JAVA Program for Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List
Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List in Java
Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List in Java is one of the simplest but most important operations you should master when learning doubly linked lists. In this article, you will understand what it means, how it works internally, and how to implement it in Java with clean code and proper time and space complexity analysis.
Java Program for Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List
What is Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List in Java?
In a doubly linked list, each node has:
- prev pointer (address of previous node)
- next pointer (address of next node)
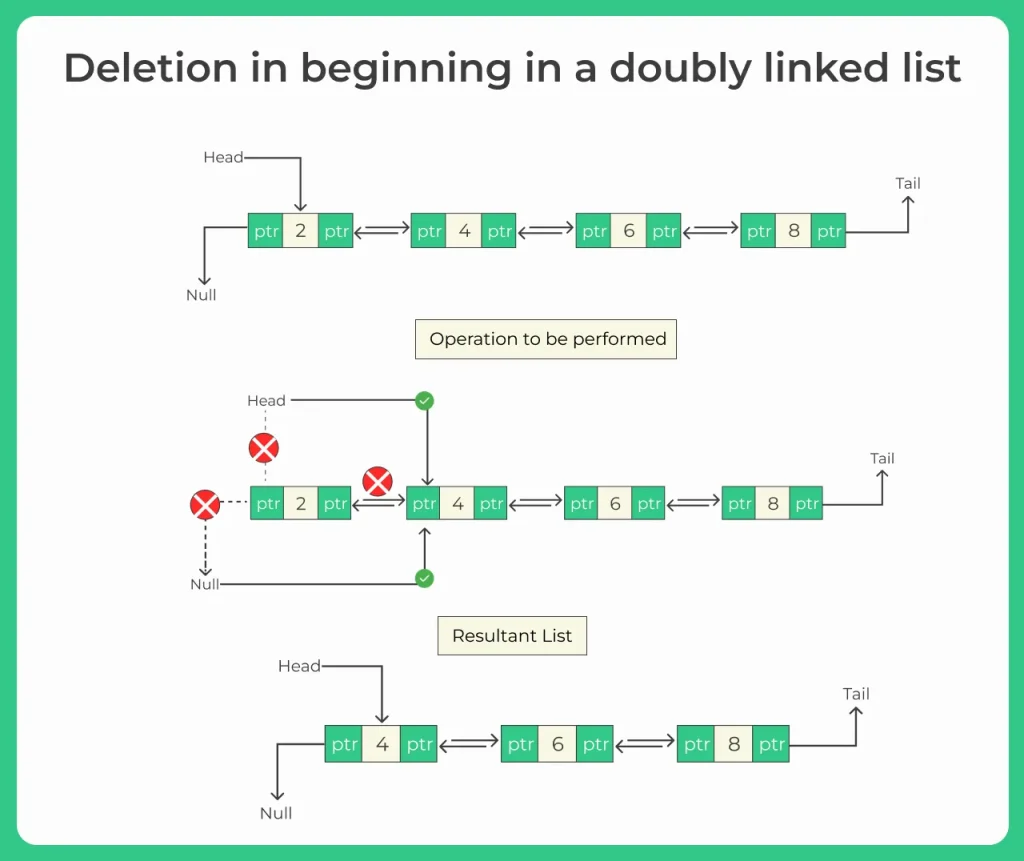
Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List using Java means removing the first node (head node) and making the second node (if it exists) the new head of the list.
Example:
Before deletion:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
After deleting from beginning:
20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
Node 10 is removed, and 20 becomes the new head.
When you perform deletion from the beginning:
- You check if the list is empty. If yes, nothing can be deleted.
- If the list has only one node:
- Deleting that node makes the list empty (head = null)
- If the list has more than one node:
Move head to head.next
Set head.prev = null so there is no link back to the deleted node
- The old head node becomes unreachable and is cleared by Java’s garbage collector.
This operation works in constant time because there is no traversal required.
Understanding Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List helps you:
- Learn how head pointer updates work.
- Understand how prev and next links are adjusted.
- Practice edge case handling. (empty list, single node list)
- Build a base for complex operations like deletion at end, deletion at position, and reverse operations.
Approaches for Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List in Java
Basically we can perform Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List using Java:
- Method 1: Standalone Function with Head Pointer
- Method 2: Deletion Using a DoublyLinkedList Class Wrapper
Each method will have Step by step algorithm, Java code, Time and space complexity.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Approach for Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 1: Standalone Function with Head Pointer
Algorithm:
- Input: head of the doubly linked list.
- If head == null, return null (no node to delete).
- If head.next == null:
Only one node in the list.
Return null (list becomes empty).
- Otherwise:
Set head = head.next
Set head.prev = null
- Return updated head.
Java Code:
class DeleteFromBeginningDLL {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// Method 1: Delete from beginning using head pointer
public static Node deleteFromBeginning(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (head.next == null) {
// Only one node
return null;
}
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
Node second = new Node(20);
Node third = new Node(30);
head.next = second;
second.prev = head;
second.next = third;
third.prev = second;
System.out.println("Before deletion from beginning:");
printList(head);
head = deleteFromBeginning(head);
System.out.println("After deletion from beginning:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30 40
Output:
20 30 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Approach for Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List
Method 2: Using a DoublyLinkedList Class Wrapper
Algorithm:
In real projects, we usually wrap the linked list inside a class and maintain head as a member variable.
- Inside the class, maintain Node head.
- If head == null, list is empty → do nothing.
- If head.next == null:
- Set head = null.
- Otherwise:
Move head to head.next.
Set head.prev = null.
- No return is required because head is a class variable.
Java Code:
class DoublyLinkedListDeleteBegin {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node head;
// Insert at end (helper to build list easily)
public void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = temp;
}
// Method 2: Delete from beginning using class head
public void deleteFromBeginning() {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (head.next == null) {
head = null;
return;
}
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
}
public void printList() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedListDeleteBegin list = new DoublyLinkedListDeleteBegin();
list.insertAtEnd(5);
list.insertAtEnd(15);
list.insertAtEnd(25);
System.out.println("Before deletion from beginning:");
list.printList();
list.deleteFromBeginning();
System.out.println("After deletion from beginning:");
list.printList();
}
}
Input:
10 20 30 40
Output:
20 30 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Conclusion:
As Time and Space Complexity of both methods are same so, both methods for Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List are equally efficient.
- Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List is a constant time operation that clearly demonstrates how bidirectional pointers help in efficient node removal.
- Since each node stores both previous and next references, updating the head pointer and clearing the backward link is straightforward.
- This operation does not require traversal and is therefore highly efficient, even for large lists.
Practicing this basic deletion prepares you for more complex operations such as deletion at the end, deletion at a specific position, and full list manipulation in real world Java applications.
FAQ's for Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List
Answer:
Deletion from beginning means removing the first node of a doubly linked list and updating the head to point to the next node, while also setting the new head’s prev to null.
Answer:
You check if the list is empty or has one node, then move head to head.next and set head.prev = null to detach the old first node.
Answer:
The time complexity is O(1) because only a few pointer changes are needed and no traversal is required.
Answer:
If the list is empty (head == null), Deletion from Beginning in a Doubly Linked List in Java does nothing and the head remains null.
Answer:
Yes, it is easier to manage previous links in a doubly linked list because you can explicitly set head.prev = null, ensuring clean detachment of the old head.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment