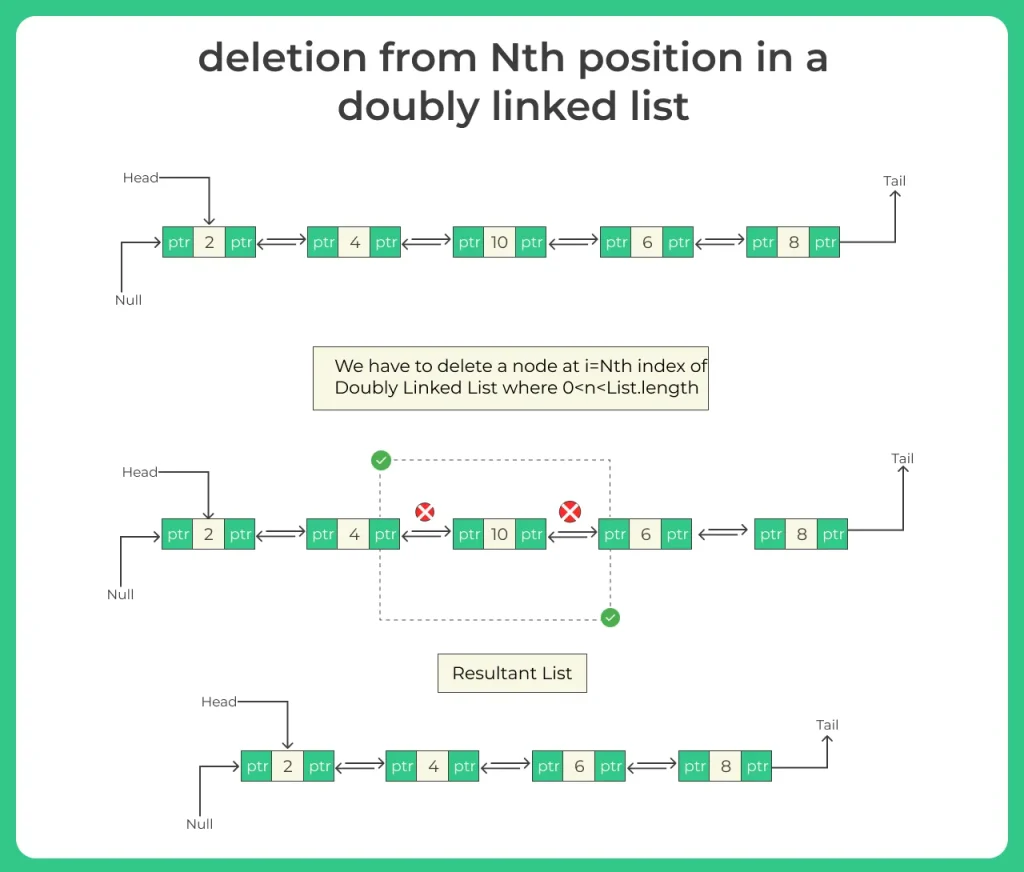
What is Deletion from Nth Position?
A doubly linked list contains nodes with:
- data
- prev pointer (to the previous node)
- next pointer (to the next node)
Deletion from the Nth position means removing the node located at index N (1-based indexing) and reconnecting its neighbors.
Example:
List before deletion:
5 ⇆ 10 ⇆ 15 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 25
Delete at position 4.
List after deletion:
5 ⇆ 10 ⇆ 15 ⇆ 25
Node 20 is removed, and the prev and next pointers of surrounding nodes update accordingly.
Understanding Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java helps in:
- Editing dynamic structures (editors, browsers, playlists)
- Removing elements efficiently without full traversal
- Handling boundary conditions
- Preparing for technical interviews
Because the prev pointer exists, deletion is easier and safer compared to singly linked lists.
When deleting the Nth node:
- If list is empty → no deletion possible
- If N = 1 → delete the head
- Traverse the list to reach the Nth node
- Connect:
node.prev.next = node.next
If node.next exists → node.next.prev = node.prev
- Disconnect the node by nulling its pointers.
Note: Java will automatically garbage collect the removed node.
Approach for Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Basically we can perform Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java:
Each method will have Step by step algorithm, Java code, Time and space complexity.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Approach for Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 1: Standalone Deletion Function
Algorithm:
If head is null → return null.
If position is 1:
Move head to next node
Set head.prev = null
Return head
Traverse using a loop to reach the Nth node
If node does not exist → return head
If node is last node:
- Update prev.next = null
- Else:
Update links:
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
- Return head.
Java Code:
class DeleteNthPositionDLL {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev, next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node deleteAtPosition(Node head, int position) {
if (head == null)
return null;
// Case: deleting the first node
if (position == 1) {
if (head.next == null)
return null;
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return head;
}
Node curr = head;
for (int i = 1; i < position && curr != null; i++)
curr = curr.next;
if (curr == null)
return head;
if (curr.next != null)
curr.next.prev = curr.prev;
if (curr.prev != null)
curr.prev.next = curr.next;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node t = head;
while (t != null) {
System.out.print(t.data + " ");
t = t.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.prev = head;
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.prev = head.next;
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next;
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteAtPosition(head, 3);
System.out.println("After deleting position 3:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
1 ⇆ 2 ⇆ 3 ⇆ 4 Delete at position: 3
Output:
1 ⇆ 2 ⇆ 4
Space Complexity: O(1)
Approach for Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 2: Using a DoublyLinkedList Class Structure
Algorithm:
If list empty → nothing to delete
If position = 1:
Move head to next
Update new head’s prev
Traverse to Nth node
If node is last:
- Update previous node’s next
- Otherwise:
- Update both prev and next links
- Node is removed.
Java Code:
class DoublyLinkedList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev, next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
Node head;
public void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = temp;
}
public void deleteAtPosition(int pos) {
if (head == null)
return;
if (pos == 1) {
if (head.next == null) {
head = null;
return;
}
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return;
}
Node curr = head;
for (int i = 1; i < pos && curr != null; i++)
curr = curr.next;
if (curr == null)
return;
if (curr.next != null)
curr.next.prev = curr.prev;
if (curr.prev != null)
curr.prev.next = curr.next;
}
public void printList() {
Node t = head;
while (t != null) {
System.out.print(t.data + " ");
t = t.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
list.insert(10);
list.insert(20);
list.insert(30);
list.insert(40);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
list.printList();
list.deleteAtPosition(2);
System.out.println("After deleting node at position 2:");
list.printList();
}
}
Input:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40 Delete at position: 2
Output:
10 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Conclusion:
Deletion from the Nth position in a doubly linked list demonstrates the structural strength of a bidirectional node system.
- With both prev and next links available, removing a node from any position becomes a simple link adjustment operation, rather than a multi step process.
- The traversal cost remains linear, but the deletion itself completes in constant time.
- This operation is fundamental for advanced list manipulations, memory based operations, and implementing efficient dynamic data structures.
Practicing the Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List using Java builds a strong understanding of how linked structures behave when elements are inserted, deleted, or repositioned.
FAQ's for Deletion from Nth Position of a Doubly Linked List in Java
Answer:
It refers to removing the node located at the given position and updating both previous and next links.
Answer:
By reaching the Nth node using traversal and connecting its previous node to its next node.
Answer:
Only until the Nth node, making complexity O(n).
Answer:
Nothing is deleted, and the list remains unchanged.
Answer:
Yes, because backward pointers help ensure correct bidirectional link updates.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment