Insertion between the nodes in doubly linked list in C++
How to insert element in between the nodes in doubly linked list in C++?
Insertion between the nodes in doubly linked list in C++ – Doubly Linked List is a improved version of singly linked list which has two pointer variables and a single data variable, the two pointer variables help us in storing the address of the next node as well as the previous node, which thus helps us in traversing in both the directions in a doubly linked list.
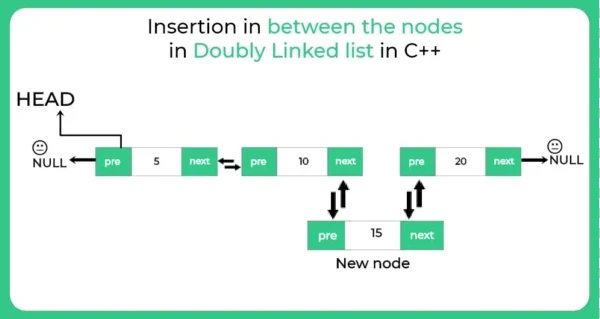
In this section, we’ll learn how to insert a new node in the middle of a doubly linked list in C++. This means placing a node after a specific node and before another, while making sure all the links between nodes are properly updated. We’ll look at the logic, the necessary steps, and the C++ code to do this safely and efficiently.

What is doubly linked list in C++?
A Doubly Linked List is a type of data structure in C++ where each element (called a node) is connected to two other nodes – one before it and one after it.
Each node has three parts:
- The actual data it holds.
- A pointer to the next node in the list.
- A pointer to the previous node in the list.
Because of this two-way connection, you can move through the list forward and backward, which makes it more flexible than a regular (singly) linked list that only goes one way.
struct Node { int Data; Struct Node* next; Struct Node* prev; };
Example:
Think of a train where each coach (node) is connected to the one in front and the one behind. You can move from one coach to the next or go back to the previous one — that’s how a doubly linked list works.
Why use it?
- Easy to insert or delete nodes from both ends.
- You can move in both directions.
- It’s useful when you need quick access to both previous and next elements.
Steps to insert element in between the nodes in doubly linked list in C++
1.) Allocate node.
2.) Put the data.
3.) Make next of new node as next of previous node
4.) Make the next of previous node as new node
5.) Make previous node as previous of new node
6.) Change previous of new node as next node
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Algorithm for insertion in between the nodes in doubly linked list in C++
- IF PTR = NULL
- SET NEW_NODE = PTR
- SET PTR = PTR -> NEXT
- SET NEW_NODE -> DATA = VAL
- SET TEMP = START
- SET I = 0
- REPEAT 8 to 10 until I
- SET TEMP = TEMP -> NEXT
- IF TEMP = NULL
- WRITE “LESS THAN DESIRED NO. OF ELEMENTS”
- SET NEW_NODE -> NEXT = TEMP -> NEXT
- SET NEW_NODE -> PREV = TEMP
- SET TEMP -> NEXT = NEW_NODE
- SET TEMP -> NEXT -> PREV = NEW_NODE
- EXIT
Program for insertion in between the nodes in doubly linked list in C++
This C++ program demonstrates how to insert a new node between existing nodes in a doubly linked list. It efficiently updates the previous and next pointers to maintain the proper linkage of all nodes in the list.
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int num;
struct node *preptr;
struct node *nextptr;
} *stnode, *ennode;
void DlListcreation (int n);
void DlLinsertNodeAtMiddle (int num, int pos);
void displayDlList ();
int main ()
{
int n, num1, a, insPlc;
stnode = NULL;
ennode = NULL;
cout << "Input the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
DlListcreation (n);
displayDlList ();
cout << "Input the position (2 to " << n - 1 << ") to insert a new node: "; cin >> insPlc;
if (insPlc <= 1 || insPlc >= n)
{
cout << "Invalid position\n";
}
else
{
cout << "Input data for the position " << insPlc << ": "; cin >> num1;
DlLinsertNodeAtMiddle (num1, insPlc);
displayDlList ();
}
return 0;
}
void DlListcreation (int n)
{
int i, num;
struct node *fnNode;
if (n >= 1)
{
stnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (stnode != NULL)
{
cout << "Input data for node 1: "; cin >> num;
stnode->num = num;
stnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
fnNode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (fnNode != NULL)
{
cout << "Input data for node " << i << ": "; cin >> num;
fnNode->num = num;
fnNode->preptr = ennode;
fnNode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode->nextptr = fnNode;
ennode = fnNode;
}
else
{
cout << "Memory cannot be allocated.";
break;
}
}
}
else
{
cout << "Memory cannot be allocated.";
}
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtMiddle (int num, int pos)
{
int i;
struct node *newnode, *tmp;
if (ennode == NULL)
{
cout << "No data found in the list!\n";
}
else
{
tmp = stnode;
i = 1;
while (i < pos) { tmp = tmp->nextptr;
i++;
}
if (tmp != NULL)
{
newnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = tmp->nextptr;
newnode->preptr = tmp;
if (tmp->nextptr != NULL)
{
tmp->nextptr->preptr = newnode;
}
tmp->nextptr = newnode;
}
else
{
cout << "The position you entered is invalid.\n";
}
}
}
void displayDlList ()
{
struct node *tmp;
tmp = stnode;
int n = 1;
while (tmp != NULL)
{
cout << " node " << n << ": " << tmp->num << "\n"; n++; tmp = tmp->nextptr; // current pointer moves to the next node
}
}
Output:
Input the number of nodes : 5 Input data for node 1: 11 Input data for node 2: 22 Input data for node 3: 33 Input data for node 4: 44 Input data for node 5: 55 Data entered in the list are : node 1: 11 node 2: 22 node 3: 33 node 4: 44 node 5: 55 Input the position ( 2 to 4) to insert a new node : 3 Input data for the position 3 : 66 After insertion the new list are : node 1: 11 node 2: 22 node 3: 66 node 4: 33 node 5: 44 node 6: 55
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Creating the doubly linked list (`DlListcreation`) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Inserting a node at a given position (`DlLinsertNodeAtMiddle`) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Displaying the list (`displayDlList`) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Program | O(n) | O(n) |
Methods for Insertion between the nodes in Doubly Linked List in C++
There are mainly four methods for Inserting between the nodes in Doubly Linked List –
- Insertion After a Given Node
- Insertion Before a Given Node
- Insertion at a Specific Position (Index-Based)
- Insertion Based on Node Value (Search and Insert)
Insertion After a Given Node
You insert a new node after a specific node by:
- Creating the new node
- Setting its next pointer to the next node
- Setting its prev pointer to the given node
- Updating the given node’s next pointer
- Updating the next node’s prev pointer (if it exists)
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data) {
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "Previous node can't be NULL.\n";
return;
}
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
new_node->prev = prev_node;
prev_node->next = new_node;
if (new_node->next != NULL)
new_node->next->prev = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* head) {
Node* temp = head;
cout << "Doubly Linked List: ";
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
Node* head = new Node{10, NULL, NULL};
Node* second = new Node{20, head, NULL};
head->next = second;
Node* third = new Node{30, second, NULL};
second->next = third;
insertAfter(second, 25); // Insert after node with data 20
printList(head);
return 0;
}Output:
Doubly Linked List: 10 20 25 30
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion after a node | O(1) | O(1) |
| Printing the list | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Program | O(n) | O(1) |
Insert Before a Given Node
- Creating the new node
- Setting its next to the given node
- Setting its prev to the previous node
- Updating the previous node’s next pointer
- Updating the given node’s prev pointer
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
void insertBefore(Node** head_ref, Node* next_node, int new_data) {
if (next_node == NULL) {
cout << "Next node can't be NULL.\n";
return;
}
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->prev = next_node->prev;
new_node->next = next_node;
next_node->prev = new_node;
if (new_node->prev != NULL)
new_node->prev->next = new_node;
else
*head_ref = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* head) {
cout << "Doubly Linked List: ";
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
Node* head = new Node{10, NULL, NULL};
Node* second = new Node{20, head, NULL};
head->next = second;
Node* third = new Node{30, second, NULL};
second->next = third;
insertBefore(&head, second, 15); // Insert 15 before 20
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Doubly Linked List: 10 15 20 30
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion before a node | O(1) | O(1) |
| Printing the list | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Program | O(n) | O(1) |
Insert at a Specific Position (Index-Based)
You can insert a node at a specific index (like position 3 or 5) by:- Traversing the list up to that position
- Using either the “insert before” or “insert after” logic depending on the exact spot
- Ensuring pointers are adjusted correctly
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
void insertAtPosition(Node** head_ref, int position, int new_data) {
if (position <= 0) {
cout << "Invalid position\n";
return;
}
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
if (position == 1) {
new_node->next = *head_ref;
new_node->prev = NULL;
if (*head_ref != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
Node* temp = *head_ref;
for (int i = 1; temp != NULL && i < position - 1; i++)
temp = temp->next;
if (temp == NULL) {
cout << "Position out of range\n";
return;
}
new_node->next = temp->next;
new_node->prev = temp;
if (temp->next != NULL)
temp->next->prev = new_node;
temp->next = new_node;
}
void printList(Node* head) {
cout << "Doubly Linked List: ";
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
Node* head = new Node{10, NULL, NULL};
Node* second = new Node{20, head, NULL};
head->next = second;
Node* third = new Node{30, second, NULL};
second->next = third;
insertAtPosition(&head, 3, 18); // Insert at position 3
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Doubly Linked List: 10 20 18 30
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at a specific position | O(n) | O(1) |
| Printing the list | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Program | O(n) | O(1) |
Insert After a Node with a Given Value
First, search for a node with a specific value, then:- Insert after or before it using the methods above
- Useful when position is unknown but node value is known
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data) {
if (prev_node == NULL) return;
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
new_node->prev = prev_node;
prev_node->next = new_node;
if (new_node->next != NULL)
new_node->next->prev = new_node;
}
void insertAfterValue(Node* head, int key, int new_data) {
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL && current->data != key)
current = current->next;
if (current == NULL) {
cout << "Node with value " << key << " not found.\n";
return;
}
insertAfter(current, new_data);
}
void printList(Node* head) {
cout << "Doubly Linked List: ";
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
Node* head = new Node{10, NULL, NULL};
Node* second = new Node{20, head, NULL};
head->next = second;
Node* third = new Node{30, second, NULL};
second->next = third;
insertAfterValue(head, 20, 22); // Insert after node with value 20
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Doubly Linked List: 10 20 22 30
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Searching for the key node | O(n) | O(1) |
| Insertion after the found node | O(1) | O(1) |
| Printing the list | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Program | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
In this tutorial on inserting a node between nodes in a doubly linked list, we explored the structure of the list, the need for correctly updating both “next” and “prev” pointers, and walked through complete C++ code to insert after a given node, before another node, at a given index, or based on a node’s value.
With a clear grasp of the underlying logic allocating the new node, adjusting four pointers, and ensuring list integrity you’re now equipped to confidently implement and debug middle insertions in a doubly linked list in C++.
FAQs
It means adding a new node somewhere in the middle of the list – not at the start or end – by placing it after one node and before the next, while updating all pointers correctly.
You need to update four pointers:
- The next of the previous node
- The prev of the next node
- The prev of the new node
- The next of the new node
Yes, as long as the position exists in the list. You should make sure the list has enough nodes and that you’re not trying to insert beyond its current length.
If any pointer is missed, the link between nodes breaks, which may lead to memory errors, crashes, or incorrect traversal of the list.
Yes, it can be slightly faster because a doubly linked list gives access to both previous and next nodes, making insertion more flexible compared to a singly linked list.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment